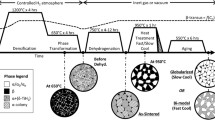
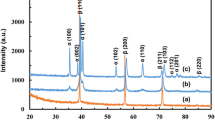
Abstract
In this article, the status of the methods and applications of the thermohydrogen processing of Titanium alloys is reviewed. Increased understanding of the mechanisms by which such processing is enhanced and the microstructure refined should lead to industrial applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.H. Froes, D. Eylon, and C. Suryanarayana, “Thermochemical Processing of Titanium Alloys,” JOM, 42 (3) (1990), pp. 26–29.
V.K. Nosov and B.A Kolachev, Hydrogen-Induced Plasticization of Titanium Alloys at Hot Deformation (Moscow, Russia: Metallurgia, 1986).
W.R. Kerr et al., “Hydrogen as an Alloying Element in Titanium (Hydrovac),” Titanium 80: Science and Technology, vol. 4, ed. H. Kimura and O. Izumi (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1980), pp. 2477–2486.
E.G. Ponyatovsky et al., “Effect of Hydrogen on Ductility and Strength of a VT20 Titanium Alloy at Temperatures from 20 to 740°C,” Physics of Metals & Metallography, 68 (6) (1989), pp. 122–128.
O.N. Senkov, E.G. Ponyatovsky, and I.O. Bashkin, “Mechanical Behaviour of a VT20 Titanium Alloy at Different Initial States and Hydrogen Contents,” Mechanical Behavior of Materials: VI. vol. 2, ed. M. Jono and T. Inoue (Oxford, U.K.: Pergamon, 1991), pp. 725–730.
N. Bida and V. DePierre, technical report AFML-TR-75-171, U.S. Air Force Materials Laboratory, Wright-Patterson AFB (1975).
F.H. Froes and D. Eylon, “Applications of HIPing to Titanium Based Alloys,” Proc. 4 Int. Conf. Isostatic Pressing ISO-4 (Shrewsbury, U.K.: MPR Publishing Services Ltd., 1990), pp. 16.1–16.30.
R.J. Lederich et al., “Influence of Hydrogen Additions on High-Temperature Superplasticity of Titanium Alloys,” Advanced Methods for Titanium, ed. D.E. Hasson and C.H. Hamilton (New York: AIME, 1982), pp. 115–128.
F.H. Froes, “Synthesis of Metallic Materials for Demanding Aerospace Applications Using Powder Metallurgy Techniques,” 1991 P/M in Aerospace and Defence Technology, Proc. PM Aerasp. Def. Technol. Symp. (Princeton, NJ: MPIF, 1991), pp. 5–33.
W.H. Kao and L.M. Orsborn, Powder Metallurgy of Titanium Alloys, ed. F.H. Froes and J.E. Smugeresky (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1980), p. 163.
K. Yong, Z.X. Guo, and D.V. Edmonds, “Processing of Titanium Matrix Composites With Hydrogen As a Temporary Alloying Element,” Scripta Metall. Mater., 27 (12) (1992), pp. 1695–1700.
K. Yang, Z.X. Guo, and D.V. Edmonds, “Study of the Effect of Hydrogen on Titanium Alloy Foils to be Used as Potential Composite Matrices,” Scripta. Metall. Mater. 27 (8) (1992), pp. 1021–1026.
Z.X. Guo et al., “The Effect of Temporary Hydrogenation on the Processing and Interface of Titanium Composites,” Composites, 25 (9) (1994), pp. 881–886.
W.R. Kerr, “The Effect of Hydrogen as a Temporary Alloying Element on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Ti-6Al-4V,” Metall. Trans. A, 16A (1986), pp. 1077–1087.
A.A. Hin, “Phase and Structure Transformations in Titanium Alloys Alloyed with Hydrogen,” Ivestiya VUZ, Tsvetnaya Metallurgiya (1) (1987), pp. 96–101.
A.A. Hin, “Some Aspects olInteraction of Hydrogen with Metallic Materials,” Izvestiya AN SSSR: Metally (5) (1994), pp. 65–70.
A.A. Hin, A.M. Mamonov, and M.Yu. Kollerov, “Scientific Fundamentals and Principles of Developing Processes of Thermohydrogen Treatment of Titanium Alloys,” Izvestiya AN SSSR: Metally (4) (1994), pp. 157–168.
B.A. Kolachev, “Reversible Alloying of Titanium Alloys with Hydrogen,” Metallovedenie i Termichesknya Obrabotkn Metallov (10) (1993), pp. 28–32.
O.N. Senkov and I.O. Bashkin, “Improved Workability, Microstructure and Final Properties of a Titanium Alloy due to Temporary Hydrogenation,” Metallurgical Processes for the TMS, 1994), pp. 271–80.
