Summary
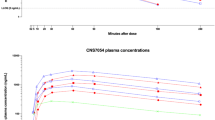
This study was designed to investigate the multiple — dose pharmacokinetics of a range of intransal doses of IS-159, a serotonin 1B/1D receptor agonist. Intranasal doses of 1, 2, 4 and 6 mg of IS-159 were administered twice at an interval of 4 hours to 17 healthy male and female subjects in a two-way crossover study. Plasma concentrations of IS-159 were determined from blood samples taken at regular intervals up to 24 hours after the first administration during both treatment periods. IS-159 was rapidly absorbed and eliminated with a tmax of approximately 15 min and a t1/2 of approximately 1.6 hours. With increasing dose, the exposure increased dose-proportionally, and IS-159 pharmacokinetics appear not to be influenced by gender and food intake. The results showed dose-proportional pharmacokinetics of IS-159 in the dose range tested and a low propensity for drug accumulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rasmussen B.K., Jensen R., Schroll M., Olesen J. (1991): Epidemiology of headache in a general population: a prevalence study. J. Clin. Epidemiol., 44. 1147–1157.
Blau J.N., Dexter S.L. (1981): The site of pain origin during migraine attacks. Cephalalgia, 1. 143–147.
Friberg L., Olesen J., Iversen H.K., Sperling B. (1991): Migraine pain associated with middle cerebral artery dilation: reversal by sumatriptan. Lancet, 338. 13–17.
Moskowitz M.A. (1992): Neurogenic versus vascular mechanisms of sumatriptan and ergot alkaloids in migraine. TIPS, 13, 307–312.
Leysen J.E., Gommeren W. (1984): In Vitro Binding Profile of Drugs Used in Migraine. In: Amery W.K., Van Nueten J.M., Wauquier A., (eds). The Pharmacological Basis of Migraine Therapy. London: Pitman Publishing, 255–266.
Tfelt-Hansen P., Saxena P.R., Ferrari M.D. (1995): Ergot Alkaloids. In: De Wolff F.A. (ed). Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Vol 21. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science, 61–78.
Kimball R.W., Friedman A.P., Vallejo E. (1960): Effect of serotonin in migraine patients. Neurology, 10. 107–111.
Sicuteri F., Testi A., Anselmi B. (1961): Biochemical investigations in headache: increase in the hydroxyindoleacetic acid excretion during migraine attacks. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol., 19. 55–58.
Ensink F.B. (1991): Subcutaneous sumatriptan in the acute treatment of migraine. Sumatriptan International Study Group. J. Neurol., 238 (Suppl 1). S66-S69.
Cady R.K., Wendt J.K., Kirchner J.R., Sargent J.D., Rothrock J.F., Skaggs H. Jr. (1991): Treatment of acute migraine with subcutaneous sumatriptan. JAMA 265. 2831–2835.
Hamel E. (1996): 5-HT1D receptors: pharmacology and therapeutic potential. Serotonin, 1. 19–29.
European Pharmacopoeia 1997. Supplement 1999 to the 3rd edition, European Pharmacopoeia Secretariat, Strasbourg.
Dingemanse J., Soubrouillard C., Paris J., Pisano P., Blin O. (2000): Pronounced effect of caprylocaproyl macrogolglycerides on nasal absorption of IS-159, a peptide serotonin 1B/1D receptor agonist. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 68. 114–121.
Volans G.N. (1978): Migraine and drug absorption. Clin. Pharmacokinet., 3. 313–318.
Pontiroli A.E., Calderara A., Pozza G. (1989): Intranasal drug delivery: potential advantages and limitations from a clinical pharmacokinetic perspective. Clin. Pharmacokinet., 17. 299–307.
Merkus F.W.H.M., Schipper N.G.M., Hermens W.A.J.J., Romeijn S.G., Verhoef J.C. (1993): Absorption enhancers in nasal drug delivery: efficacy and safety. J. Controlled Release, 24. 201–208.
Batts A.H., Marriott C., Martin G.P., Bond S.W., Greaves J.L., Wilson C.G. (1991): The use of a radiolabelled saccharin solution to monitor the effect of the preservatives thiomersal, benzalkonium chloride and EDTA on human nasal clearance. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 43. 180–185.
Roon K.I., Soons P.A., Uitendaal M.P., de Beukelaar F., Ferrari M.D. (1999): Pharmacokinetic profile of alnitidan nasal spray during and outside migraine attacks. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 47. 285–290.
Tfelt-Hansen P. (1998): Efficacy and adverse events of subcutaneous, oral, and intranasal sumatriptan used for migraine treatment: a systematic review based on number needed to treat. Cephalalgia, 18. 532–538.
Duquesnoy C., Mamet J.P., Sumner D., Fuseau E. (1998): Comparative pharmacokinetics of single doses of sumatriptan following subcutaneous, oral, rectal and intranasal administration. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 6. 99–104.
Dahlöf C.G.H., Boes-Hansen S., Cederberg C.-G., Hardebo J.-E., Henriksson A. (1998): How does sumatriptan nasal spray perform in clinical practice? Cephalalgia, 18. 278–282.
Tepper S.J., Rapoport A.M. (1999): The triptans: a summary. CNS Drugs, 12. 403–417.
Dingemanse J., Gray J.A., Soubrouillard C., Jouve E., Chauveau J., Blin O. (1999): Pilot efficacy study of IS-159, a peptide serotonin 1B/1D receptor agonist, after intranasal application in migraineurs. 9th Congress of the International Headache Society, Barcelona, Spain, 22–26.
Seaber E.J., Peck R.W., Smith D.A., Allanson J., Hefting N.R., van Lier J.J., Sollie F.A., Wemer J., Jonkman J.H.G. (1998): The absolute bioavailability and effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of zolmitriptan in healthy volunteers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 46. 433–439.
Lee Y., Conroy J.A., Stepanavage M.E., Mendel C.M., Somers G., McLoughlin D.A., Olah T.V., De Smet M., Keymeulen B., Rogers J.D. (1999): Pharmacokinetics and tolerability of oral rizatriptan in healthy male and female volunteers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 47. 373–378.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Giersbergen, P.L.M., Dingemanse, J. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of intranasally administered IS-159 in healthy subjects. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 28, 49–54 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190866
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190866