Summary
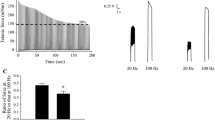
The effect of inositol trisphosphate (IP3) was investigated in mechanically skinned fibres which had the endogenous level of sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ and in which the normal excitation-contraction (E-C) coupling mechanism was still functional. Application of 50 or 100 μM IP3 failed to induce a detectable force response in any such skinned fibre from either the extensor digitorum longus muscle of the rat or iliofibularis muscle of the toad, irrespective of whether the fibre was: (a) in its normally polarized, resting state; (b) chronically depolarized to inactivate the voltage sensors; (c) paralysed with D600; or (d) depolarized to threshold for force activation. Furthermore, the size of the response to subsequent depolarization or exposure to caffeine (2 mM) or reduced myoplasmic [Mg2+] indicated that little if any Ca2+ had been lost from the SR during the period of IP3 exposure (≥1 min). Also, IP3 did not induce a detectable force response when SR Ca2+ uptake was potently inhibited with 20 μM TBQ. Exposure to IP3 (50 μM) slightly potentiated the peak force response to depolarization in toad fibres, and this was probably because of an accompanying small increase in Ca2+ sensitivity of the contractile apparatus. These results appear inconsistent with the proposal that IP3 acts as the second messenger in E-C coupling in skeletal muscle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BAKKER, A. J., LAMB, G. D. & STEPHENSON, D. G. (1996) The effect of 2,5-di(tertbutyl)-1,4-hydroquinone on force responses and the contractile apparatus in mechnically skinned muscle fibres of the rat and toad. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 17, 55–67.
BERWE, D., GOTTSCHALK, G. & LÜTTGAU, H. Ch. (1987) Effects of the calcium antagonist gallopamil (D600) upon excitation-contraction coupling in toe muscle fibres of the frog. J. Physiol. 385, 693–707.
CHU, A. & STEFANI, E. (1991) Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate-induced Ca2+ release from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum terminal cisternal membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 12, 7699–7705.
COONAN, J. R. & LAMB, G. D. (1996) The role of chloride ions in the excitation of skinned skeletal muscle fibres of the toad and rat. Proc. Aust. Physiol. Pharmacol. Soc. 27, 95P.
DONALDSON, S. K. (1989) Inactivated state rather than transverse tubule depolarization increases peeled skeletal muscle fiber sensitivity to inositol trisphosphate. Biophys. J. 55, 236a.
DONALDSON, S. K., GOLDBERG, N. D., WALSETH, T. F. & HUETTEMAN, D. A. (1987) Inositol trisphosphate stimulates calcium release from peeled skeletal muscle fibers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 927, 92–9.
DONALDSON, S. K., GOLDBERG, N.D., WALSETH, T. F. & HUETTEMAN, D. A. (1988) Voltage dependence of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release in peeled skeletal muscle fibers. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 85, 5749–53.
ENDO, M. (1985) Calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Curr. Topics Memb. Transport 25, 181–230.
FILL, M.D. & BEST, P.M. (1988) Contractile activation and recovery in skinned frog muscle stimulated by ionic substitution. Am. J. Physiol. 254, C107–14.
FRUEN, B. R., KANE, P. K., MICKELSON, J. R. & LOUIS, C. F. (1996) Chloride-dependent sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release correlates with increased Ca2+ activation of ryanodine receptors. Biophys. J. 71, 2522–30.
HANNON, J. D., LEE, N. K.-M., YANDONG, C. & BLINKS, J. R. (1992) Inositol trisphosphate (InsP3) causes contraction in skeletal muscle only under artificial conditions: evidence that Ca2+ release can result from depolarization of T-tubules. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 13, 447–56.
HIDALGO, C., JORQUERA, J., TAPIA, V. & DONOSO, P. (1993) Triads and transverse tubules isolated from skeletal muscle contain high levels of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 15111–7.
JAIMOVICH, E. (1991) Chemical transmission at the triad: InsP3? J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 12, 316–20.
KOBAYASHI, M., MUROYAMA, A. & OHIZUMI, Y. (1989) Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate enhances calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal muscle. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 163, 1487–91.
LAMB, G. D. (1992) DHP receptors and excitation-contraction coupling. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 13, 394–405.
LAMB, G. D., JUNANKAR., P. R. & STEPHENSON, D. G. (1995) Raised intracellular [Ca2+] abolishes excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle fibres of rat and toad. J. Physiol. 489, 349–62.
LAMB, G. D., POSTERINO, G. S. & STEPHENSON, D. G. (1994) Effects of heparin on excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle of toad and rat. J. Physiol. 474, 319–29.
