Summary
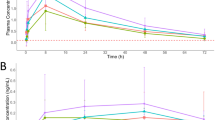
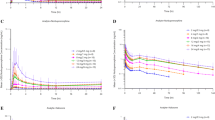
Buprenorphine is a newly-developed strong analgesic. A selected ion monitoring method has been developed to measure its plasma levels over the concentration range 20–3000ng ml−1. Six baboons each received intravenous and intramuscular doses of buprenorphine hydrochloride at a level of 5mg/kg in a cross-over study. The mean peak plasma concentrations (± standard deviation) were 2290±357ng ml−1 and 805±416ng ml−1 respectively and the corresponding times to the peak levels were 4.0±1.5 minutes and 30.3±24.6 minutes suggesting the rapid release of the drug from intramuscular sites. Comparison of areas under the plasma concentration versus time curves to 24 hours after dosing showed the mean bioavailability of buprenorphine from the intramuscular doses was 70% of that from the reference intravenous doses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kay B. (1978) A double-blind comparison of morphine and buprenorphine in the prevention of pain after operation. Br. J. Anaesth.,50, (6), 605–609.
Adriansen H. and Van De Walle J. (1976) Clinical use of buprenorphine in chronic administration. Acta. Anaesthiol. Belg.,27, (3), 187–191.
De Castro J. and Parmentier P. (1976). Buprenorphine in analgesic anaesthesia. Report on 200 cases. Sixth World Congress of Anaesthesiology, Mexico City. Societe d’ Anesthesie de Charleroi, Belgium. 103–155.
Cowan A., Lewis J.W. and Macfarlane I.R. (1971). Analgesic and dependence studies with oripavine partial agonists. Br. J. Pharmacol.,43, 461–462 p.
Hipps P.P., Eveland M.R., Meyer E.R., Sherman, W.R. and Cicero, T.J. (1976). Mass fragmentography of morphine: Relationship between brain levels and analgesic activity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.196, (3), 642–648.
Jindal S.P. and Vestergaard P. (1978). Quantitation of etorphine in urine by selective ion monitoring using tritiated etorphine as an internal standard. J. Pharm. Sei.67, (2), 260–261.
Ehrsson H. Walle T. and Buotell H. (1971). Quantitative gas-chromatographic determination of picogram quantities of amino and alcoholic compounds by electron capture detection. Acta. Pharm. Suecica.8, 27–38.
Blau K. and King G. (1977). The handbook of deriva-tives for chromatography. Heyden and Son, London.
Davies L.O. (1949). Statistical methods in research and production. 2nd ed. London, Oliver and Boyd.
Draper N.R. and Smith H. (1966). Applied regression analysis. 1st ed. Wiley and Sons, New York.
Cochran W.G. and Cox G.M. Ecperimental Designs. Wiley and Sons, New York. 1957.
Spector S. (1971) Quantitative determination of morphine in serum by radioimmunoassay. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.178, 253–258.
Dahlstrom B.E. and Paalzow L.K. (1978). Pharmacokinetic interpretation of the enterohepatic recirculation and first-pass elimination of morphine in the rat. J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm.6, 505–519.
Smith R.L. (1973). The excretory function of bile. Chapman and Hall, London.
Wolen R.L., Gruber Jr. C.M., Kiplinger G.F. and Scholz N.E. (1971) Concentration of propoxyphene in human plasma following oral, intramuscular and intravenous administration. Toxic. Appl. Pharmac.19, 480–492.
Kostenbauder H.B., Rapp R.P., McGroven J.P., Foster T. S., Perrier D.G., Blacker H.M., Hulon W.C. and Kinkel A.W. (1975) Bioavailability of single dose pharmacokinetics of intramuscular phenytoin. Clin. Pharm. Ther.18. 449–456.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lloyd-Jones, J.G., Robinson, P., Henson, R. et al. Plasma concentration and disposition of buprenorphine after intravenous and intramuscular doses to baboons. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 5, 233–239 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189469
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189469