Abstract
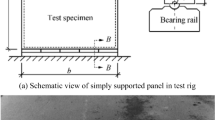
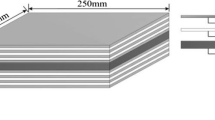
The present paper describes how the cladding of chromium plate with dissimilar metals improves the plastic bendability of the chromium. Three-point bending tests at various temperatures were performed for three types of chromium specimens: a monolithic chromium plate, aluminium- and steel-clad chromium plate. The aluminium-clad chromium plate was bent at 343 K up to a bent angle of 90 degrees without failure, even when the chromium layer was located outside of the plate (tension side), while the monolithic chromium plate could be bent exclusively at temperatures above 403 K. When the chromium layer was located inside of the steel-clad chromium plate (compression side), the plate was successfully bent at 307 K. The FE stress analysis of bending proved that the cladding of chromium plates with proper metals of different kinds is effective to reduce the tensile stress in chromium induced during bending and also the residual stress existing after bending operation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. E. Cairns and N. J. Grant,Trans. Met. Soc. AIME 230, 1150(1964).
A. Gilbert and M. J. Klein,Acta metall. 14, 541 (1966).
K. E. Solie and O. N. Carlson,Trans. Met. Soc. AIME 230, 480 (1964).
H. Johansen and Asai, JohansenJ. Electrochem. Soc. 101, 604 (1954).
H. L. Wain, S. T. M. Johnstone and F. Henderson,J. Inst. Metals 91, 41 (1962).
F. P. Bullen, F. Henderson and H. L. Wain,Phil, Mag. 9, 803 (1964).
A. Ball, F. P. Bullen and H. L. Wain,Phil, Mag. 21, 701 (1970).
H. G. Mellor and A. S. Wronski,Acta metall. 18, 765 (1970).
M. Itoh, F. Yoshida, M. Ohmori, T. Honda and Y. Z. Tai, inProc. Sixth Int. Conf. Mechanical Behaviour of Materials (eds., M. Jono and T. Inoue), Vol. 3, p. 569, Pergamon (1991).
Y. Harada, M. Ohmori, F. Yoshida and M. Itoh, inAdvanced Technology of Plasticity 1990 (edited by Japan Soc. Technol. Plastocity), Vol. 2, p. 719 (1990).
M. Ohmori, K. Tanimoto, M. Yoshida, F. Yoshida and T. Okada, inAdvanced Technology of Plasticity 1993, (eds., Z. R. Wang and He Yuxin), p. 687 (1993), International Academic Publishers.
M. Ohmori, Y. Harada and M. Yoshida, inAdvanced Technology of Plasticity 1996 (ed., T. Altan), Vol. 1, p. 251 (1996).
F. Yoshida, T. Okada, T. Sato, Y. Harada and M. Ohmori,J. Soc. Mater. Sci. Jpn. 46-9, 914 (1997), in Japanese.
E. W. Billington and A. Tate,The Physics of Deformation and Flow, Chap. 14, MacGraw-Hill (1981).
ABAQUS - Standard (Version 5.6) Manual, Hibbitt, Karlsson & Sorensen, Inc. (1996).
H. Verguts and R. Sowerby,Int. J. Mech. Sci. 17, 31 (1975).
S. A. Majlessi and P. Dadras,Int. J. Mech. Sci. 25, 1 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, F., Okada, T., Itoh, M. et al. Bendability of aluminiumand steel-clad chromium plates. Metals and Materials 4, 426–431 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03187803
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03187803