Abstract
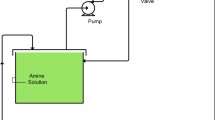
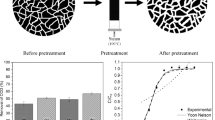
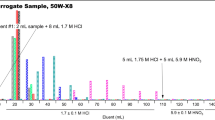
A preliminary assessment of the available options to recover soluble salts from salt-cake slag material has been carried out. From limited benchscale experiments, it was demonstrated that in a semicontinuous batchmode operation, about 85% of the chlorides in a one-stage or close to 100% in a multistage series of exhaustion operations can be converted to bicarbonates through an ion-exchange, resin-based option.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.M. Reynolds et al., “The Engitec System for Treatment of Salt Slag from Secondary Aluminum Smelters,” Second International Symposium—Recycling of Metals and Engineered Materials, ed. J.H.L. van Linden et al. (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1990), pp. 439–450.
C.L. Smithsonet al., “Non-Catalytic Heterogeneous Kinetics in the Engel-Precht Potassium Carbonate Process,” Ind. Eng. Chern. Process Des. Dev., 15 (13) (1976), p. 450.
Rolf Brannland et al., “New In-Plant Technology to Reduce Pollution from a Sodium Base Sulphite Mill,” Svensk Papporstidning, 79 (18) (1976), pp. 591–594.
A.C. Sheth et al., “Anion-Exchange Resin-Based Dechlorination Concept” (Paper presented at the 1990 SO2 Control Symposium, New Orleans, Louisiana, May 8–11, 1990).
A.C. Sheth et al., Anion-Exchange Resin-Based Desulfurization Process, Final Report, DOE/PC/90309-13, UTSI, Tullahoma, Tennessee (January 1994).
Advanced Separation Technologies, Inc., Lakeland, Florida (Sales Brochure).
S.D. Strevel, “The Anion-Exchange Resin-Based Desulfurization Concept,” M.S. thesis, University of Tennessee (December 1992).
K.S. Dharmapurikar, “The Anion-Exchange Resin-Based Desulfurization Process for Spent Seed Regeneration in an MHD Power Plant,” M.S. thesis, University of Tennessee (May 1994).
C.S. Brooks et al., Metal Recovery from Industrial Waste (Chelsea, MI: Lewis Publishers, 1991).
“Amberlite/Duolite Ion-Exchange Resins-Technical Notes,” Rohm and Haas Company (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheth, A.C., Parks, K.D. & Parthasarathy, S. Recycling salt-cake slag using a resin-based option. JOM 48, 32–37 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03223022
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03223022