Summary
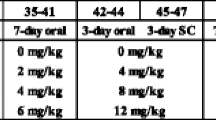
Parenteral phenytoin solution (Dilantin®) was given rectally three times a day for three days to two beagle dogs. This was well tolerated, with no evidence of mucosal irritation noted either on endoscopic nor on rectal mucosal biopsy. When given in this manner, phenytoin is absorbed to a limited degree in canines. Parenteral phenytoin solution can be safely administered rectally, despite a pH of 12. Further study in normal volunteers is needed to assess the usefulness of this route of administration in situations in which the oral and/or parenteral route of administration is unavailable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cloyd J.C., Kriel R.L. (1981): Bioavailability of rectally administered valproic acid syrup. Neurology (NI) 31, 1348–1352.
Graves N.M., Kriel R.L., Jones-Saete C., Cloyd J.C. (1985): Relative bioavailability of rectally administered carbarnazepine suspension in humans. Epilepsia 26, 429–433.
Snead O.C., Miles M.V. (1985): Treatment of status epilepticus in children with rectal sodium valproete. J. Pediatr, 196, 323–325.
Knudsen F.U. (1985): Effective short-tenn diazepam propylaxis in febrile convulsions. J. Pediatr, 106, 487–490.
Milligan N.M., Dhillon S., Griffiths A., Oxley J., Richens A. (1984). A clinicallrial of single dose rectal and oral administration of diazepam for the prevention of serial seizures in adult epileptic patients. J. Neurol, Neurosurg. Psychiatr. 47, 235–240.
Graves N.M., Kriel R.L. (1987): Bioavailebility of rectally administered lorazeparn. Clin. Neuropharmacol, 10(6), 555–559.
de Boer A.G., Moolenar F., de Leede L.G.J., Breimer D.D. (1982): Rectal drug administration: Clinical phannacokinetic considerations. Clin. Phannacokinet. 7, 286–311.
Magnussen I. et al. (1979): Absorption of diazepam in man following rectal and parenteral administration. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol, 45, 87–90.
Hoppu K. et al. (1981): Diazepam rectal solution for home treatment of acute seizures in children. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 70, 369–372.
Johannessen S.I. et al., (1984): Metabolism of Antiepileptic Drugs. New York:Raven Press, pp. 61–71.
Jensen P.K. et al. (1982): Serum concentration of clonazepam after rectal administration. Acta Neurol. Scand. 68, 417–420.
Levine H.L., Cohen M.E., Duffner P.K., Lacey D.J., Karpynec R., Shen D.D. (1982): Rectal absorption and disposition of secobarbital in epileptic children. Pediatr, Phannacol. 2, 33–38.
Kvan L. Johannessen S. (1975): Lack of efficacy of phenytoin suppositories in antiepileptic treatment. Acta Neurol. Scand. 55, 103–104.
Moolenaar S., Jelsma R.B.H., Visser J., Meijer D.K.F. (1981): Manipulation of rectal absorption rate of phenytoin in man. Pharm. Weekbl. [Sci.] 1, 175–180.
Martindale (1982): The Extra Pharmacopoeia. London: Pharmaceutical Press, pp. 709–711.
Yu D.K. et al., (1985): Phannacokinetics of propylene glycol in humans during multiple dosing regimens. J. Pharm, Sci. 74, 876–879.
Csaky T.Z. (1984): Phannacology of Intestinal Permeation. Handbook of experimental pharmacology. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, Vol. 70 (1), pp. 81.
Frey H.H., Loseher W. (1980): Clinical pharmacokinetics of phenytoin in the dog: A reevaluation. Am. J. Vet. Res. 41, 1635–1638.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuerst, R.H., Graves, N.M., Kriel, R.L. et al. Absorption and safety of rectally administered phenytoin. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 13, 257–260 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190088
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190088