Abstract
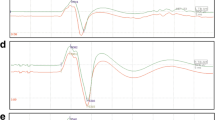
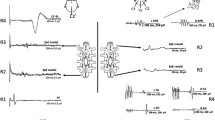
Objective: To assess the utility of spinal cord monitorings for prediction of spinal cord ischemia, we investigated the role of both motor evoked potentials and sensory evoked potentials during thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm surgeries.Methods: We monitored two kinds of sensory evoked potentials; descending evoked spinal cord potentials from the lumbar enlargement after cervical spinal cord stimulation and segmental evoked spinal cord potentials at the lumbar enlargement elicited by peroneal nerve stimulation, and motor evoked potentials from the lumbar enlargement elicited by direct subcranial stimulation in 9 thoracoabdomonal aortic aneurysm surgeries.Results: Postoperative paraplegia occurred in one case in which the patients died during the perioperative period. One case showed transient paraparesis, but recovered following rehabilitatation. These cases showed a decrease in the amplitude of descending evoked spinal cord potentials and motor evoked potentials.Conclusion: The recovery of the amplitude of the motor evoked potentials and the descending evoked spinal cord potentials after declamping correlated with the neurologic outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crawford ES, Snyder DM, Gwen CC, Roethan JOE Jr. Progress in treatment of thoracoabdominal and abdominal aortic aneurysms involving celiac, superior mesenteric and renal arteries. Ann Surg 1978; 188: 404–22.
Laschinger JG, Izumoto H, Kouchoukus NT. Evolving concepts in prevention of spinal cord injury during operation on the descending thoracic and thoracoabdominal aorta. Ann Thorac Surg 1987; 44: 667–74.
North RB, Drenger B, Beattie C, McPherson RW, Parker S, Reitz BA et al. Monitoring of spinal cord stimulation evoked potentials during thoracoabdominal aneurysm surgery. Neurosurgery 1991; 28: 325–30.
Crawford ES, Mizrahi EM, Hess KR, Caselli JS, Safi HJ, Patel VM. The impact of distal aortic perfusion and somatosensory evoked potentials monitoring on prevention of paraplegia after aortic aneurysm operation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1988; 95: 357–67.
Tanaka S, Fujimoto Y, Sasaki M, Oka S, Ikuta Y, Sueda T. Effect of spinal cord ischemia on spinal cord evoked potentials. J Electrodiagnosis Spinal Cord 1997; 19: 21–4.
Cunningham JN Jr, Laschinger JC, Spencer FC. Monitoring of somatosensory evoked potentials during surgical procedures on the thoracoabdominal aorta: IV. Clinical observations and results. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1987; 94: 275–85.
Grabitz K, Freye E, Rtuhmeier K, Sandman W. Spinal evoked potential in patients undergoing thoracoabdominal aortic reconstruction: a prognostic indicator of postoperative motor deficit. J Clin Monit 1993; 9: 186–90.
Yamamoto N, Takano H, Kitagawa H, Kawaguchi Y, Tsuji H. Evoked spinal cord potential changes during spinal cord ischemia and the resultant hind limb dysfunction in cats. J Spinal Disord 1994; 7: 285–95.
Okamoto Y, Murakami M, Makagawa T, Murata A, Moriya H. Intraoperative spinal cord monitoring during surgery for aortic aneurysm: application of spinal cord evoked potential. Electroenchephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1992; 84: 315–20.
Yamamoto N, Takano H, Kitagawa H, Kawaguchi Y, Tsuji H, Uozaki Y. Monitoring for spinal cord ischemia by use of the evoked spinal cord potentials during aortic aneurysm surgery. J Vasc Surg 1994; 20: 826–33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sueda, T., Okada, K., Watari, M. et al. Evaluation of motor- and sensory-evoked potentials for spinal cord monitoring during thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm surgery. Jpn J Thorac Caridovasc Surg 48, 60–65 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03218086
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03218086