Abstract
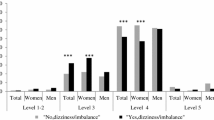
Background and aims: Dizziness is common in older adults, and may be associated with limitations in physical performance. The purpose of this study was to investigate if leg muscle weakness and imbalance exist in older dizzy patients. Methods: Twenty-three older dizzy patients and an age-matched group of 16 healthy non-dizzy older adults participated in the study. Isometric strength of leg muscles, center of pressure (COP) during quiet standing, and maximal distance of reaching forward in standing were tested. All patients answered the Dizziness Handicap Inventory (DHI). Results: Most patients reported that they were handicapped by dizziness (DHI mean 31.8, SD 22.1). Compared with the healthy group, they showed significantly weaker strength in hip extension, knee extension and ankle dorsiflexion (all p<0.000). Imbalance, indicated by greater COP trajectory (p=0.008) and anteroposterior range of displacement (p=0.001) duringquiet standing, and a smaller forward reach distance (p<0.000), was also found in patients. Conclusions: Leg muscle weakness and imbalance were more common in older dizzy patients than in healthy subjects. Clinical management should include assessment and therapy for these problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Colledge NR, Barr-Hamilton RM, Lewis SJ, Sellar RJ, Wilson JA. Evaluation of investigations to diagnose the cause of dizziness in elderly people: A community based controlled study. BMJ 1996; 313: 788–93.
Lawson J, Fitzgerald J, Bircball J, Aldren CP, Kenny RA. Diagnosis of geriatric patients with severe dizziness. J Am Geriatr Soc 1999; 47: 12–7.
Katsarkas A. Dizziness in aging: a retrospective study of 1194 cases. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1994; 110: 296–301.
Tinetti ME, Williams CS, Gill TM. Dizziness among older adults: a possible geriatric syndrome. Ann Intern Med 2000; 132: 337–44.
Mallinson AI, Longridge NS. Dizziness from whiplash and head injury: differences between whiplash and head injury. Am J Otol 1998; 19: 814–8.
Sloane PD, Baloh RW. Persistent dizziness in geriatric patients. J Am Geriatr Soc 1989; 37: 1031–8.
Colledge N, Wilson JA, Macintyre CCA, MacLennan WJ. The prevalence and characteristics of dizziness in an elderly community. Age Ageing 1994; 23: 117–20.
Baloh RW. Dizziness in older people. J Am Geriatr Soc 1992; 40: 713–21.
Burke M. Dizziness in the elderly: etiology and treatment. Nurse Pract 1995; 20: 28–35.
Baloh RW. The dizzy patient: presence of vertigo points to vestibular cause. Postgrad Med 1999; 105: 161–72.
Yardley L, Owen N, Nazareth I, Luxon L. Prevalence and presentation of dizziness in a general practice community sample of working age people. Br J Gene Pract 1998; 48: 1131–5.
Nazareth I, Yardley L, Owen N, Luxon L. Outcome of symptoms of dizziness in a general practice community sample. Fam Pract 1999; 16: 616–8.
Grimby A, Rosenhall U. Health-related quality of life and dizziness in old age. Gerontology 1995; 41: 286–98.
Boult C, Murphy J, Sloane P, Mor V, Drone C. The relation of dizziness to functional decline. J Am Geriatr Soc 1991; 39: 858–61.
Rubenstein LZ, Josephson KR, Robbins AS. Falls in the nursing home. Ann Intern Med 1994; 121: 442–51.
Kroenke K, Mangelsdorff A. Common symptoms in ambulatory care: incidence, evaluation, therapy, and outcome. Am J Med 1989; 86: 262–5.
Derebery MJ. The diagnosis and treatment of dizziness. Med Clin North Am 1999; 83: 163–77.
Sloane PD, Hill C. Dizziness in primary care. Results from the national ambulatory medical care survey. J Fam Pract 1989; 29: 33–8.
Lin SI, Lin RM. Sensorimotor and balance function in older adults with lumbar nerve root compression. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2002; 394: 146–53.
