Abstract
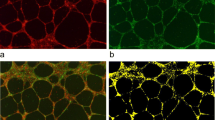
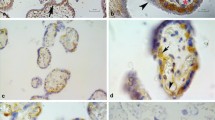
The target molecule of monoclonal antibody AA98 (AA for short) is a new vascular endothelial cell related factor and plays a role in angiogenesis as indicated by the previous data. To investigate its role in angiogenesis and placentation in primate, we examined its expression in the implantation sites on D17, 19, 28 and 34 of gestation in rhesus monkey by immunohistochemistry and Western immunoblot. Western blot analysis showed that the primary antibody used in this study was specific for its epitope. AA protein was mainly expressed in small blood vessels and in some cytotrophoblast cells. The AA staining was found mainly in the endothelial cells and vascular small muscle. This observation supported the AA's role in angiogenesis. AA was spatio-temporarily expressed in cytotrophoblasts: weak in proliferating trophoblast within cell column and endovascular trophoblast, strong in trophoblastic subpopulation within the basal plate and vascular trophoblast; AA staining within the basal plate was down-regulated during early placentation. The shift of AA98 expression in extravillous trophoblasts suggestes a role of this new factor during the course of cytotrophoblast metastasis and spiral artery remodeling. The spatio-temporarily expression indicats that AA98 could be also used as a trophoblast cellular marker to characterize the acquisition of a vascular endothelial and invasive phenotype.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Floridon, C, Nielsen, O, Holund, B. et al., Localization of Ecadherin in villous, extravillous and vascular trophoblasts during intrauterine, ectopic and molar pregnancy, Mol. Hum. Reprod., 2000, 6: 943–950.
Smith, S. K., Angiogenesis and implantation, Hum. Reprod., 2000, 15(suppl. 6): 59–66.
Zhang, Z. Q, Yan, X. Y., Tumorous angiogenesis and the related targets, Chinese Science Bulletin (in Chinese), 2001, 12: 969–976.
Zhang, E. G, Smith, S. K, Charnock-Jones, D. S., Placenta expression of human angiopoietin-2 and Tie-2 but not angiopoietin-1 or Tie-1 are regulated during gestation, J. Soc. Gynecol. Invest., 1999, 6: 86A.
Ghosh, D, Sharkey, A. M, Charnock-Jones, D. S. et al., Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and placental growth factor (PLGF) in conceptus and endometrium during implantation in the rhesus monkey, Mol. Hum. Reprod., 2000, 6: 935–941.
Gao, H. J, Chen, X. L, Shi, L. et al., Expression of steroidogenic acute regulatiory protein and its regulation by interferon-gamma in rat corpus luteum, 2000, Chinese Science Bulletin, 45: 2152–2157.
Gao, F, Wei, P, Chen, X. L. et al., Apoptosis occurs in early stage of pregnancy, Contraception, 2002, 64: 193–200.
Yue, Z. P, Yang, Z. M, Wei, P. et al., Leukemia inhibitory factor, leukemia inhibitory factor receptor, and glycoprotein 130 in rhesus monkey uterus during menstrual cycle and early pregnancy, Biol. Reprod., 2000, 63: 508–512.
Reynolds, L. P, Kirsch, J. D, Kraft, K. C. et al., Time-course of the uterine response to estradiol-17β in ovariectomied ewes expression of angiogenic factors, Biol. Reprod., 1998, 59: 613–620.
Samathanam, C. A, Adesanya, O. O, Zhou, J. et al., Fibroblast growth factors 1 and 2 in the primate uterus, Biol. Reprod., 1998, 59: 491–496.
Morrish, D. W, Dakour, J, Li, H., functional regulation of human trophoblast differentiation, J. Reprod. Immunol., 1998, 39: 179–195.
Goldman-Wohl, D. S, Ariel, L, Greenfield, C. et al., Tie-2 and angiopoietin-2 expression at the fetal-maternal interface: a receptor ligand model for vascular remodeling, Mol. Hum. Reprod., 2000, 6: 81–87.
Liu, Y. X, Hu, Z. Y, Feng, Q. et al., Studies on expression and function of MT1-MMP and TIMP, in human early placentation, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45: 1483–1488.
Hu, Z. Y, Feng, Q, Gao, H. J. et al., Studies on localization and passible role of plasminogen activator and inhibitors in early stage of placentation, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45: 2056–2061.
Gao, F, Wei, P, Hu, Z. Y. et al., Relationship between uterine expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors and endometrial receptivity, Science in China, Ser. C, 2002, 45: 406–411.
Iruela-Arispe, M. L., Normal placentation:a tale that requires an epithelial-to-endothelial conversion, J. Clin. Invest., 1997, 99: 2057–2058.
Zhou, Y, Fisher, S. J, Janatpour, M. et al., Human cytotrophoblasts adopt a vascular phenotype as they differentiate. A strategy for successful endovascular invasion? J. Clin. Invest., 1997, 99: 2139–2151.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, P., Zhang, Z., Chen, X. et al. Expression and function of a new angiogenic factor AA98 target molecule at the maternal-embryonic boundary of rhesus monkey. Chin.Sci.Bull. 48, 881–886 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325669
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325669