Abstract
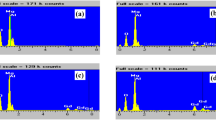
Nanometer MCM-41 molecular sieve was prepared under a base condition by using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide as template and tetraethyl orthosilicate as silica source by means of hydrothermal method. Lanthanum(III) was incorporated into the nanometer MCM-41 by a liquid phase grafting method. The prepared nanocomposite materials were characterized by means of powder X-ray diffraction, spectrophotometric anaylsis, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, low temperature nitrogen adsorption-desorption technique, solid diffuse reflectance absorption spectra and luminescence. The powder X-ray diffraction studies show that the nanometer MCM-41 molecular sieve is successfully prepared. The highly ordered mesoporous two-dimensional hexagonal channel structure and framework of the support MCM-41 is retained intact in the prepared composite material La-(nanometer MCM-41). The spectrophotometric anaylsis indicates that lanthanum exists in the prepared nanocomposite materials. The Fourier transform infrared spectra indicate that the framework of the MCM-41 molecular sieve still remains in the prepared nanocomposite materials and some framework vibration peaks show blue shifts relative to those of the MCM-41 molecular sieve. The low temperature nitrogen adsorption-desorption indicates that the guest locates in the channel of the molecular sieve. Compared with bulk lanthanum oxide, the guest in the channel of the molecular sieve has smaller particle size and shows a significant blue shift of optical absorption band in solid diffuse reflectance absorption spectra. The observed blue shift in the solid state diffuse reflectance absorption spectra of the lanthanum-(nanometer MCM-41) sample show the obvious stereoscopic confinement effect of the channel of the host on the guest, which further indicates the successful encapsulation of the guest in the host. The La-(nanometer MCM-41) sample shows luminescence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.E. Davis, Nature 417 (2002) 813.
G.D. Stucky, J.E. MacDougall, Science 247 (1990) 669.
G.A. Ozin, Adv. Mater. 4 (1992) 612.
R.R. Xu, W.Q. Pang, Molecular Sieve and Porous Material Chemistry (in Chinese). jing, China: Scientific Press 2004, pp. 566–586.
Q. Cai, Z.S. Luo, W.Q. Pang, Chem. Mater. 13 (2001) 258.
J.C.P. Broekhoff, J.H. de Boer, J. Catal. 10 (1968) 368.
K.S.W. Sing, D.H. Everett, R.A.W. Haul, Pure. Appl. Chem. 57 (1985) 603.
E.P. Barrett, L.G. Joyner, P.P. Halenda, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 73 (1951) 373.
Q.Z. Zhai, Y.C. Kim, Chin. J. Spectr. Lab. 15 (1998) 82.
Q.Y. Luo, Z.H. Lei, X.M. Yu, Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 12 (1984) 985.
IUPAC, Pure. Appl. Chem. 87 (1957) 603.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, Q.Z., Wang, P. Preparation, characterization and optical properties of lanthanum-(nanometer MCM-41) composite material. JICS 5, 268–273 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03246117
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03246117