O.N. Senkov, E.Y. Konopleva, and E.G. Ponyatovsky, “Transformation-Induced Plasticity of a Hydrogen Alloyed Titanium Alloy,” Microstructure/properties Relationships of Titanium Alloys, ed. S. Ankem and J.A. Hall (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1994), pp. 207–214.
A. San-Martin and E.D. Manchester, “The H-Ti (Hydrogen-Titanium) System,” Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams, 8 (1) (1987), pp. 31–42.
B. Liao et al., “Effect of Hydrogen on (a1+β)/β Transus Temperature of Super- α2 Alloy,” Scripta Metall. Mater., 32 (2) (1995), pp. 277–281.
O.N. Senkov, E.Y. Konopleva, and E.G. Ponyatovsky, “The Influence of the Initial Phase Composition and Microstructure on Deformation Properties of a Hydrogen-Alloyed Titanium Alloy,” Fizika Metallov i Metallovedenie, 77 (3) (1994), pp. 142–151.
A.A. Hin and A.M. Marnonov, “Temperature-Concentration Diagrams of Phase Composition of Hydrogen-Bearing Multicomponent Titanium Alloys,” Russian Metallurgy (5) (1994), pp. 52–57.
E.Y. Konopleva and Y.M. Bayazitov, “Effect of Hydrogen on Temperature of the Alpha to Beta Transition in a Titanium Alloy VT20,” Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov (1) (1992), pp. 33–35.
O.N. Senkov and E.C. Ponyatovsky, “TransformationInduced Plasticity of a Hydrogen Alloyed Titanium Alloy,” Strength of Materials (ICSMA 10), ed. H. Oikawa et al. (Tokyo: Japan Institute of Metals, 1994), pp. 639–642.
O.N. Senkov et al., “Structure of VT20 Titanium Alloy After Hydrogen Treatment and Deformation at Moderate Temperatures,” Fizika Metallov i Metallovedenie, 76 (1) (1993), pp. 128–138.
S.B. Belova, V.K. Nosov, and A.A. Hin, “Conditions of Development of the Hydrogen Plasticization Effect in a-Titanium Alloy VT5-1,” Izvestiya VUZ, Tsvetnaya Metallurgiya (5) (1987), pp. 83–86.
B.A. Kolachev et al., “Hydrogen Effect on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of a Titanium Alloy VT3-1,” Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov (1) (1992), pp. 32–33.
O.N. Senkov, I.O. Bashkin, and E.G. Ponyatovsky, “The Combined Effect of Temporary Hydrogen Alloying and Deformation on Microstructure and Properties of a HighStrength Titanium Alloy,” Microstructure/properties Relationships of Titanium Alloys, ed. S. Ankem and J.A. Hall (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1994), pp. 191–198.
R.J. Smickley and L.E. Darid, U.S. patent no. 4,505,746 (1985).
L. Levin et al., Proc. 5th Int. Conf. on Titanium, ed. G. Lütjering, U. Zwicker, and W. Bunk (Munich, Germany: Deutsche Gesellschaft für Metallkunde E.V., 1984), pp. 2107–2114.
C.E Yolton, D. Eylon, and F.H. Froes, Proc. 6th Int. Conf. on Titanium, ed. P. Lacombe, R. Tricot, and G. Beranger (Cannes, France: les Editions de Physique, 1988), pp. 1641–1646.
M.Yu. Kollerov, A.A. Hin, and S.V. Skvortsova, “Martensitic Transformation and Effects of Inelastic Behavior in Hydrogen-Containing Titanium Alloys,” Izvestiya AN SSSR: Metally (5) (1994), pp. 118–125.
O.N. Senkov, “Microstructure Evolution in a HydrogenAlloyed Titanium Alloy during Deformation at Elevated Temperatures,” Strength of Materials (ICSMA 10), ed. H. Oikawa et al. (Tokyo: Japan Institute of Metals, 1994), pp. 635–638.
O.N. Senkov and J.J. Jonas, “Effect of Phase Composition and Hydrogen Level on the Deformation Behavior of Titanium-Hydrogen Alloys,” Metal. & Mater. Trans. A, 27 (7) (1996).
Z. Xu et al., “Effect of Hydrogen on High Temperature Plasticity of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy,” Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 27 (4) (1991), pp. A270–A273.
B. Gong et al., “Strength and Toughness of Microstructurally Controlled Alpha+Beta Type Titanium Alloys by Thermochemical Processing with Hydrogen,” Keikinzoku/Journ. Jap. Inst. Light Metals, 42 (11) (1992), pp. 638–643.
V.K. Nosov, V.K. Uvarov, and V.M. Ilin, “Characteristics of Isothermal Upsetting of a Titanium Alloy with Varying Hydrogen Content,” Russian Metallurgy (4) (1986), pp. 71–77.
