Summary
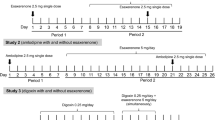
This study investigated the effect of mibefradil on digoxin pharmacokinetics an pharmacodynamics. Following a loading dose of digoxin (0.375 mg, three times, day 1), 0.375 mg was administered once daily to 40 healthy subjects (days 2–15). Mibefradil was administered daily at 50 mg, 100 mg, or 150 mg (days 9–15). With co-administration of 50 mg or 100 mg mibefradil (the recommended doses), mean digoxin Cmax values increased 1.19- and 1.32-fold, respectively; Cmin values were 0.95- and 1.04-fold, respectively; mean AUC0−24h increased 1.05- and 1.11-fold, respectively; and the total amount of digoxin excreted in urine remained unchanged. Digoxin monotherapy produced modest but transient prolongations of PQ interval, small decreases in heart rate, and no changes in blood pressure. With the addition of mibefradil, no effects on trough blood pressure or cardiac index were observed, but there was a further increase in PQ interval and decrease in heart rate. In a previous study, mibefradil had no significant effect on trough plasma digoxin concentration in patients with congestive heart failure and ischemia. Therefore, while the vast majority of patients should not need their digoxin dosages adjusted when given mibefradil, an occasional patient may require dose reductions based on clinical response and plasma digoxin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mishra S., Hermsmeyer K. (1994): Selective inhibition of T-type Ca2+ channels by Ro 40−5967. Circ. Res., 75: 144–148.
Clozel J-P., Banken L., Osterrieder W. (1989): Effects of Ro 40–5 967, a novel calcium antagonist, on myocardial function during ischemia induced by lowering coronary perfusion pressure in dogs. comparison with verapamil. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol., 14: 713–721.
Clozel J-P., Véniant M., Osterrieder W. (1990): The structurally novel Ca2+ channel blocker Ro 40–5967, which binds to the [3H]-desmethoxyverapamil receptor, is devoid of the negative inotropic effects of verapamil in normal and failing rat hearts. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther., 4: 731–736.
Schmitt R., Kleinbloesem, C., Belz, G.et al. (1992): Hemodynamic and humoral effects of the novel calcium antagonist Ro 40–5967 in patients with hypertension. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 52: 314–323.
Bernink P., Prager G., Schelling A., Kobrin I. (1996): Antihypertensive properties of the novel calcium antagonist mibefradil (Ro 40–5967): a new generation of calcium antagonists? Hypertension, 27: 426–432.
Bursztyn M., Kadr H., Tilvis R.et al. (1997): Mibefradil, a novel calcium antagonist, in elderly hypertensives: favorable hemodynamics and pharmacokinetics. Am. Heart J., 134: 238–247.
Carney S., Wing L., Ribeiro A.et al. (1997): The addition of mibefradil to chronic hydrochlorothiazide therapy in hypertensive patients is associated with a significant antihypertensive effect. J. Hum. Hypertens., 11: 387–393.
Oparil S., Kobrin I., Abernethy D., Levine B., Reif M., Shepherd A. (1997)b: Dose-response characteristics of mibefradil, a novel calcium antagonist, in the treatment of essential hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens., 10: 735–742.
Alpert J., Kobrin I., DeQuattro V., Friedman R., Shepherd A., Fenster P. (1997): Additional anti-anginal and anti-ischemic efficacy of mibefradil in patients pretreated with a beta-blocker for chronic stable angina pectoris. Am. J. Cardiol., 79: 1025–1030.
Bakx A., van der Wall E., Braun S., Emanuelsson H., Bruschke A., Kobrin I. (1995): Effects of the new calcium antagonist mibefradil (Ro 40–5967) on exercise duration in patients with chronic stable angina pectoris: a multicenter, placebo-controlled study. Am. Heart J., 130: 748–757.
Braun S., van der Wall E., Emanuelsson H., Kobrin I. (1996): Effects of a new calcium antagonist, mibefradil (Ro 40–5967), on silent ischemia in patients with stable chronic angina pectoris-. a multicenter placebo-controlled study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 27: 317–322.
Reuning R., Geraets D., Rocei, M., Vlasses P. (1992): Digoxin. In: Evans W., Schentag J., Jusko W. (Eds) Applied pharmacokinetics: principles of therapeutic monitoring. Vancouver: Applied Therapeutics, 20-1–20-48.
Klein H. Lang R., DiSegni E., Kaplinsky E. (1980): Verapamil-digoxin interaction. N. Engl. J. Med., 303: 160.
Belz G., Aust P., Munkes R. (1981): Digoxin plasma concentrations and nifedipine. Lancet, 1: 844–845.
Pedersen K., Dorph-Pedersen A., Hvidt S., Klitgaard N., Kjaer K., Nielsen-Kudsk F. (1982): Effect of nifedipine on digoxin kinetics in healthy subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 32: 562–565.
Pederson K., Dorph-Pederson A., Hvidt S., Klitgaard N., Pederson, K. (1982): The long-term effect of verapamil on plasma digoxin concentration and renal digoxin clearance in healthy subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 221: 123–127.
Siepmann M., Kleinbloesem C., Kirch W. (1995): The interaction of the calcium antagonist Ro 40–5967 wity digoxin. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 39: 491–496.
Chen C., Lindberg E., Welker H., Kobrin I. (1996): Population pharmacodynamic analysis (using NONMEM) of mibefradil in patients with ischemic congestive heart failure [Abstract]. Pharm. Res., 13: S424.
Gibaldi M., Perrier D. (1982): Pharmacokinetics. New York: Marcel Dekker.
Schwartz J. (1988): Effects of amlodipine on steady-state digoxin concentrations and renal digoxin clearance. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol., 12: 1–5.
Dunselman P., Scaf A., Kuntze C., Lie K., Wesseling H. (1988): Digoxin-felodipine interaction in patients with congestive heart failure. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 35: 461–465.
Kelly R., Smith T. (1996): Pharmacological treatment of heart failure. In: Hardman J., Limbird L., Molinoff P., Ruddon R., Gilman A. (Eds) Goodman and Gilman’s: The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 9th edn. New York. McGraw-Hill, 809–838.
Orito K., Satoh K., Taira N. (1993): Cardiovascular profile of Ro 40–5967, a new nondihydropyridine calcium antagonist, delineated in isolated, blood-perfused dog hearts. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol., 22: 293–299.
Rosenquist M., Brembilla-Perrot B., Meinertz T.et al. (1997): The acute effects of intravenously administered mibefradil on the electrophysiologic characteristics of the human heart. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 52: 7–12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peters, J., Welker, H.A. & Bullingham, R. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic aspects of concomitant mibefradil-digoxin therapy at therapeutic doses. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 24, 133–140 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190358
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190358