Abstract
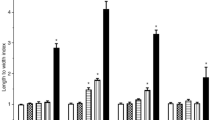
The relationship between DNA damage and repair of peripheral blood leukocytes, liver, kidney and brain cells was investigated in Swiss albino mice (Mus musculus L.) after exposure to sevoflurane (2.4 vol% for 2 h daily, for 3 days). Genetic damage of mouse cells was investigated by the comet assay and micronucleus test. To perform the comet assay, mice were divided into a control group and 4 groups of exposed mice sacrificed on day 3 of the experiment, at 0, 2, 6 or 24 h after the last exposure to sevoflurane. Mean tail length (TL), tail moment (TM), and tail intensity (TI) values were significantly higher in exposed mice (all examined organs) than in the control group. Significant DNA damage immediately after exposure to sevoflurane was observed in leukocytes. Damage induction in the liver, kidney, and brain occurred 6 h later than in leukocytes, as expected according to the toxicokinetics of the drug, where blood is the first compartment to absorb sevoflurane. However, none of the tested tissues revealed signs of repair until 24 h after the exposure. To distinguish the unrepaired genome damage in vivo, the micronucleus test was applied. Number of micronuclei in reticulocytes showed a statistically significant increase, as compared with the control group at all observed times after the treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bienengraeber MW, Weihrauch D, Kersten JR, Pagel PS, Warltier DC, 2005. Cardioprotection by volatile anesthetics.Vascul Pharmacol 42: 243–252.
Brozovic G, Orsolic N, Knezevic F, Horvat Knezevic A, Benkovic V, Vrdoljak DV, Saric A, 2008. Evaluation of DNA damage in vivo induced by combined application of cisplatin and sevoflurane. Eur J Anaesthesiol 25: 642–647.
Byhahn C, Heller K, Lischke V, Westphal K, 2001. Surgeon’s occupational exposure to nitrous oxide and sevoflurane during pediatric surgery. World J Surg 25: 1109–1112.
Dusinska M, Collins AR, 2008. The comet assay in human biomonitoring: gene-environment interactions. Mutagenesis 23: 191–205.
Halliwell B, Cross CE, 1994. Oxygen-derived species: their relation to human disease and environmental stress. Environ Health Perspect 102, Supplement 10: 5–12.
Hayashi M, Hashimoto S, Sakamoto Y, Hamada C, Sofuni T, Yoshimura I, 1994. Statistical analysis of data in mutagenicity assays: rodent micronucleus assay. Environ Health Perspect 102, Supplement 1: 49–52.
Heddle JA, Cimino MC, Hayashi M, Romagna F, Shelby MD, Tucker JD, et al. 1991. Micronuclei as an index of cytogenetic damage: past, present, and future. Environ Mol Mutagen 18: 277–291.
Hobbhahn J, Wiesner G, Taeger K, 1998. Occupational exposure and environmental pollution: the roleofinhalation anesthetics with special consideration of sevoflurane. Anaesthesist 47: 77–86.
Holden HE, Majeska JB, Studwell D, 1997. A direct comparison of mouse and rat bone marrow and blood as target tissues in the micronucleus assay. Mutat Res 391: 87–89.
Jagetia GC, Nayak V, 2000. Effect of doxorubicin on cell survival and micronuclei formation in HeLa cells exposed to different doses of gamma-radiation. Strahlenther Onkol 176: 422–428.
Jaloszyński P, Kujawski M, Wasowicz M, Szulc R, Szyfter K, 1999. Genotoxicity of inhalation an esthetics halothane and isoflurane in human lymphocytes studied in vitro using the cometassay. Mutat Res 439: 199–206.
Karabiyik L, Sardaş S, Polat U, Kocaba SNA, Karakaya AE, 2001. Comparison of genotoxicity of sevoflurane and isoflurane in human lymphocytes studied in vivo using the comet assay. Mutat Res 492: 99–107.
Keaney A, Diviney D, Harte S, Lyons B, 2004. Postoperative behavioral changes following anesthesia with sevoflurane. Paediatr Anaesth 14: 866–870.
Kharasch ED, 1995. Biotransformation of sevoflurane. Anesth Analg 81, Supplement 6: 27–38.
Laurent C, Voisin P, Pouget JP, 2006. DNA damage in cultured skin microvascular endothelial cells exposed to gamma rays and treated by the combination pentoxifylline and alpha-tocopherol. Int J Radiat Biol 82: 309–321.
Meyer RR, Münster P, Werner C, Brambrink AM, 2007. Isoflurane is associated with a similar incidence of emergence agitation/delirium as sevoflurane in young children — a randomized controlled study. Paediatr Anaesth 17: 56–60.
Morgan WF, 2003. Non-targeted and delayed effects of exposure to ionizing radiation: I. Radiation-induced genomic instability and bystander effects in vitro. Radiat Res 159: 567–580.
Morgan WF, 2003. Non-targeted and delayed effects of exposure to ionizing radiation: II. Radiation-induced genomic instability and bystander effects in vivo, clastogenic factors and transgenerational effects. Radiat Res 159: 581–596.
Nishiyama T, Fujimoto T, Hanaoka K, 2004. Comparison of liver function after hepatectomy in cirrhotic patients between sevoflurane and isoflurane in anesthesia with nitrous oxide and epidural block. Anesth Analg 98: 990–993.
Pihlainen K, Ojanperä I, 1998. Analytical toxicology of fluorinated inhalation anaesthetics. Forensic Sci Int 97: 117–133.
Rozgaj R, Kasuba V, Brozović G, Jazbec A, 2009. Genotoxic effects of anaesthetics in operating theatre personnel evaluated by the comet assay and micronucleus test. Int J Hyg Environ Health 212: 11–17.
Sardaş S, Aygün N, Gamli M, Unal Y, Unal N, Berk N, Karakaya AE, 1998. Use of alkaline comet assay (single cell gel electrophoresis technique) to detect DNA damages in lymphocytes of operating room personnel occupationally exposed to anaesthetic gases. Mutat Res 418: 93–100.
Sasaki YF, Nishidate E, Izumiyama F, Matsusaka N, Tsuda S, 1997. Simple detection of chemical mutagens by the alkaline single-cell gel electrophoresis (comet) assay in multiple mouse organs (liver, lung, spleen, kidney and bone marrow). Mutat Res 391: 215–231.
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL, 1988. A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175: 184–191.
Szyfter K, Szulc R, Mikstacki A, Stachecki I, Rydzanicz M, Jałoszyński P, 2004. Genotoxicity of inhalation anaesthetics: DNA lesions generated by sevoflurane in vitro and in vivo. J Appl Genet 45: 369–374.
Wiesner G, Schiewe-Langgartner F, Lindner R, Gruber M, 2008. Increased formation of sister chromatid exchanges, but not of micronuclei, in anaesthetists exposed to low levels of sevoflurane. Anaesthesia 63: 861–864.
Wong CH, Liu TZ, Chye SM, Lu FJ, Liu YC, Lin ZC, Chen CH, 2006. Sevoflurane-induced oxidative stress and cellular injury in human peripheral polymorphonuclear neutrophils Food Chem Toxicol 44: 1399–1407.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The study was carried out at the Department of Animal Physiology, Faculty of Science, University of Zagreb
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brozovic, G., Orsolic, N., Rozgaj, R. et al. DNA damage and repair after exposure to sevoflurane in vivo, evaluated in Swiss albino mice by the alkaline comet assay and micronucleus test. J Appl Genet 51, 79–86 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03195714
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03195714