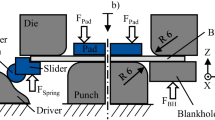
Abstract
Fundamental and informative data of axisymmetric stretch-drawing of several sheet metals with thichness of 0.7~1.0 mm are presented especially for single and double operations. Very small radius is applied to the die-profile (or -shoulder) in all operations to induce wall-thinning by the effect of bending-under-tension, from which the name ‘stretch-drawing’ comes. It is clearly demonstrated that deeper cups could be formed by the single and double stretch-drawings from smaller cirlcular blanks due to such wall-thinning action than in the usual deep-drawing of larger blanks. From this fact, it is emphasized that the deep-drawability of a sheet metal is not evaluated simply by the conventional LDR (=limiting drawing ratio), but the depth of the drawn cup should also be taken into account. Many experimental data about various metals and thicknesses given in this paper offer a valueable information on this process for more general use which recommends to replace the conventional deep-drawing process by the stretch-drawing process both for single and double operations. In the single stretch-drawing, it is also confirmed that a deeper cup can be produced by raising the blank-holding force at later stage of operation. Fracturing is found to occur at the middle section of the wall part or at the die-profile other than at the punch profile common in the usual deep-drawing process. Numerical simulation of the single stretch-drawing process is also performed by use of DYNA-3D code to confirm that a satisfactory prediction especially in the depth of the drawn-cup can be done at least in a practical sense, although this kind of numerical analysis is very difficult because of the severity or localization of deformation around the die profile. The drawn cup of SUS304 among others fractures in a couple of weeks after the operation due to the residual circumferential tensile stress, whereas that of SUS304L does not. In the double stretch-drawing, it is confirmed that very deeper cups can be produced when compared to the usual re-drawing process, which assures typically the usefulness of this operation as a practical process. Fracture often takes place circumferentially or, very peculiarly, even in a spiral mode for SUS304 at the middle of the wall part of the cup.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
K. Imazuet al, Trans. JSME 215, 581 (1993).
e.g., M. Gotoh,Theory of Plasticity, p. 95, Korona-sha (1982).
M. Gotoh, M. Katoh & M. Yamashita,J. Materials Processing Technology 63, 123 (1997).
e.g., N.Kawai,Plasticity in Process, p. 191, Asakura (1982).
J. O. Halliquist,DYNA-3D User’s Manual (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gotoh, M., Kim, Ys. & Yamashita, M. A Fundamental Study of Stretch-Drawing Process of Sheet Metals : Single and Double Operations. Metals and Materials 4, 436–443 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03187805
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03187805