Summary
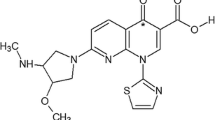
Etoposide is mainly metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A and is a substrate for P-glycoprotein (P-gp). This study examined the effects of verapamil, a CYP3A and P-gp inhibitor, on the pharmacokinetics of etoposide in rats. A single dose of etoposide was administered via oral (p.o.; 10 mg/kg) or intravenous (i.v.; 3.3 mg/kg) routes to rats alone (control animals) or together in combination with verapamil (2 or 6 mg/kg; experimental animals). The presence of verapamil significantly increased the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC); (P<0.05; 39.2–47.6%) and significantly reduced (P<0.01; 27.8–31.2%) the total body clearance (CLt) of p.o. administered etoposide. The absolute bioavailability (F) of etoposide increased by 1.38- to 1.47-fold. The presence of verapamil significantly increased (P<0.01; 38.3–38.9%) the AUC and significantly reduced (P<0.01; approximately 27%) the total body clearance (CLt) of i.v. administered etoposide. This increased bioavailability suggests that verapamil inhibits metabolic activity and elimination etoposide. The increased bioavailability of etoposide in the presence of verapamil should be taken into consideration for dosage regimens due to a potential drug interaction (DI).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Higgins C.F. (1992): ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol., 8, 67–113.
Borst P., Evers R., Kool M., Wijnholds J. (2000): A family of drug transporters: the multidrug resistance-associated proteins. J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 92, 1295–1302.
Chan L.M., Lowes S., Hirst B.H. (2004): The ABCs of drug transport in intestine and liver: efflux proteins limiting drug absorption and bioavailability. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 21, 25–51.
Sutherland L., Ebner T., Burchell B. (1993): The expression of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases of the UGT1 family in human liver and kidney and in response to drugs. Biochem. Pharmacol., 45, 295–301.
Turgeon D., Carrier J.S., Levesque E., Hum D.W., Belanger A. (2001): Relative enzymatic activity, protein stability, and tissue distribution of human steroid-metabolizing UGT2B subfamily members. Endocrinology, 142, 778–787.
Clark P.I., Slevin M.L. (1987): The clinical pharmacology of etoposide and teniposide. Clin. Pharmacokinet., 12, 223–252.
Relling M.V., Nemec J., Schuetz E.G., Schuetz J.D., Gonzalez F. J., Korzekwa K.R. (1994): O-demethylation of epipodo-phyl-lotoxins is catalyzed by human cytochrome P450 3A4. Mol. Pharmacol., 45, 352–358.
van Maanen J.M., de Vries J., Pappie D., van den Akker E., Lafleur V.M., Retel J., van der Greef J., Pinedo H.M. (1987): Cytochrome P-450-mediatedO-demethylation: a route in the metabolic activation of etoposide (VP-16-213). Cancer Res., 47, 4658–4662.
Kawashiro T., Yamashita K., Zhao X.J., Koyama E., Tani M., Chiba K., Ishizaki T. (1998): A study on the metabolism of etoposide and possible interactions with antitumor or sup-porting agents by human liver microsomes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 286, 1294–1300.
Leu B.L., Huang J.D. (1995): Inhibition of intestinal P-glyco-protein and effects on etoposide absorption. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol., 35: 432–436.
Kan W.M., Liu Y.T., Hsiao C.L., Shieh C.Y., Kuo J.H., Huang J.D., Su S.F. (2001): Effect of hydroxyzine on the transport of etoposide in rat small intestine. Anticancer Drugs, 12, 267–273.
Gottesman M.M., Mickisch G.H., Pastan I. (1994): In vivo models of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Cancer Treat. Res., 73, 107–128.
Lin J.H., Yamazaki M. (2003): Role of P-glycoprotein in pharmacokinetics: clinical implications. Clin. Pharmacol., 42, 59–98.
Bjornsson T.D., Callaghan J.T., Einolf H.J., Fischer V., Gan L., Grimm S., Kao J., King S.P., Miwa G., Ni L., Kumar G., McLeod J., Obach S.R., Roberts S., Roe A., Shah A., Snikeris F., Sullivan J.T., Tweekie D., Vega J.M., Walsh J., Wrighton S.A. (2003): The conduct of in vitro and in vivo drug-drug interaction studies: a PhRMA perspective. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 43, 443–469.
Li X., Yun J.K., Choi J.S. (2007): Effects of morin on the pharmacokinetics of etoposide in rats. Biopharm. Drug Dispos., 28, 151–156.
Kovarik J.M., Beyer D., Bizot M.N., Jiang Q., Allison M.J., Schmouder R.L. (2005): Pharmacokinetic interaction between verapamil and everolimus in healthy subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 60, 434–437.
Carcel-Trullols J., Torres-Molina F., Araico A., Saadeddin A., Peris J.E. (2004): Effect of cyclosporine A on the tissue distribution and pharmacokinetics of etoposide. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol., 54, 153–160.
Spahn-Langguth H., Baktir G., Radschuweit A., Okyar A., Terhaag B., Ader P., Hanafy A., Langguth P. (1998): P-glyco-protein transporters and the gastrointestinal tract: evaluation of the potential in vivo relevance of in vitro data employing talinolol as model compound. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Then, 36, 16–24.
Hollt V., Kouba M., Dietel M., Vogt G. (1992): Stereoisomers of calcium antagonists which differ markedly in their potencies as calcium blockers are equally effective in modulating drug transport by P-glycoprotein. Biochem. Pharmacol., 43, 2601–2608.
Vogelgesang B., Echizen H., Schmidt E., Eichelbaum M. (1984): Stereoselective first-pass metabolism of highly cleared drugs studies of the bioavailability of L- and D-verapamil examined with a stable isotope technique. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 18, 733–740.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piao, YJ., Li, X. & Choi, JS. Effects of verapamil on etoposide pharmacokinetics after intravenous and oral administration in rats. Eur. J. Drug Metabol. Pharmacokinet. 33, 159–164 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191113
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191113