Yu.A. Aksyonov, L.I. Anisimova, and V.L. Kolmogorov, “Reversible Addition of Hydrogen to Titanium Alloys,” J. Mater. Process. Technol., 40, (3-4) (1994), pp. 477–489.
H. Yoshimura et al., “Ultra-fine Equiaxed Grain Refinement and Improvement of Mechanical Properties of (a+β) Type Titanium Alloys by Hydrogenation, Hot Working, Heat Treatment and Dehydrogenation,” Mater. Trans. JIM, 35 (4) (1994), pp. 266–272.
H. Yoshimura, K. Kimura, and M. Hayashi, Ultra-fine Equiaxed Grain Refinement of Titanium Alloys by Hydrogenation, Hot Working, Heat Treatment and Dehydrogenation, Nippon Steel technical report no. 62 (1994), pp. 80–84.
I.O. Bashkin et al., “The Effect of Strain Rate on the Hydrogen-Enhanced Plasticity of Titanium Alloy VT20 in the Range 500 to 800°C,” Phys. Met. Metallogr., 69 (2) (1990), pp. 167–174.
O.N. Senkov and J.J. Jonas, “Effect of Slrain Rate and Temperature on the Flow Stress of β-Phase Titanium Hydrogen Alloys,” Metal. & Mater. Trans. A, 27 (5) (1996), pp. 1303–1312.
A.A. Hin et al., “Effect of Hydrogen on Diffusion Mobility of Atoms in the Beta-Phase of Titanium Alloys,” Russian Metallurgy (5) (1994), pp. 74–77.
Yu.A. Aksyonov et al., “Influence of Hydrogen on the Ductility and Resistance to Deformation of Commercial T Titanium VTI-0 at Temperatures up to 750°C,” Phys. Metals & Metallography, 67 (5) (1989), pp. 157–163.
I.O. Bashkin et al., “Influence of Hydrogen on the Ductility and Resistance to Deformation of Titanium Alloy VT6 at Temperatures up to 930°C,” Phys. Metals & Metallography, 69 (5) (1990), pp. 158–164.
B.A. Kolachev et al., Titanium ′92 Science and Technology, vol. 1, ed. F.H. Froes and I.L. Caplan (Warrendale, PA TMS, 1993), pp. 861–868.
O.N. Senkov and J.J. Jonas, “Effect of Hydrogen Content on the Deformation Behavior ofTitanium-Hydrogen Alloys,” Eighth World Conference on Titanium, (London: Institute of Materials, 1995) in press.
I.O. Bashkin, E.I. Rabkin, and B.B. Straumal, “Titanium Diffusion in Zirconium-Hydrogen and Zirconium-Deiterium Systems,” Fizika Metallov i Metallovedenie (3) (1992), pp. 73–80.
O.N. Senkov et al., “Peculiarities of Plastic Flow of Hydrogen-Modified Titanium Alloy VT20 in the Temperature Range 823 to 1073 K,” Phys. Met. Metallogr., 70 (1) (1990), pp. 111–119.
Z. Shaoqing and Z. Linruo, “Effect of Hydrogen on the Superplasticity and Microstructure of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy,” J. Alloys & Compounds, 218 (2) (1995), pp. 233–236.
B. Gong, C.B. Zhang, and Z.H. Lai, “Improvement of Superplastic Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy by Temporary Alloying with Hydrogen,” J. Mater. Sci. Letters, 13 (21) (1994), pp. 1561–1563.
T.L. Mackay, S.M.L. Sastry, and C.E Yolton, U.S. technical report AFWAL-TR-80-4038, Air Force Materials Laboratory, Wright-Patterson AFB, Ohio (1980).
B.A. Kolachev et al., “Favorable Effect of Hydrogen on Formability of Titanium Alloys,” Tekhnologiya Legkih Splavov (Light Alloy Technology) (7) (1974), pp. 32–35.
A.Y. Malkov, B.A. Kolachev, and I.D. Nizkin, “Effect of Hydrogen on Ductility of a VT16 Alloy,” Izv. VUZ, Tsvetnaya Metallurgiya (6) (1990), pp. 96–100.
B.A. Kolachev et al., “On the Possibility of Temperature Decreasing for Hot Heating of Bolts Made ofVT16 Titanium Alloy by Reversible Hydrogenation,” Izvestiya AN SSSR: Metally (3) (1991), pp. 67–69.
B.A. Kolachev and V.D. Talalaev, Titan (Titanium), vol. 1 (Moscow, Russia: Aviation Publishing House, 1993), p. 43.
L.S. Steele, D. Eylon, and F.H. Froes, “Microstructure Control of Titanium Aluminide Powder Compacts by Thermo-Chemical Treatment,” 1990 Advances in Powder Metallurgy (Princeton, NJ: MPIF, 1990), pp. 509–523.
F.H. Froes et al., Bull. Mater. Sci., (6) (1989), pp. 1–19.
