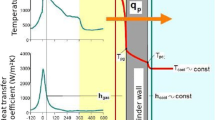
Abstract
A new, effective and reliable simulation model for predicting the combustion wall temperature in internal combustion engines has been developed at the Institute for Automotive Research (IVK) of the University of Stuttgart.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiodi, M.: Literaturrecherche zum Thema Wandtemperaturmodell. In: FVV Abschlussbericht (1999), Heft 684.
Brüggemann, H.; Dietrich, A.; Hüttebräucker, D.; Puchas, C.: Die Weiterentwicklung der Vierzylinder-Ottomotoren für die neue mittlere Baureihe von Mercedes-Benz. In: MTZ; Heft 56 (1995) Seite 5.
Kaplan, J.A.; Heywood, J.B.: Modelling The Spark Ignition Engine Warm-Up Process To Predict Component Temperatures. Master Thesis. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1990.
Gnielinski, V.: Neue Gleichungen für den Wärme- und den Stoffübergang in turbulent durchströmten Rohren und Kanälen. In: Forschung im Ingenieurwesen 41 (1975), Seite 8–16.
Fischer, G.; Hohenberg, G.: Reibmitteldruck — Ottomotor. In: FVV Abschlussbericht (1999), Heft 685.
Chen, J.C.: A correlation for Boiling Heat Transfer to Saturated Fluids in Convective Flow. In: Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. and Dev., 1966.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sargenti, R., Bargende, M. A model for simulating combustion chamber wall temperatures. AutoTechnol 5, 68–71 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03246901
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03246901