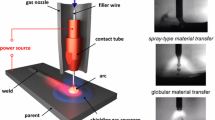
Abstract
Current numerical models of gas metal arc welding (GMAW) attempt to combine a magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) model of the arc and a volume-of-fluid (VoF) model of metal transfer. But in these models vaporization of metal is neglected and the arc region is assumed to be composed of pure argon, as it is common practice for models of gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW). These models predict temperatures over 20 000 K and a temperature distribution similar to GTAW arcs. However, recent spectroscopic temperature measurements in GMAW arcs have demonstrated much lower arc temperatures. In contrast to GTAW arcs, they found a central local minimum of the radial temperature distribution. The paper presents a GMAW arc model that considers metal vapour and which is in very good agreement with experimentally observed temperatures. Furthermore, the model is able to predict the local central minimum in the radial temperature and the radial electric current density distributions for the first time. The axially symmetric model of the welding torch, the workpiece, the wire and the arc (fluid domain) implements MHD as well as turbulent mixing and thermal demixing of metal vapour in argon. The mass fraction of iron vapour obtained from the simulation shows an accumulation in the arc core and another accumulation on the fringes of the arc at 2 000 to 5 000 K. The demixing effects lead to very low concentrations of iron between these two regions. Sensitive analyses demonstrate the influence of the transport and radiation properties of metal vapour, the welding current and the evaporation rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Radaj D.: Schweißprozesssimulation: Grundlagen und Anwendung — Simulation of welding processes: fundamentals and applications, Verlag für Schweißen und verwandte Verfahren DVS-Verlag GmbH, Düsseldorf, 1999 (in German).
Hirt C. and Nichols B.: Volume of fluid method for the dynamics of free boundaries, Journal of Computational Physics, 1981, vol. 39, no. 1, pp. 201–225.
Wang Y., Shi Q. and Tsai H.L.: Modelling of the effects of surface-active elements on flow patterns and weld penetration, Metallurgical Transactions B, 2001, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 145–161.
Haidar J.: An analysis of the formation of metal droplets in arc welding, Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 1998, vol. 31, no. 10, pp. 1233–1244.
Hu J. and Tsai H.L.: Heat and mass transfer in gas metal arc welding, Part I: The arc, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2007, vol. 50, no. 5-6, pp. 802–820.
Hu J. and Tsai H.L.: Heat and mass transfer in gas metal arc welding, Part II: The metal, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2007, vol. 50, no. 5-6, pp. 833–846.
Spille-Kohoff A.: Numerische Simulation des ChopArc-Schweißprozesses — Numerical simulation of ChopArc-welding process, Final Report ChopArc, Fraunhofer IRB Verlag, 2005 (in German).
Lowke J.J., Morrow R. and Haidar J.: A simplified unified theory of arcs and their electrodes, Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 1997, vol. 30, no. 14, pp. 2033–2042.
Sansonnens L., Haidar J. and Lowke J.J.: Prediction of properties of free burning arcs including effects of ambipolar diffusion, Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2000, vol. 33, no. 2, pp. 148–157.
Metzke E. and Schöpp H.: Spektralanalyse Metall-Lichtbogenplasma, Optical spectral analyses of arc plasmas within metal vapour, Final Report ChopArc, Frauenhofer IRB Verlag, 2005 (in German).
Goecke S.F.: Auswirkungen von Aktivgaszumischungen im vpm-Bereich zu Argon auf das MIG-Impulsschweißen von Aluminium, Active gas additions in range of vpm in argon and their influence on pulsed MIG-welding of aluminium, PhD Thesis, TU Berlin, 2004 (in German).
Briand F., Zielińska S., Musiol K., Pellerin N., Pellerin S., de Izarra Ch., Richard F. and Opderbecke T.: Experimental investigations of the arc in MIG-MAG welding, IIW Doc. SG 212-1123-08, 2008.
Tashiro S., Tanaka M., Nakata K., Iwao T., Koshiishi F., Suzuki K. and Yamazaki K.: Plasma properties of helium gas tungsten arc with metal vapour, Quarterly Journal of the Japan Welding Society, 2006, vol. 24, no. 1, pp. 143–148.
Yamamoto K., Tanaka M., Tashiro S., Nakata K., Yamamoto E., Yamazaki K., Suzuki K., Murphy A.B. and Lowke J.J.: Numerical simulation of diffusion of multiple metal vapours in a TIG arc plasma for welding of stainless steel, Doc. IIW-1963, Welding in the World, 2009, vol. 53, no. 7/8, pp. R166–R170.
Lago F., Gonzalez J.J., Freton P. and Gleizes A.: A numerical modelling of an electric arc and its interaction with the anode: Part I The two dimensional model, Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2003, vol. 37, no. 6, pp. 883–897.
Lowke J.J. and Tanaka M.: ‘LTE-diffusion approximation’ for arc calculations, Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2006, vol. 39, no. 16, pp. 3634–3643.
Hertel M., Schnick M., Füssel U., Gorchakow S. and Uhrlandt D.: Numerical simulation of GMAW processes including effects of metal vapour and sheath mechanisms at the electrodes. Magnetohydrodynamics, 2010, vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 363–370.
Murphy A.B.: Thermal plasmas in gas mixtures (Topical Review), Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2001, vol. 34, no. 20, pp. R151–R173.
Murphy A.B. and Arundell C.J.: Transport coefficients of argon, nitrogen, oxygen, argon-nitrogen and argon-oxygen plasmas, Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 1994, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 451–490.
Menart J. and Malik S.: Net emission coefficients for argon-iron thermal plasmas, Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2002, vol. 35, no. 9, pp. 867–874.
Menter F.R.: Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications, AIAA Journal, 1994, vol. 32, no. 8, pp. 1598–1605.
Murphy A.B.: A comparison of treatments of diffusion in thermal plasmas, Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 1996, vol. 29, no. 7, pp. 1922–1932.
Murphy A.B.: Diffusion in equilibrium mixtures of ionized gases, Physical Review E: Statistical Physics, Plasmas, Fluids, and Related Interdisciplinary Topics, 1993, vol. 48, no. 5, pp. 3594–3603.
Murphy A.B.: The effects of metal vapour in arc welding, Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2010, vol. 43, no. 43, p. 434001.
Schnick M., Fuessel U., Hertel M., Spille-Kohoff A. and Murphy A.B: Metal vapour causes a central minimum in arc temperature in gas-metal arc welding through increased radiative emission, Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2010, vol. 43, no. 2, pp. 022001–022005.
Haidar J.: The dynamics effects of metal vapour in gas metal arc welding, Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2010, vol. 43, no. 16, p. 165204.
Schnick M., Fuessel U., Hertel M., Haessler M., Spille-Kohoff A. and Murphy A.B.: Modelling of gas-metal arc welding taking into account metal vapour, Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2010, vol. 43, no. 43, p. 434008.
Rose S., Schnick M., Hertel M., Zschetzsche J. and Füssel U.: Transient simulation of gas metal arc welding (GMAW) processes and experimental validation, Magnetohydrodynamics, 2010, vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 403–412.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schnick, M., Füssel, U., Hertel, M. et al. Numerical Investigations of the Influence of Metal Vapour in GMA Welding. Weld World 55, 114–120 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03321549
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03321549