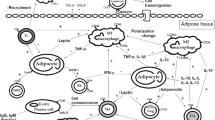
Abstract
Besides adipocytes, specialized in lipid handling and involved in energy balance regulation, white adipose tissue (WAT) is mainly composed of other cell types among which lymphocytes represent a non-negligible proportion. Different types of lymphocytes (B, αβT, γδT, NK and NKT) have been detected in WAT of rodents or humans, and vary in their relative proportion according to the fat pad anatomical location. The lymphocytes found in intra-abdominal, visceral fat pads seem representative of innate immunity, while those present in subcutaneous fat depots are part of adaptive immunity, at least in mice. Both the number and the activity of the different lymphocyte classes, except B lymphocytes, are modified in obesity. Several of these modifications in the relative proportions of the lymphocyte classes depend on the degree of obesity, or on leptin concentration, or even fat depot anatomical location. Recent studies suggest that alterations of lymphocyte number and composition precede the macrophage increase and the enhanced inflammatory state of WAT found in obesity. Lymphocytes express receptors to adipokines while several proinflammatory chemokines are produced in WAT, rendering intricate crosstalk between fat and immune cells. However, the evidences and controversies available so far are in favour of an involvement of lymphocytes in the control of the number of other cells in WAT, either adipocytes or immune cells and of their secretory and metabolic activities. Therefore, immunotherapy deserves to be considered as a promising approach to treat the endocrino-metabolic disorders associated to excessive fat mass development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ablamunits, V., Weisberg, S.P., Lemieux, J.E., Combs, T.P., Klebanov, S. (2007): Reduced adiposity in ob/ob mice following total body irradiation and bone marrow transplantation. Obesity, 15, 1419–1429.
Antuna-Puente, B., Fève, B., Fellahi, S., Bastard, J.P. (2008): Adipokines: the missing link between insulin resistance and obesity. Diabetes Metab, 34, 2–11.
Bouloumié, A., Casteilla, L., Lafontan, M. (2008): Adipose tissue lymphocytes and macrophages in obesity and insulin resistance: makers or markers, and which comes first?Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 28, 1211–1213.
Bouloumié, A., Curat, C.A., Sengenès, C., Lolmède, K. et al. (2005): Role of macrophage tissue infiltration in metabolic diseases. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care, 8, 347–354.
Bour, S., Caspar-Bauguil, S., Iffiú-Soltész, Z., Nibbelink, M. et al.(2009): Semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase/vascular adhesion protein-1 deficiency reduces leukocyte infiltration into adipose tissue and favors fat deposition. Am J Pathol, 174, 1075–1083.
Cancello, R., Hengar, C., Viguerie, N., Taleb, S. et al. (2005): Reduction of macrophage infiltration and chemoattractant gene expression changes in white adipose tissue of morbidly obeses subjects after surgery-induced weight loss. Diabetes, 54, 277–2286.
Caspar-Bauguil, S., Cousin, B., André, M., Nibbelink, M. et al. (2006): Weight-dependent changes of immune system in adipose tissue: Importance of leptin. Exp Cell Res, 312, 2195–2202.
Caspar-Bauguil, S., Cousin, B., Galinier, A., Segafredo, C. et al. (2005): Adipose tissues as ancestral immune organ: site-specific change in obesity. FEBS Lett, 579, 3487–3492.
Champagne, E., Martínez, L. O., Vantourout, P., Collet, X., Barbaras, R. (2005): Role of apolipoproteins in gamma delta and NKT cell-mediated innate immunity. Immunol Res, 33, 241–255.
Cinti, S., Mitchell, G., Barbatelli, G., Murano, I. et al. (2005): Adipocyte death defines macrophage localization and function in adipose tissue of obese mice and humans. J Lipid Res, 46, 2347–2355.
Clément, K., Viguerie, N., Poitou, C., Carette, C. et al. (2004): Weight loss regulates inflammation related genes in white adipose tissue of obese subjects. FASEB J, 18, 1657–1669.
Cousin, B., André, M., Arnaud, E., Pénicaud, L., Casteilla, L. (2003): Reconstitution of lethally irradiated mice by cells isolated from adipose tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 301, 1016–1022.
Cousin, B., André, M., Casteilla, L., Pénicaud, L. (2001): Altered macrophage-like functions of preadipocytes in inflammation and genetic obesity. J Cell Physiol, 186, 380–386.
Cousin, B., Munoz, O., André, M., Fontanilles, A. M. et al. (1999): A role for preadipocytes as macrophage-like cells. FASEB J, 13, 305–312.
Curat, C.A., Miranville, A., Sengenès, C., Diehl, M. et al. (2004): From blood monocytes to adipose tissue-resident macrophages: induction of diapedesis by human mature adipocytes. Diabetes, 53, 1285–1292.
Dandona, P., Aljada, A., Bandyopadhyay, A. (2004): Inflammation: the link between insulin resistance, obesity and diabetes. Trends Immunol, 25, 4–7.
DeClercq, V., Taylor, C., Zahradka, P. (2008): Adipose tissue: the link between obesity and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets, 8, 228–237.
