Abstract
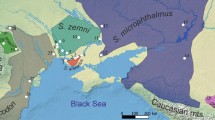
Mole-rats from Karonga, Malawi, the type locality ofCryptomys hottentotus whytei, and a single female mole-rat from the Malawian Nyika Plateau exhibit a karyotype 2n = 4 6 chromosomes, wit h 1 5 metacentr ic an d 8 acrocentr ic chromosome, s ie NF (female) = 76. This trait, together with several morphological features and a previously published genetic analysis (Ingramet al. 2004), identifies this species as a good species, unrelated toCryptomys hottentotus of South Africa, which belongs to the Zambezian clade of the genusCryptomys sensu lato (cf Ingramet al. 2004) and should be therefore called Whyte’s mole-rat,Cryptomys whytei. Available data on ecology and reproductive biology sugges t simila r characteristic s a s i n othe r mole-rat s o f th e genu.s Unexpecte d findin g of lar ge complicat ed undergroun d burro w system s contrasted, howev,e r wi th ve ry f ew abo ve grou nd moun.d s
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar G. H. 1993. The karyotype and taxonomic status ofCryptomys hottentotus darlingi (Rodentia: Bathyergidae). South African Journal of Zoology 28: 201–204.
Bennett N. G. and Faulkes C. G. 2000. African mole rats: Ecology and eusociality. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 1–273.
Burda H., Zima J., Scharff A., Macholan M. and Kawalika M. 1999. The karyotypes ofCryptomys anselli sp. nova andCryptomys kafuensis sp. nova: new species of the common mole-rat from Zambia (Rodentia, Bathyergidae). Zeitschrift für Säugetierkunde 64: 36–50.
Burda H., Honeycutt R. L., Begall S., Grütjen O. and Scharff A. 2000. Are naked and common mole-rats eusocial and if so, why? Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 47: 293–303.
Faulkes C. G., Verheye E., Verheyen W., Jarvis J. U. M. and Bennett N. C. 2004. Phylogeographic patterns of speciation and genetic divergence in African mole-rats (Family Bathyergidae). Molecular Ecology: 613–629.
Filippucci M. G., Burda H., Nevo E. and Kocka J. 1994. Allozyme divergence and systematics of common mole-rats (Cryptomys, Bathyergidae, Rodentia) from Zambia. Zeitschrift für Säugetierkunde 59: 42–51.
Ford C. E. and Hamerton J. L. 1956. A colchicine, hypotonic citrate, squash sequence for mammalian chromosomes. Stain Technolology 31: 247–251.
Honeycutt R. L., Allard M. W., Edwards S. V. and Schlitter D. A. 1991. Systematics and evolution of the family Bathyergidae. [In: The biology of the naked mole-rat. P. W. Sherman, J. U. M. Jarvis and R. D. Alexander, eds]. Princeton University Press, Princeton: 66–96.
Ingram C. M., Burda H. and Honeycutt R. L. 2004. Molecular phylogenetics and taxonomy of the African mole-rats, genusCryptomys and the new genusCoetomys Gray, 1864. Molecular Phylogeny and Evolution 31: 997–1014.
Kawalika M., Burda H. and Brüggert D. 2001. Was Zambia a cradle of the genus Cryptomys (Bathyergidae, Rodentia)? A further new ancestral (?) species ofCryptomys from Zambia. [In: African Small Mammals. C. Denys, L. Granjon L. and A. Poulet, eds]. IRD Editions, Collection Colloques et seminaires, Paris: 253–261.
Lee M. R. 1969. A widely applicable technic for direct processing of bone marrow for chromosomes of vertebrates. Stain Technology 44(3): 155–158.
Macholán M., Burda, H., Zima J., Míšek I. and Kawalika M. 1993. Karyotype of the giant mole-rat,Cryptomys mechowi (Bathyergidae, Rodentia). Cytogenetics and Cell Genetics 64: 261–263.
Macholán M., Scharff A., Burda H., Zima J. and Grütjen O. 1998. The karyotype and taxonomic status ofCryptomys amatus (Wroughton, 1907) from Zambia (Rodentia, Bathyergidae). Zeitschrift für Säugetierkunde 63: 186–190.
Nevo E., Ben-Shlomo R., Beiles A., Jarvis J. U. M. and Hickman G. C. 1987. Allozyme differentiation and systematics of the endemic subterranean mole rats of South Africa. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology 15: 489–502.
Nevo E., Capanna E., Corti M., Jarvis J. U. M. and Hickman G. C. 1986. Karyotype differentiation in the endemic subterranean Mole rats of South Africa (Rodentia, Bathyergidae). Zeitschrift für Säugetierkunde 51: 36–49.
Šumbera R, Chitaukali W. N., Elichová M., Kubová J. and Burda H. 2004. Microclimatic stability in burrows of an Afrotropical solitary bathyergid rodent, the silvery mole-rat (Heliophobius argenteocinereus). Journal of Zoology, London 263: 409–416.
Thomas O. 1897. Exhibition of small mammals collected by Mr. Alexander Whyte during his expedition to the Nyika plateau and Masuka Mountains, NR Nyasa. Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London 1897: 430–436.
Van Daele P. A. A. G., Dammann P., Kawalika M., Meier J.-L., Van De Woestijne C. and Burda H. 2004. Chromosomal diversity inCryptomys mole-rats (Rodentia: Bathyergidae) in Zambia; with the description of new karyotypes. Journal of Zoology, London 264: 317–326.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Associate Editor was Andrzej Zalewski.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burda, H., šumbera, R., Chitaukali, W.N. et al. Taxonomic status and remarks on ecology of the Malawian mole-ratCryptomys whytei (Rodentia, Bathyergidae). Acta Theriol 50, 529–536 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03192646
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03192646