Summary
The pharmacokinetics and the metabolic profile of tomoxiprole, a new analgesic antiinflammatory agent belonging to the class of 3-alkyl-2-aryl-3H-naphth (1,2-d)imidazoles, were studied in the rat.
After oral administration (5 mg/kg) to male rats, tomoxiprole was rapidly absorbed, mostly by the gut, and reached maximum plasma levels of about 0.5 μg/ml in 0.25-2 h. A metabolic first pass reduced the extent of oral bioavailability of the parent compound to about half, while absorption (total14C data) was estimated to be complete.
After intravenous injection (2.5 mg/kg), the plasma kinetics of tomoxiprole in male rats showed a bi-exponential profile, and the terminal elimination half-life was 4.2 h. The apparent volume of distribution was high, suggesting a wide distribution of the drug.
Increasing the oral dose by ten times (50 mg/kg), resulted in linear kinetics with a proportional increase of the C max and AUC values a n d the same value of terminal elimination half-life. In females given a 5 mg/kg dose, the plasma levels of14C, tomoxiprole and AUC values were somewhat higher than in males.
The plasma levels of total14C after iv or po treatments were higher a n d more sustained than those of tomoxiprole. The kinetic profile after iv administration was described by a three exponential terms equation and the terminal elimination half-life was 38.7 h. Upon iv administration, total14C was rapidly distributed in highly vascularized tissues while in others, like the bone, fat, gonads, pancreas and skin the equilibrium with the central compartment was attained later.
Target organs were the adrenals, liver, lungs, pancreas, thyroid, stomach and above all the fat tissue. Elimination from tissues was almost complete 48 h after the treatment.14C was eliminated mainly in the feces (80% of dose) as metabolites.
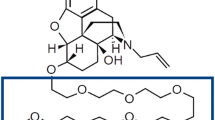
In the bile, five polar metabolites were detected; one of them, desmethyl tomoxiprole glucuronide, accounting alone for more than 80% of the total biliary radioactivity: was purified and its structure assigned.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Toja E., Selva D., and Schiatti P. (1984): 3-Alkyl-2-aryl-3H-naphth (1,2-d) imidazoles, a novel class of non-acidic antiinflammatory agents. J. Med. Chem.,27, 610–616.
Schiatti P., Selva D., Galliani G., Baldoli E., Toja E. and Glässer A. (1985): Highly selective antiinflammatory and analgesic activity of 3-(1-methyl-ethyl)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3H-naphth(1,2-d)imidazole (tomoxiprole), a new non-acidic molecule. Arzneimittel Forsch. Drug. Res. (in press).
Luzzani F., Colombo G., Schiatti P., Selva D. and Glässer A. (1984): Inhibition of PG-production by tomoxiprole, a new steroidal non acidic antiinflammatory compound in rat gastric mucosa a n d inflammatory exudate. IRCS Med. Sei.,12, 77–78.
Odasso G. and Toja E. (1983): One pot synthesis of 3-(1-methylethyl)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3H-naphth-(1,2-d) imidazole. J. Lab. and Radiopharm.,20, 1189–1192.
Bernareggi A., Ratti B. and Toselli A. (1984): High-performance liquid chromatography of MDL-035 in the plasma of rats, dogs and humans. J. Liquid Chrom.,7, 2093–2101.
Shen T.Y. (1981): Toward more selective antiarthritic therapy. J. Med. Chem.,24, 1–5.
Schanker L.S. (1971): Absorption of drugs from the gastrointestinal tract. Concepts in Biochemical Pharmacology. Brodie BB and Gillette J.R. eds. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York,1, 9–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Assandri, A., Bernareggi, A., Ripamonti, A. et al. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of tomoxiprole, a new analgesic antiinflammatory agent, in the rat. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 10, 161–170 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189711
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189711