Abstract
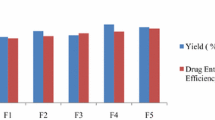
In order to the development of the delivery device of long-acting local anesthetics for postoperative analgesia and control of chronic pain of cancer patient, fentanyl-loaded poly(l-lactide-co-glycolide)|(PLGA, molecular weight, 5,000 g/mole; 50∶50 mole ratio by lactide to glycolide)|microspheres (FMS)|were studied. FMS were prepared by an emulsion solvent-evaporation method. The influence of several preparation parameters such as initial drug loading, PLGA concentration, emulsifier concentration, oil phase volume, and fabrication temperature has been investigated on the fentanyl release profiles. Generally, the drug showed the biphasic release patterns, with an initial diffusion followed by a lag period before the onset of the degradation phase, but there was no lag time in our system. Fentanyl was slowly released from FMS over 10 daysin vitro with a quasi-zero order property. The release rate increased with increasing drug loading as well as decreasing polymer concentration with relatively small initial burst effect. From the results, FMS may be a good formulation to deliver the anesthetic for the treatment of chronic pain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. C. Baselt,Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man, 2nd Eds., Davis, Ed., Biomedical Publications, 1982, pp 325.
W. R. Hammargren and G. L. Henderson,J. Anal. Toxicol.,12, 183 (1988).
B. E. Marchall and D. E. Longnecker,General Anesthetics, A. G. Gilman, T. W. Rall, A. S. Nies, and P. Taylor, Eds., Pegamon Press, New York, 1990, pp 305–327.
J. C. Garriott, R. Rodriquez, and V. J. M. Di Mario,J. Anal. Toxicol.,8, 288 (1984).
(5)E. M. Pare, J. R. Monforte, R. Gaul, and H. Mirchandani,J. Anal. Toxicol.,11, 272 (1987).
R. J. Matecjczyk,J. Anal. Toxicol.,12, 236 (1988).
B. Levine, J. C. Goodin, and Y. H. Caplan,Forensic Sci. Int.,45, 247 (1990).
H. S. Choi, H. C. Shin, G. Khang, J. M. Rhee and H. B. Lee,J. Chromatography B.,765, 63 (2001).
H. S. Choi, S.-A. Seo, G. Khang. J. M. Rhee, and H. B. Lee,Int. J. Pharm.,234, 195 (2002).
S. -A. Seo, H. S. Choi, G. Khang, J. M. Rhee, and H. B. Lee,Int. J. Pharm.,239, 93 (2002).
L. R. Beck, V. Z. Pope, T. R. Tice, and R. M. Gilley,Adv. Contracept.,1, 19 (1985).
A. C. Moffat, inClarke’s Isolation, Identification of Drugs in Pharmaceuticals, Body Fluids and Post-Mortem Materials, Pharmaceutical Press, London, 1986, pp 617–638.
R. Ikeda and C. Pelton,J. Med.,152, 617 (1990).
H. B. Lee, G. Khang, J. C. Cho, J. M. Rhee, and J. S. Lee,Polymer Preprints,40, 288 (1999).
G. Khang, J. M. Rhee, J. S. Lee, and H. B. Lee,Polymer Sci. Tech.,12, 4 (2001).
G. Khang, D. S. Moon, H. S. Seong, J. M. Rhee, J. S. Lee, and H. B. Lee,Biomater. Res.,4, 107 (2000).
J. C. Cho, G. Khang, J. M. Rhee, Y. S. Kim, J. S. Lee, and H. B. Lee,Korea Polym. J.,7, 79 (1999).
G. Khang, J. C. Cho, J. W. Lee, J. M. Rhee, and H. B. Lee,Bio-Med. Mater. Eng.,9, 49 (1999).
G. Khang, J. H. Lee, J. W. Lee, J. C. Cho, and H. B. Lee,Korea Polym. J.,8, 80 (2000).
J. C. Cho, G. Khang, H. S. Choi, J. M. Rhee, S. C. Yoon, J. C. Cho, and H. B. Lee,Polymer (Korea),24, 728 (2000).
G. Khang, H. S. Choi, J. M. Rhee, S. C. Yoon, J. C. Cho, and H. B. Lee,Korea Polym. J.,8, 253 (2000).
W.-I. Son, D. I. Yun, G. Khang, B.-S. Kim, and, H. B. Lee,Biomater. Res.,4, 92 (2000).
J. C. Cho, G. Khang, J. M. Rhee, Y. S. Kim, J. S. Lee, and H. B. Lee,Biomater. Res.,4, 136 (2000).
G. Khang, S. W. Kim, J. C. Cho, J. M. Rhee, S. C. Yoon, and H. B. Lee,Bio-Med. Mater. Eng.,11, 89 (2001).
M. K. Choi, G. Khang, I. Lee, J. M. Rhee, and H. B. Lee,Polymer (Korea),25, 318 (2001).
S.-A. Seo, H. S. Choi, D. H. Lee, G. Khang, J. M. Rhee, and H. B. Lee,Polymer (Korea),25, 884 (2001).
S.-A. Seo, H. S. Choi, J. C. Cho, G. Khang, J. M. Rhee, and H. B. Lee,Biomater. Res.,5, 35 (2001).
S. J. Lee, G. Khang, Y. M. Lee, and H. B. Lee,J. Biomater. Sci., Polym. Ed.,13, 197 (2002).
G. Khang and H. B. Lee, inCell-synthetic Surface Interaction: Physicochemical Surface Modification, A. Atala and R. Lanza, Eds., Academic Press, London, 2001, Section II, pp 771–797.
G. Khang and H. B. Lee,Biomedical Polymer, Korea Chemical Society Press, Munundang, Seoul, Korea, 2001.
D. H. Lewis, inControlled Release of Bioactive Agents from Lactide/Glycolide Polymers, Biodegradable Polymers as Drug Delivery Systems, M. Chasin and R. Langer, Eds., Academic Press, New York, 1990, pp 1–41.
R. Arshady,J. Bioact. Compatible Polym.,5, 315 (1990).
R. Jalil and J. R. Nixon,J. Microencapsul.,7, 297 (1990).
R. Jalil and J. R. Nixon,J. Microencapsul.,7, 53 (1990). (35)|Y.-Y. Yang, T.-S. Chung, and N. P. Ng,Biomaterials,22, 231 (2001).
C. Sturesson, J. Carlfores, K. Edman, and M. Andersson,Int. J. Pharm.,89, 235 (1993).
M. Guyot and F. Fawaz,Int. J. Pharm.,175, 61 (1998).
R. Jalil and J. R. Nixon,J. Microencapsul.,7, 245 (1990). (39)|R. Jalil and J. R. Nixon,J. Microencapsul.,7, 41 (1990).
F. Wada, S. Hyon, and Y. Ikada,J. Pharm. Pharmacol.,43, 605 (1991).
G. Raouf, S. Cecilia, and C. Johan, Int. J. Pharm.,141, 205 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khang, G., Seo, SA., Choi, H.S. et al. Evaluation ofin vitro release profiles of fentanyl-loaded PLGA oligomer microspheres. Macromol. Res. 10, 246–252 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03218313
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03218313