Abstract
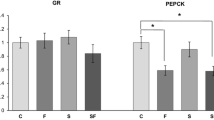
11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (HSDs) enzymes regulate the activity of glucocorticoids in target organs. HSD1, one of the two existing isoforms, locates mainly in CNS, liver and adipose tissue. HSD1 is involved in the pathogenesis of diseases such as obesity, insulin resistance, arterial hypertension and the Metabolic Syndrome. The stress produced by HCl overload triggers metabolic acidosis and increases liver HSD1 activity associated with increased phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, a regulatory enzyme of gluconeogenesis that is activated by glucocorticoids, with increased glycaemia and glycogen breakdown. The aim of this study was to analyze whether the metabolic modifications triggered by HCl stress are due to increased liver HSD1 activity. Glycyrrhetinic acid, a potent HDS inhibitor, was administered subcutaneously (20 mg/ml) to stressed and unstressed four months old maleSprague Dawley rats to investigate changes in liver HSD1, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PECPK) and glycogen phosphorylase activities and plasma glucose levels. It was observed that all these parameters increased in stressed animals, but that treatment with glycyrrhetinic acid significantly reduced their levels. In conclusion, our results demonstrate the involvement of HSD1 in stress induced carbohydrate disturbances and could contribute to the impact of HSD1 inhibitors on carbohydrate metabolism and its relevance in the study of Metabolic Syndrome Disorder and non insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altuna M.E., Lelli S.M., San Martin de Viale L.C. and Damasco M.C. (2006): Effect of stress on hepatic 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity and its influence on carbohydrate metabolism. Can J Physiol Pharmacol, 84, 977–984.
Ayes, B.N. (1966): Assay of inorganic phosphate, total phosphate and phosphatases. In: “Methods in Enzymology, vol. VIII: Carbohydrate Metabolism, Part E” (Neufeld, E.F., Ginsburg, V. eds.) New York/Academic Press, pp 115–118.
Baker, D.J., Timmons J.A. and Greenhaff, P.L. (2005): Glycogen phosphorylase inhibition in type 2 diabetes therapy: a systematic evaluation of metabolic and functional effects in rat skeletal muscle. Diabetes, 54, 2453–2459
Bradford, M. (1976): A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem, 72, 248–254.
Cuadri-Tome, C., Baron, C., Jara-Perez, V., Parody-Morreale, A., Martínez J.C. and Camara-Artigas A. (2006): Kinetic analysis and modelling of the allosteric behaviour of liver and muscle glycogen phosphorylases. J Mol Recognit, 19, 451–457.
Ercan-Fang, N., Gannon M.C., Rath V.L., Treadway J.L., Taylor, M.R., and Nuttall, F.Q. (2002): Integrated effects of multiple modulators on human liver glycogen phosphorylase a. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 283, E29-E37.
Ercan-Fang, N., Taylor, M.R.., Treadway, J.L., Levy, C.B., Genereux, P.E., Gibbs, E.M., Rath, V.L., Kwon, Y., Gannon, M.C. and Nuttal, F.Q. (2005): Endogenous effectors of human liver glycogen phosphorylase modulate effects of indole-site inhibitors. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 289, E366-E372.
Freeman, S, Bartlett, J.B., Convey, G., Hardern I., Teague, J.L., Loxham, S.J., Allen, J.M., Poucher, S.M. and Charles, A.D. (2006): Sensitivity of glycogen phosphorylase isoforms to indole site inhibitors is markedly dependent on the activation state of the enzyme. Br J Pharmacol, 149, 775–785.
Hanson, R.W., and Reshef, L. (1997): Regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem, 66, 581–611,
Harris, H.J., Kotelevtsev Y., Mullins, J.J., Seckl J.R. and Holmes, M.C. (2001): Intracellular regeneration of glucocorticoids by 11 betahydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (11beta-HSD)-1 plays a key role in regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: analysis of 11 beta- HSD-1-deficient mice. Endocrinology, 142, 114–120.
Henke, B.R and Sparks, S.M. (2006): Glycogen phosphorylase inhibitors. Mini Reviews in Med Chem, 6, 845–857.
Hermanowski-Vosatka, A, Balkovec, J.M., Cheng, K., Chen, H.Y. et al. (2005): 11beta-HSD1 inhibition ameliorates metabolic syndrome and prevents progresion of atherosclerosis in mice. J Exp Med, 202, 517–527.
Hiroshi, H., Masato, H., Toshihiko, H. and Kitaro, O. (1999): Glycyrrhetinic acid-induced apoptosis in thymocytes: impact of 11 betahydroysteroid dehydrogenase inhibition. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 277, E624-E630.
Hu, G.X., Lin, H., Sottas. C.M, Morris D.J., Hardy, M.P. and Ge R.S. (2008): Inhibition of 11beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Enzymatic Activities by Glycyrrhetinic AcidIn Vivo Supports Direct Glucocorticoid-Mediated Suppression of Steroidogenesis in Leydig Cells. J Androl, 29, 345–351.