L.S. Apgar and D. Eylon, “Microstructure Control of Titanium Aluminide Powder Compacts by Thermochemical Processing,” ISIJ International, 31 (8) (1991), pp. 915–921.
L.S. Apgar and D. Eylon, “Development of Ultrafine Microstructures in Titanium Aluminide Powder Compacts,” 1990 Advances in Powder Metallurgy (Princeton, NJ: MPIF, 1990), pp. 173–186.
K. Ameyama et al., “Injection Molding of Titanium Powder,” 1989 Advances in Powder Metallurgy, vol. 2 (Princeton, NJ: MPIF, 1989), pp. 121–126.
F.H. Froes et al., “Synthesis of Titanium Aluminide Intermetallics by Mechanical Alloying,” P/M in Aerospace, Defence and Demanding Applications (Princeton, NJ: MPIF, 1993), pp. 3–24.
D.K. Mukhopadhyay, C. Suryanarayana, and F.H. Froes, Second Int. Conf. on Structural Applications of Mechanical Alloying, ed. J.J. deBarbadillo, F.H. Froes, and R. Schwarz (Material Parks, OH: ASM, 1993), p. 131.
S.T. Ahn, Y.G. Kim, and J.Y. Lee, “Formation of the Amorphous Phase in Zr2Al by Hydrogen Absorption and the Effect of Titanium Substitution on the Amorphization Behavior,” Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 186 (1) (1992), pp. 45–52.
A. Memezawa, K. Aoki, and T. Matsumoto, “Amorphization of Ti-Zr Powders by the Collaborated Interaction of Mechanical Alloying and Hydrogenation,” Scripta Metall. Mater., 28 (3) (1993), pp. 361–365.
M. Barkco et al., “Structural and Thennodynamic Aspects of Glass Formation in Cu-Ti-H: Role of Hydrogen in Mechanical Alloying,” J. Non-Crystalline Solids, 156-158 (2) (1993), pp. 527–531.
K. Aoki, A. Memezawa, and T. Masumoto, “Amorphization of the TiV System by Mechanical Alloying and Mechanical Grinding in a Hydrogen and Nitrogen Atmosphere,” J. Mater. Research, 9 (1) (1994), pp. 39–46.
R. Boyer, G. Welsch, and E.W. Collings, ed., Materials Properties Handbook: Titanium Alloys (Materials Park, OH: ASM, 1994).
M. Niinomi et al., “Fracture Characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-5Al-2.5Fe with Refined Microstructure using Hydrogen,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 26 (5) (1995), pp. 1141–1151.
R.J. Smickley and E. Sardi, U.S. patent 4505764 (March 19, 1985).
B.A. Kolachev, V.K. Nosov, and L.A. Lebedev, Izv. VUZ, Tsvetnaya Metallurgiya (3) (1985), pp. 104–107.
B.A. Kolachev and A.A. Hin, “Thermohydrogen Processing of Titanium Alloys,” Metallovedenie i Obrabotka Titanovih i Zharoprochnih Splavov (Moscow: All-Russian Institute of Light Alloys, 1991), pp. 132–142.
F.H. Froes, D. Eliezer, and H.G. Nelson, “Hydrogen Effects in Titanium,” Fifth Intern. Conf. on Hydrogen Effects on Metals, ed. N.R Moody and R.W. Thompson (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1995).
C.E. Yolton and F.H. Froes, U.S. patent 4,219,357 (August 26, 1980).
W.Y. Chu and A.W. Thompson, Hydrogen Effects on Material Behaviour, eds. N.R Moody and A.W. Thompson (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1990), p. 285.
D.S. Shong, et al., “Hot Isostatic Pressing of g-TiAl Alloy and ψ-TiAl Metal Matrix Composites,” 1989 Advances in Powder Metallurgy (Princeton, NJ: MPIF, 1989), pp. 359–371.
J.A. Graves et al., Scripta Metal., 21 (1987), pp. 567–572.
M. Saqib et al., “Microstructure and Phase Morphology During Thermochemical Processing of Alpha(2)-Based Titanium Aluminide Castings,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, A201 (1-2) (1995), pp. 169–181.
K. Yang and D.V. Edmonds, “Thermochemical Processing with Hydrogen of Super- α2 Alloy,” J. Mater. Sci., 29 (8) (1994), pp. 2126–2132.
K. Yang and D.V. Edmonds, “Effect of Hydrogen as a Temporary Alloying Element on the Microstructure of a Ti3Al Intermetallic,” Scripta Metal. Mater., 28 (1) (1993), pp. 71–76.
R.G. Vogt, Private communication, Howmet Corp., Whitehall, MI (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Senkov, O.N., Jonas, J.J. & Froes, F.H. Recent advances in the thermohydrogen processing of titanium alloys. JOM 48, 42–47 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03222997
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03222997