Abstract
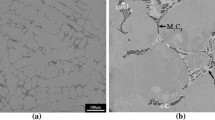
Nickel-base Colmonoy (AWS ER NiCr) alloys find extensive application for hardfacing of austenitic stainless steel (SS) components in Fast Breeder Reactors. Gas Tungsten Arc deposited Colmonoy alloys suffer from significant loss in hardness and wear properties due to dilution from the austenitic SS substrate. In a multilayer deposit, dilution in first layer is highest and dilution decreases progressively in the subsequent layers. Although, both Colmonoy alloys and austenitic SS are non-magnetic, the deposit of Colmonoy on austenitic SS is ferromagnetic. The susceptibility to magnetic attraction in the hardface deposits is highest for maximum level of dilution and reduces with decreasing dilution. In the present study, Colmonoy-6 alloy co-deposited with austenitic SS filler wire, to obtain deposits with different levels of dilution, have been non-destructively evaluated by eddy current (EC) and magnetic Barkhausen (MB) techniques. The deposits were also characterized by microstructural and hardness studies. The EC parameters viz. magnitude and phase angle of the induced voltage showed an increasing trend with increasing dilution of the deposits. MB root mean square (RMS) voltage and peak height also indicated similar trend with dilution. The results produced from nondestructive tests could be correlated with hardness and microstructure of the deposits. Thus, it is possible to develop a non-destructive technique to predict hardness of the Colmonoy hardfacing alloy, which can serve as quality control tool in estimating the hardness of the hardfaced coating to ensure that dilution of the deposit by the substrate does not bring down the hardness of the deposit below the acceptable minimum values.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohriner E.K., Wada T., Whelan E.P. and Ocken H.: The chemistry, structure of wear resistant, iron-base hard-facing alloy, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, vol. 22, No. 5, 1991, pp. 983–991.
Ocken H.: Reducing the cobalt inventory in light water reactor, Nuclear Technology, vol. 68, No. 1, 1985, pp. 18–28.
ASM Metals Handbook,vol.6, 9th ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, USA, 1993, pp. 794-795.
Rigney D.A.: The roles of hardness in the sliding behavior of material, Wear, vol. 175, No. 1–2, 1994, pp. 63–69.
Schimdt T.R.: The remote field eddy current inspection techniques, Materials Evaluation, Vol. 42, 1984, pp. 225–230.
Raj B. and Jayakumar T.: NDE methodologies for characterisation of defects, stresses and microstructures in pressure vessels and pipes, International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, vol. 73, No. 2, 1997, pp. 133–146.
Saquet O., Chicois J. and Vincent A.: Barkhausen noise from plain carbon steels: analysis of the influence of microstructure, Materials Science and Engineering A, vol. 269, No. 1–2, 1999, pp. 73–82.
Ng D.H.L., Cho K.S., Wong M.L., Chan S.L.I., Ma X.Y. and Lo C.C.H.: Study of microstructure, mechanical properties and magnetization process in low carbon steel by Barkhausen emission, Materials Science and Engineering A, vol. 358, No. 1–2, 2003, pp. 186–198.
McMaster R.C.: Nondestructive Testing Handbook: 2nd Edition; Volume 4 Electromagnetic Testing ASNT; ASM 1986.
Mercier D., Lesage J., Decoopman X. and Chicot D.: Eddy currents and hardness testing for evaluation of steel decarburizing, NDT & E International, vol. 39, No. 8, 2006, pp. 652–660.
McNab A. and Thomson J.: An eddy current array instrument for application on ferritic welds, NDT & E International, vol. 28, No. 2, 1995, pp. 103–112.
Rajkumar K.V., Rao B.P.C., Sasi B., Kumar A., Jayakumar T., Raj B. and Ray K.K.: Characterization of aging behaviour in M250 grade maraging steel using eddy current non-destructive methodology, Materials Science and Engineering A, vol. 464, No. 1–2, 2007, pp. 233–240.
Habiby F., Ul Haq A., Khan A.Q.: Influence of austenite on the coercive force as function of temperature, Materials & Design, vol. 13, No. 5, 1992, pp. 259–264.
Chikazumi S.: Physics of magnetism, 1st ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons 1964.
Goodenough J.B.: A theory of domain creation and coercive force in polycrystalline ferromagnetics, Physical Review, vol. 95, No.4, pp. 917–932.
Li Q., Zhang D., Lei T., Chen C. and Chen W.: Comparison of laser-clad and furnace-melted Ni-based alloy Microstructures, Surface and Coatings Technology, vol. 137, No. 2–3, 2001, pp. 122–135.
Navas C., Colaco R., de Damborenea J. and Vilar R.: Abrasive wear behaviour of laser clad and flame sprayed melted NiCrBSi coatings, Surface and Coatings Technology, vol. 200, No. 24, 2006, pp. 6854–6862.
Ramasubbu V., Chakraborty G., Albert S. K. and Bhaduri A. K.: Effect of dilution on GTAW Colmonoy 6 (AWS NiCr-C) hardfaced deposit made on 316LN stainless steel, Materials Science and Technology, vol. 27, No. 2, 2011, pp. 573–580.
Das C.R., Albert S.K., Bhaduri A.K. and Nithya R.: Effects of dilution on microstructure and wear behaviour of NiCr hardface deposits, Materials Science and Technology, vol. 23, No. 7, 2007, pp. 771–779.
O’Handley R.C., in: Modern Magnetic materials: Principals and Applications, John Wiley & Sons, 2000.
Moorthy V., Choudhary B.K., Vaidyanathan S., Jayakumar T., Bhanu K., S. Rao and Raj B.: An assessment of low cycle fatigue damage using magnetic Barkhausen emission in 9Cr-1 Mo ferritic steel, International Journal of Fatigue, Vol 21, No. 3, 1999, pp. 263–269.
Moorthy V., Vaidyanathan S., Laha K., Jayakumar T., Bhanu K., S. Rao and Raj B.: Evaluation of microstructures in 2.25Cr-1Mo and 9Cr-1Mo steel weldments using magnetic Barkhausen noise, Materials Science and Engineering A, vol. 231, No. 1–2, 1997, pp. 98–104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakraborty, G., Viswanath, A., Mukhopadhyay, C.K. et al. Non-Destructive Characterization of Nickel-Base Hardface Deposit on Austenitic Stainless Steel Through Eddy Current and Magnetic Barkhausen Techniques. Weld World 56, 59–65 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03321396
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03321396