Jacobson GP, Newman CW, Hunter L, Balzer GK. Balance function test correlates of the Dizziness Handicap Inventory. J Am Acad Audiol 1991; 2: 253–60.
Jacobson GP, Calder JH. A screening version of the dizziness handicap inventory (DHI-S). Am J Otol 1998; 19: 804–8.
Jacobson GP, Newman CW. The development of the dizziness handicap inventory. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1990; 116: 424–7.
Kendall FP, McCreary EK, Provance PG. Muscles: Testing and function, 4th Ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins, 1993, pp. 201–13.
Duncan PW, Weiner DK, Chandler J, Studenski S. Functional reach: a new clinical measure of balance. J Gerontol 1990; 45: 192–7.
Sloane PD, Blazer D, George LK. Dizziness in a community elderly population. J Am Geriatr Soc 1989; 37: 101–8.
Isaacson JE, Rubin AM. Otolaryngologic management of dizziness in the older patient. Clin Geriatr Med 1999; 15: 179–91.
Charette SL, McEvoy L, Pyka G, et al. Muscle hypertrophy response to resistance training. J Appl Physiol 1991; 70: 1912–6.
Lord SR, Lloyd DG, Nirui M, Raymon J, Williams P, Stewart RA. The effect of exercise on gait patterns in older women: a randomized controlled trial. J Gerontol 1996; 51: M64–70.
McMurdo ME, Johnstone R. A randomized controlled trial of a home exercise programme for elderly people with poor mobility. Age Ageing 1995; 24: 425–8.
Pruitt LA, Taaffe DR, Marcus R. Effects of a one-year high-intensity versus low-intensity resistance training program on bone mineral density in older women. J Bone Miner Res 1995; 10: 1788–95.
Skelton DA, Young A, Greig CA, Malbut KE. Effects of resistance training on strength, power, and selected functional abilities of women aged 75 and older. J Am Geriatr Soc 1995; 43: 1081–7.
Buchner DM, Cress ME, de Lateur BJ, et al. The effect of strength and endurance training on gait, balance, fall risk, and health services use in community-living older adults. J Gerontol 1997; 52: M218–24.
Judge JO, Lindsey C, Underwood M, Winsemius D. Balance improvements in older women: effects of exercise training. Phys Ther 1993; 73: 254–65.
Wolf SL, Barnhart HX, Ellison GL, Coogler CE. The effect of Tai Chi Quan and computerized balance training on postural stability in older subjects. Phys Ther 1997; 77: 371–81.
Wolfson L, Whipple R, Judge J, et al. Training balance and strength in the elderly to improve function. J Am Geriatr Soc 1993; 41: 341–3.
Skelton DA, Greig CA, Davies JM, Young A. Strength, power and related functional ability of healthy people aged 65–89 years. Age Ageing 1994; 23: 371–7.
Rantanen T, Guralnik JM, Ferrucci L, Leveille S, Fried LP. Coimpairments: strength and balance as predictors of severe walking disability. J Gerontol 1999; 54: M172–6.
Scarborough DM, Krebs DE, Harris BA. Quadriceps muscle strength and dynamic stability in elderly persons. Gait Posture 1999; 10: 10–20.
Bean J, Kiely DK, Herman S, et al. The relationship between leg power and physical performance in mobility-limited older people. J Am Geriatr Soc 2002; 50: 461–7.
Sixt E, Landahl S. Disturbances in a 75-year-old population: I. Prevalence and functional consequences. Age Ageing 1987; 16: 393–8.
Topp R, Mikesky A, Thompson K. Determinants of four functional tasks among older adults: an exploratory regression analysis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 1998; 27: 144–53.
Gill-Body KM, Beninato M, Kerbs DE. Relationship among balance impairments, functional performance, and disability in people with peripheral vestibular hypofunction. Phys Ther 2000; 80: 748–58.
Robertson DD, Ireland DJ. Dizziness handicap inventory correlates of computerized dynamic posturography. J Otolaryngol 1995; 24: 118–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, SI., Tsai, TT. Muscle weakness and imbalance in older dizzy patients. Aging Clin Exp Res 17, 168–173 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03324592
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03324592