Doherty, D.G., O’Farrelly, C. (2000): Innate and adaptive lymphoid cells in the human liver. Immunol Rev, 174, 5–20.
Dong, Z.M., Gutierrez-Ramos, J.-C., Coxon, A., Mayadas, T. N., Wagner, D. D. (1997): A new class of obesity genes encodes leukocyte adhesion receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 94, 7526–7530.
Duffaut, C., Galitzky, J., Lafontan, M., Bouloumié, A. (2009): Unexpected trafficking of immune cells within the adipose tissue during the onset of obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 384, 482–485.
Duffaut, C., Zakaroff-Girard, A., Bourlier, V., Decaunes, P. et al. (2009): Interplay between human adipocytes and T lymphocytes in obesity. CCL20 as an adipochemokine and T lymphocytes as lipogenic modulators. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 29, 1608–1614.
Faggioni, R., Feingold, K.R., Grunfeld, C. (2001): Leptin regulation of the immune response and the immunodeficiency of malnutrition. FASEB J, 15, 2565–2571.
Fain, J.N., Madan, A.K., Hiler, M.L., Cheema, P., Bahouth, S. W. (2004): Comparison of the release of adipokines by adipose tissue, adipose tissue matrix, and adipocytes from visceral and subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissues of obese humans. Endocrinology 145, 2273–2282.
Fantuzzi, G. (2005): Adipose tissue, adipokines, and inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 115, 911–919.
Farooqi, I.S., Matarese, G., Lord, G. M., Keogh, J. M. et al. (2002): Beneficial effects of leptin on obesity, T cell hyporesponsiveness, and neuroendocrine/metabolic dysfunction of human congenital leptin deficiency. J Clin Invest, 110, 1093–1103.
Feuerer, M., Herrero, L., Cipolletta, D., Naaz, A. et al. (2009): Lean, but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of regulatory T cells that affect metabolic parameters. Nat Med, 15, 930–939
Fischer-Posovszky, P., Wabitsch, M., Hochberg, Z. (2007): Endocrinology of adipose tissue — an update. Horm Metab Res, 39, 314–321.
Friedman, J. M. (2009): Leptin at 14 y of age: an ongoing story. Am J Clin Nutr, 89, 973S-979S.
Friedman, J.M., Halaas, J.L. (1998): Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature, 395, 763–770.
Galinier, A., Carriere, A., Fernández, Y., Caspar-Bauguil, S. et al. (2006): Site specific changes of redox metabolism in adipose tissue of obese Zucker rats. FEBS Lett, 580, 6391–6398.
Hotamisligil, G.S. (2006): Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature, 444, 860–867.
Howard, J.K., Lord, G. M., Matarese, G., Vendetti, S. et al. (1999): Leptin protects mice from starvation-induced lymphoid atrophy and increases thymic cellularity in ob/ob mice. J Clin Invest, 104, 1051–1059.
Kaufman, S.H.E. (1996): γ/δ and other unconventional T lymphocytes: what do they see and what do they do?Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 93, 2272–2279
Kim, K.Y., Kim, J.K., Han, S.H., Lim, J.S. et al. (2006): Adiponectin is a negative regulator of NK cell cytotoxicity. J Immunol, 176, 5958–5964.
Kintscher, U., Hartge, M., Hess, K., Foryst-Ludwig, A. et al. (2008): T-lymphocyte infiltration in visceral adipose tissue: a primary event in adipose tissue inflammation and the development of obesity-mediated insulin resistance. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 28, 1304–1310.
La Cava, A., Matarese, G. (2004): The weight of leptin in immunity. Nat Rev Immunol, 4, 371–379.
Lamas, O., Martínez, J.A., Marti, A. (2003): Effect of a beta3-adrenergic agonist on the immune response in diet-induced (cafeteria) obese animals. J Physiol Biochem, 59, 183–192.
Lord, G.M. (2006): Leptin as a proinflammatory cytokine. Contrib Nephrol, 151, 151–164.
Lord, G. M., Matarese, G., Howard, J. K., Baker, R.J. et al. (1998): Leptin modulates the Tcell immune response and reverses starvationinduced immunosuppression. Nature, 394, 897–901.
Lumeng, C.N., Maillard, I., Saltiel, A. R. (2009): T-ing up inflammation in fat. Nat Med, 15, 846–847.
Marrades, M.P., Martínez, J.A., Moreno-Aliaga, M.J. (2008): ZAG, a lipid mobilizing adipokine, is downregulated in human obesity. J Physiol Biochem, 64, 61–66.
Marti, A., Marcos, A., Martínez, J.A. (2001): Obesity and immune function relationships. Obes Rev, 2, 131–140.
Matarese, G., La Cava, A. (2004): The intricate interface between immune system and metabolism. Trends Immunol, 25, 193–200.
Miyazaki, Y., Iwabuchi, K., Iwata, D., Miyazaki, A. et al. (2008): Effect of high fat diet on NKT cell function and NKT cell-mediated regulation of Th1 responses. Scand J Immunol, 67, 230–237.