LAMB, G. D. & STEPHENSON, D. G. (1990) Calcium release in skinned muscle fibres of the toad by transverse tubule depolarization or by direct stimulation. J. Physiol. 423, 495–517.
LAMB, G. D. & STEPHENSON, D. G. (1991a) Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle fibres of rat and toad in the presence of GTPγS. J. Physiol. 444, 65–84.
LAMB, G. D. & STEPHENSON, D. G. (1991b) Effect of Mg2+ on the control of Ca2+ release in skeletal muscle fibres of the toad. J. Physiol. 434, 507–28.
LAMB, G. D. & STEPHENSON, D. G. (1994) Effects of intracellular pH and [Mg2+] on excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle fibres of the rat. J. Physiol. 478, 331–9.
LEA, T. J., GRIFFITHS, P. J., TREGEAR, R. T. & ASHLEY, C. C. (1986) An examination of the ability of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to induce calcium release and tension development in skinned skeletal muscle fibres of frog and crustacea. FEBS Lett. 207, 153–61.
LOPEZ, J. R. & PARRA, L. (1991) Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate increases myoplasmic [Ca2+] in isolated muscle fibers. Depolarization enhances its effects. Cell Calcium 12, 543–57.
MARGRETH, A., DAMIANI, E. & TOBALDIN, G. (1993) Ratio of dihydropyridine to ryanodine receptors in mammalian and frog twitch muscles in relation to the mechanical hypothesis of excitation-contraction coupling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 197, 1303–11.
MAYR, G. W. & THIELECZEK, R. (1991) Masses of inositol phosphates in resting and tetanically stimulated vertebrate skeletal muscles. Biochem. J. 280, 631–40.
MELZER, W., HERRMANN-FRANK, A. & LÜTTGAU, H. Ch. (1995) The role of Ca2+ ions on excitation-contraction coupling of skeletal muscle fibres. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1241, 59–116.
MOSCHELLA, M. C., WATRAS, J., JAYARAMAN, T. & MARKS, A. R. (1995) Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in skeletal muscle: differential expression in myofibres. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 16, 390–400.
OGAWA, Y. & HARAFUJI, H. (1989) Ca-release by phosphoinositides from sarcoplasmic reticulum of frog skeletal muscle. J. Biochem. 106, 864–7.
OWEN, V. J., LAMB, G. D., STEPHENSON, D. G. & FRYER, M. W. (1997) Relationship between depolarization-induced force responses and Ca2+ content in skeletal muscle fibres of rat and toad. J. Physiol. 498, 571–86.
PAPE, P. C., KONISHI, M., BAYLOR, S. M. & SOMLYO, A. P. (1988) Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle fibers injected with the InsP3 blocker, heparin. FEBS Lett. 235, 57–62.
ROJAS, C. & JAIMOVICH, E. (1990) Calcium release modulated by inositol trisphosphate in ruptured fibers from frog skeletal muscle. Pflügers Arch. 416, 296–304.
THIELECZEK, R. & HEILMEYER, L. M. G., JR (1986) Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate enhances Ca2+-sensitivity of the contractile mechanism of chemically skinned rabbit skeletal muscle fibres. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 135, 662–9.
VALDIVIA, C., VAUGHAN, D., POTTER, B. V. L. & CORONADO, R. (1992) Fast release of 45Ca2+ induced by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and Ca2+ in the sarcoplasmic reticulum of rabbit skeletal muscle: evidence for two types of Ca2+ release channels. Biophys. J. 61, 1184–93.
VERGARA, J., TSIEN, R. Y. & DELAY, M. (1985) Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate: a possible chemical link in excitation-contraction coupling in muscle. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 82, 6352–6.
VILVEN, J. & CORONADO, R. (1988) Opening of dihydropyridine calcium channels in skeletal muscle membranes by inositol trisphosphate. Nature 336, 587–9.
VOLPE, P., di VIRGILIO, F., POZZAN, T. & SALVIATI, G. (1985) Inositol (1,4,5) trisphosphate induces calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle. Nature 316, 347–9.
WALKER, J. W., SOMLYO, A. V., GOLDMAN, Y. E., SOMLYO, A. P. & TRENTHAM, D. R. (1987) Kinetics of smooth and skeletal muscle activation by laser pulse photolysis of caged inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature 327, 249–52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Posterino, G.S., Lamb, G.D. Investigation of the effect of inositol trisphosphate in skinned skeletal muscle fibres with functional excitation-contraction coupling. Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility 19, 67–74 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03257391
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03257391