Abstract
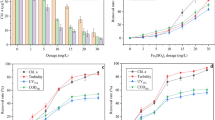
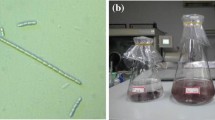
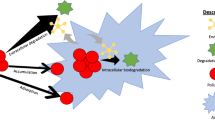
Both O3 and ClO2 have a high effect on inactivating-algae in source water with no forming THMs which do harm to human in producing drinking water, so they will be favorably substituted for Cl2. In order to make certain of the mechanism of inactivating algae with O3 and ClO2, the algal cell number change and its different characteristics of figures and structures in treated and untreated water have been studied by the microscopy and SEM and the mode of inactivating algae has been inferred. The results show that the mechanism of inactivating algae by O3 is not completely identical with that by ClO2. The actual reaction process and efficiency have been controlled by many factors, such as the different characteristics of oxidants and algal cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu, G. Z, Liu, J, Wang, Z. S., Effects of the Algae Characteristics on the drinking water treatment processes, Research of Environmental Sciences (in Chinese), 2000, 13(6): 56–59.
Wang, Z. S, Liu, W. J, Micro-polluted Source Drinking Water Treatment (in Chinese), Beijing: China Architecture Industry Press, 2001.
Huang, J. L, Wang, L, Ren, N. Q. et al., Disinfection effect of chlorine dioxide on viruses, algae and animal planktons in water, Wat. Res., 1997, 31(3): 455–460.
Sun, X, Zhang, J. S., Advances in research on pre-ozonization of drinking water, Water & Wastewater Treatment, 2002, 28(4): 7–9.
Xu, Z. L, Lu, K, Zhao, A. G. et al., The use of chlorine dioxide for inactivating algae and eliminating odor in water plant, Water Purification Technology (in Chinese), 2001, 20(1): 31–32.
Li, W. L, Yu, Z. B, Cai, X. P. et al., Trihalomethanes formation in water treated with chlorine dioxide, Wat. Res., 1996, 30(10): 2371–2376.
Staehelin, J, Bühler, R. E, Hoigné, J., Ozone decomposition in water studied by pulse radiolysis. 2. OH and HO4 as chain intermediates, J. Phys. Chem., 1984, 88(24): 5999–6004.
Qiao, Y., Zhang, Y. X., Use and contrast of chlorine dioxide and ozone in water treatment, Chemical Standard, Measure and Quality (in Chinese), 2001(8): 21–25, 37.
Jeanine, D. P, James, K. E., Effect of ozone on algae as precursors for trihalomethane and haloacetic acid production, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2001, 35(18): 3661–3668.
David, L. W, Kimberly, A. G, Kim, S. M., Removal of algal-derived organic material by preozonation and coagulation: monitoring changes in organic quality by pyrolysis-GC-MS, Wat. Res., 1996, 30(11): 2621–2632.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, W., Liu, P. & Pei, H. Characteristic and mechanism of inactivating algae with O3 and ClO2 . Chin.Sci.Bull. 48, 862–868 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325665
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325665