Nishimura, S., Manabe, I., Nagasaki, M., Eto, K., Yamashita, H. et al. (2009): CD8+ effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and adipose tissue inflammation in obesity. Nat Med, 15, 914–920.
Palming, J., Gabrielsson, B.G., Jennische, E., Smith, U. et al. (2006): Plasma cells and Fc receptors in human adipose tissue —lipogenic and antiinflammatory effects of immunoglobulins on adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 343, 43–48.
Pinho, M.B., Hurtado, S.P., El-Cheikh, M.C., Rossi, M.I.D. et al. (2002): Myelopoiesis in the omentum of normal mice and during abdominal inflammatory processes. Cell Tissue Res, 308, 87–96.
Poggi, M., Jager, J., Paulmyer-Lacroix, O., Peiretti, F. et al. (2009): The inflammatory receptor CD40 is expressed on human adipocytes: contribution to crosstalk between lymphocytes and adipocytes. Diabetologia, 52, 1152–1163.
Pond, C.M. (2003): Paracrine relationships between adipose and lymphoid tissues: implications for the mechanism of HIV-associated adipose redistribution syndrome. Trends Immunol, 24, 13–18.
Pond, C.M. (2005): Adipose tissue and the immune system. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids, 73, 17–30.
Rausch, M.E., Weisberg, S., Vardhana, P., Tortoriello, D.V. (2008): Obesity in C57BL/6J mice is characterized by adipose tissue hypoxia and cytotoxic T-cell infiltration. Int J Obes (Lond), 32, 451–463.
Robker, R., Collins, R.G., Beaudet, A.L., Mersmann, H.J., Smith, C.W. (2004): Leukocyte migration in adipose tissue of mice null for ICAM-1 and Mac-1 adhesion receptors. Obes Res, 12, 936–940.
Sánchez-Margalet, V., Martin-Romero, C., Santos-Alvarez, J., Goberna, R. et al. (2003): Role of leptin as an immunomodulator of blood mononuclear cells: mechanisms of action. Clin Exp Immunol, 133, 11–19.
Sbarbati, A., Osculati, F., Silvagni, D., Benati, D. et al. (2006): Obesity and inflammation: evidence for an elementary lesion. Pediatrics, 117, 220–223.
Schäffler, A., Müller-Ladner, U., Schölmerich, J., Büchler, C. (2006): Role of adipose tissue as an inflammatory organ in human diseases. Endocr Rev, 27, 449–467.
Skurk, T., Mack, I., Kempf, K., Kolb, H. et al. (2009): Expression and secretion of RANTES (CCL5) in human adipocytes in response to immunological stimuli and hypoxia. Horm Metab Res, 41, 183–189.
Sultan, A., Strodthoff, D., Robertson, A.K., Paulsson-Berne, G. et al. (2009): T cell-mediated inflammation in adipose tissue does not cause insulin resistance in hyperlipidemic mice. Circ Res, 104, 961–968.
Sundstrom, J.B., Ansari, A.A. (1995): Comparative study of the role of professional versus semiprofessional or nonprofessional antigen presenting cells in the rejection of vascularized organ allografts. Transpl Immunol, 3, 273–289.
Szatmari, I., Rajnavolgyi, E., Nagy, L. (2006): PPARgamma, a lipid-activated transcription factor as a regulator of dendritic cell function. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 1088, 207–218.
Tian, Z., Sun, R., Wei, H., Gao, B. (2002): Impaired natural killer (NK) cell activity in leptin receptor deficient mice: leptin as a critical regulator in NK cell development and activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 298, 297–302.
Villena, J.A., Cousin, B., Penicaud, L., Casteilla, L. (2001): Adipose tissues display differential phagocytic and microbicidal activities depending on their localization. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord, 25, 1275–1280.
Weisberg, S., McCann, D., Desai, M., Rosenbaum, M. et al. (2003): Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest, 112, 1796–1808.
Wellen, K. E., Hotamisligil, G. S. (2005): Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J Clin Invest, 115, 1111–1119.
Winer, S., Chan, Y., Paltser, G., Truong, D. et al. (2009): Normalization of obesity-associated insulin resistance through immunotherapy. Nat Med, 15, 921–929.
Wood, S., Trayhurn, P. (2006): Adipokines and the signaling role of adipose tissue in inflammation and obesity. Future Lipidol, 1, 81–89.
Wu, H., Ghosh, S., Perrard, X., Feng, L. et al. (2007): T-cell accumulation and regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted upregulation in adipose tissue in obesity. Circulation, 115, 1029–1038.
Xu, H., Barnes, G. T., Yang, Q., Tan, G. et al. (2003): Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest, 112, 1821–1830.
Zhao, Y., Sun, R., You, L., Gao, C., Tian, Z. (2003): Expression of leptin receptors and response to leptin stimulation of human natural killer cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 300, 247–252
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13105-011-0094-2.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caspar-Bauguil, S., Cousin, B., Bour, S. et al. Adipose tissue lymphocytes: types and roles. J Physiol Biochem 65, 423–436 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03185938
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03185938