Abstract
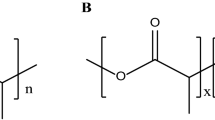
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) is a microbial storage polymer with biodegradable properties. In order to improve the cell compatibility of PHBV surfaces, the physicochemical treatments have been demonstrated. In this study, physical method was corona discharge treatment and chemical method was chloric acid mixture solution treatment. The physicochemically treated PHBV film surfaces were characterized by the measurement of water contact angle, electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The water contact angle of the physicochemically treated PHBV surfaces decreased from 75 to 30∼40 degree, increased hydrophilicity, due to the introduction of oxygen-based functional group onto the PHBV backbone chain. The mouse NIH/3T3 fibroblasts cultured onto the physicochemically treated PHBV film surfaces with different wettability. The effect of the PHBV surface with different wettability was determined by SEM as counts of cell number and [3H]thymidine incorporation as measures of cell proliferation. As the surface wettability increased, the number of the cell adhered and proliferated on the surface was increased. The result seems closely related with the serum protein adsorption on the physicochemically treated PHBV surface. In conclusion, this study demonstrated that the surface wettability of biodegradable polymer as the PHBV plays an important role for cell adhesion and proliferation behavior for biomedical application.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Gogolewski, M. Jovanoic, S. M. Perren, J. G. Dillon, and M. K. Hughes,J. Biomed. Mater. Res.,27, 1135 (1993).
S. Akhtar and C. W. Pouton,Drug News Perspectives,2, 89 (1989).
K. Juni and M. Nakano,CRC Crit. Rev. Therap. Drug Carrier Syst.,3, 209 (1987).
S. J. Lee, G. Khang, J. H. Lee, Y. M. Lee, and H. B. Lee,Polymer(Korea),24(6), 877 (2000).
G. Khang, S. J. Lee, J. H. Jeon, J. H. Lee, and H. B. Lee,Polymer(Korea),24(6), 869 (2000).
G. Khang, S. J. Lee, J. H. Lee, and H. B. Lee,Korea Polym. J.,7, 102 (1999).
J. M. Schakenraad, H. J. Busscher, C. H. R. Wildevuur, and J. Arends,J. Biomed. Mater. Res.,20, 773 (1986).
P. B. Van Wachem, T. Beugeling, J. Feijen, A. Bantjes, J. P. Detmers, and W. G. Van Aken,Biomaterials,6, 403 (1985).
Y. Tamada and Y. Ikada,J. Colloid Interface Sci.,155, 334 (1993).
P. B. Van Wachem, A. H. Hogt, T. Beugeling, J. Feijen, A. Bantjes, J. P. Detmers, and W. G. Van Aken,Biomaterials,8, 323 (1987).
D. E. Gregonis, R. Hsu, D. E. Buerger, L. M. Smith, and J. D. Andrade, inMacromolecular Solutions, R. B. Seymoor and D. A. Stahl, Eds., Pergamon, New York, 1982, pp 120.
D. L. Coleman, D. E. Gregonis, and J. D. Andrade,J. Biomed. Mater. Res.,16, 381 (1982).
T. A. Horbett, M. B. Schway, and B. D. Ratner,J. Colloid Interface Sci.,104, 28 (1985).
D. L. Walker, M. D. Gregonis, and W. M. Richert,J. Colloid Interface Sci.,157, 41 (1993).
M. J. Lydon, T. W. Minett, and B. J. Tighe,Biomerials,6, 396 (1985).
J. H. Lee, H. Kim, G. Khang, H. B. Lee, and M. S. Jhon,J. Colloid Interf. Sci.,152, 563 (1992).
H. B. Lee and J. H. Lee,Biocompatibility of solid substrates based on surface wettability, inEncyclopedic Handbook of Biomaterials and Bioengineering: Part A. Materials, D. L. Wise, D. J. Trantolo, D. E. Altobelli, M. J. Yaszemski, J. D. Gresser, and E. R. Schwartz, Eds., Marcel Dekker, New York, 1995. Vol. 1, pp 371–398.
J. H. Lee and H. B. Lee,J. Biomater. Sci., Polym. Edn.,4, 467 (1993).
B. J. Jeong, J. H. Lee, and H. B. Lee,J. Colloid Interf. Sci.,178, 757 (1996).
J. H. Lee, B. J. Jeong, and H. B. Lee,J. Biomed. Mater. Res.,34, 105 (1997).
J. H. Lee, G. Khang, J. W. Lee, and H. B. Lee,Makromol. Chem., Macromol. Symp.,118, 571 (1997).
G. Khang, J. W. Lee, J. H. Jeon, J. H. Lee, and H. B. Lee,Biomaterials Res.,1, 1 (1997).
J. H. Lee, J. W. Lee, G. Khang, and H. B. Lee,Biomaterials,18, 351 (1997).
J. H. Lee and H. B. Lee,J. Biomed. Mater. Res.,41, 304 (1998).
J. H. Lee, G. Khang, J. W. Lee, and H. B. Lee,J. Biomed. Mater. Res.,40, 180 (1998).
Y. Iwasaki, K. Ishihara, N. Nakabayashi, G. Khang, J. H. Jeon, J. W. Lee, and H. B. Lee,J. Biomater. Sci., Polym. Edn.,9, 801 (1998).
J. H. Lee, G. Khang, J. W. Lee, and H. B. Lee,J. Colloid Interf. Sci.,205, 323 (1998).
G. Khang, J. H. Jeon, J. C. Cho, J. M. Rhee, and H. B. Lee,Polymer(Korea),23, 861 (1999).
G. Khang, S. J. Lee, J. H. Jeon, J. H. Lee, and H. B. Lee,Polymer(Korea),24, 869 (2000).
G. Khang, C. S. Park, J. M. Rhee, S. J. Lee, Y. M. Lee, M. K. Choi, I. Lee, and H. B. Lee,Korea Polym. J.,9, 267 (2001).
G. Khang, J.-H. Choee, J. M. Rhee, and H. B. Lee,J. Appl. Polym. Sci., in press (2001).
J. H. Lee, S. J. Lee, G. Khang, and H. B. Lee,J. Colloid Interf. Sci.,230, 84 (2000).
J. H. Lee, H. W. Jung, I. K. Kang, and H. B. Lee,Biomaterials,15, 705 (1994).
P. B. van Wachem, T. Beugeling, J. Feijen, A. Bantjes, J. P. Detmers and W. G. van Aken,Biomaterials,6, 403 (1985).
P. B. van Wachem, A. H. Hogt and T. Beugeling,Biomaterials,8, 323 (1987).
Y. Tamada and Y. Ikada, inPolymers in Medicine II, E. Cheillin, P. Giusti, C. Migliaresl, and L. Nicolas, Eds., Plenum Press, New York, 1986, pp 101.
Y. Tamada and Y. Ikada,J. Colloid Interf. Sci.,155, 334 (1993).
Y. Tamada and Y. Ikada,J. Biomed. Mater. Res.,28, 783 (1994).
G. Khang,. J. H. Lee, J. M. Rhee, and H. B. Lee,Korea Polym. J.,8, 276 (2000).
G. Khang, S. J. Lee, Y. M. Lee, J. H. Lee, and H. B. Lee,Korea Polym. J.,8, 179 (2000).
J. H. Lee, D. K. Kim, G. Khang, and J. S. Lee,Biomaterials Res.,2, 8 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.J., Lee, Y.M., Khang, G. et al. Effect of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) surface with different wettability on fibroblast behavior. Macromol. Res. 10, 150–157 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03218265
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03218265