Igarreta, P, Calvo, J.C, and Damasco, M.C. (1999): Activity of renal 11betahydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 (11betaHSD2) in stressed animals. Life Sci, 64, 2285–2290.
Jin J.Y., DuBois, D.C., Almon, R.R and Jusko, W.J (2004): Receptor/gene-mediated pharmacodynamic effects of methylprednisolone on phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase regulation in rat liver. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 309, 328–339.
Kageyama, Y., Suzuki, H., Saruta, T. (1992): Glycyrrhizin induces mineralocorticoid activity through alterations in cortisol metabolism in the human kidney. J Endocrinol, 135, 147–152.
Lelli, S.M., San Martin de Viale, L.C. and Mazzetti, M.B. (2005): Response of glucose metabolism enzymes in an acute porphyria model. Role of reactive oxygen species. Toxicology, 216, 49–58.
Li, R.S., Nakagawa, Y., Nakanishi, T., Fujisawa, Y. and Ohzeki, T. (2004): Different responsiveness in body weight and hepatic 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (11beta-HSD) type 1 mRNA to 11beta-HSD inhibition by glycyrrhetinic acid treatment in obese and lean zucker rats. Metabolism, 53, 600–606.
Livingstone, D.E., Jones, G.C., Smith, K., Jamieson, P.M., Andrew, R., Kenyon, C.J. and Walker B.R (2000): Understanding the role of glucocorticoids in obesity: tissue-specific alterations of corticosterone metabolism in obese Zucker rats. Endocrinology, 141, 560–563.
Livingstone, D.E. and Walker, B.R. (2003): Is 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 a therapeutic target? Effects of carbenoxolone in lean and obese Zucker rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 305, 167–172.
Mazzetti, M.B., Taira M.C., Lelli S.M., Dascal E., Basabe J.C. and San Martín de Viale L.C. (2004): Hexachlorobenzene impairs glucose metabolism in a rat model of porphyria cutanea tarda: a mechanistic approach. Arch Toxicol, 78, 25–33.
Newman, J.D. and Armstrong, J.M. (1978): On the activities of glycogen phosphorylase and glycogen synthase in the liver of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta, 544, 225–233.
Ogg, D., Elleby, B., Norstrom, C., Stefansson, K., Abrahmsen, L., Oppermann, U. and Svensson. S. (2005): The crystal structure of guinea pig 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 provides a model for enzyme-lipid bilayer interactions. J Biol Chem, 280, 3789–3794.
Oppermann, U.C., Persson, B. and Jornvall, H. (1997): Function, gene organization and protein structures of 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase isoforms. Eur J Biochem, 249, 355–360.
Petrescu, I., Bojan, O., Saied, M., Barzu, O., Schmidt, F., Kuhnle, H.F. (1979): Determination of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase activity with deoxyguanosine 5′-diphosphate as nucleotide substrate. Anal Biochem, 96, 279–281.
Seckl, J.R. and Walker B.R. (2001): Minireview: 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 — a tissue specific amplifier of glucocorticoid action. Endocrinology, 142, 1371–1376,
Seckl, J.R. (1997): 11beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in the brain: a novel regulator of glucocorticoid action?Front Neuroendocrinol, 18, 49–99,
Shimoyama, Y., Hirabayashi, K., Matsumoto, H., Sato. T., Shibata, S. and Inoue, H. (2003): Effects of glycyrrhetinic acid derivatives on hepatic and renal 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activities in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol, 55, 811–817.
Stewart, P.M and Krozowski, Z.S. (1999): 11 beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Vitam Horm, 57, 249–324.
Stimson, R.H. and Walker B.R. (2007): Glucocorticoids and 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Minerva Endocrinol, 32, 141–159.
Walker, BR. (2006): Cortisol: cause and cure for metabolic syndrome?Diabet Med, 23, 1281–1288.
Whorwood, C.B., Sheppard, M.C. and Stewart, P.M. (1993): Licorice inhibits 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase messenger ribonucleic acid levels and potentiates glucocorticoid hormone action. Endocrinology, 132, 2287–2292.
Zallocchi, M., Matkovic, L. and Damasco, M.C. (2004): Adrenal 11-beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity in response to stress. Can J Physiol Pharmacol, 82, 422–425.
Zallocchi, M.L., Matkovic, L., Calvo, J.C. and Damasco, M.C. (2004): Adrenal gland involvement in the regulation of renal 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2. J Cell Biochem, 92, 591–602.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altuna, M.E., Mazzetti, M.B., Rago, L.F. et al. Hepatic 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 involvement in alterations of glucose metabolism produced by acidotic stress in rat. J Physiol Biochem 65, 329–337 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03185927
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03185927