Abstract
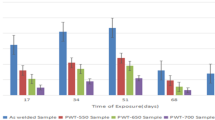
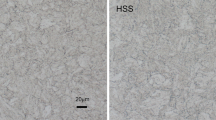
The contents of this paper include the evaluation of corrosion characteristics and the behaviour of stress corrosion cracking (SCC) for the weldment and post weld heat treatment (PWHT) specimen and parent of HT-60 steel using a slow strain rate test (SSRT) in synthetic seawater. Corrosion characteristics were obtained from the polarization curves by potentiostat, and SCC phenomena were evaluated through the parameters such as reduction of area and time to failure by comparing the experimental results in corrosive environment with those obtained in air. Corrosion rate of the weldment was the fastest, followed by parent and PWHT specimen. SCC phenomena between the weldment of HT-60 steel and synthetic seawater were shown. Besides, SCC was dependent upon the pulling speed greatly. Maximum severity of SCC was obtained at a speed of 10−6 mm/min, whereas SCC could not be seen almost at 10−4 mm/min. The resistance to SCC for PWHT specimen was improved considerably compared that of the weldment at 10−6 mm/min. In case of SCC failure, it was verified from SEM examination that brittle mode and lots of pits could be seen at the fractured region near the surface of the specimen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ann, Y. T., 1998, “Study on the Characteristics of Stress Corrosion Cracking for the Welded Zone of High Strength Steel using a Slow Strain Rate Test Method,” Kunsan National Univ., Korea.
ASTM D1141-86, 1986, Standard Specification for Substitute Ocean Water.
ASTM G5-72, 1984, “Standard Recommended Practice for Standard Reference Method for Making Potentiostatic and Potentiodynamic Anodic Polarization Measurements,” Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol. 03.02.
Brown, B. F., 1972, “A Preface to the Problem of Stress Corrosion Cracking,” ASTM STP 518, pp. 3–15.
Lee, J. I., 1988, “About the Damage of Power Plant Installation,” Journal of Korean Corrosion, Vol. 17, pp. 172–181.
Na, E. G., 1987, “Effect of PWHT on Corrosion Fatigue in Weld HAZ of Steels,” Chonbuk National Univ.
Shreir, L. L., 1979, Corrosion, Vol. 1. pp. 12–13.
Son, U. T., 1980, Corrosion Science of Metals, pp. 108–109.
Stephen Tait, W., 1994, “An Introduction to Electrochemical Corrosion Testing for Practicing Engineers and Scientists,” Ohio State University, pp. 53–62.
Theus, G. J. and Cels, J. R., 1975, “Slow Strain Rate Technique to Stress Corrosion Cracking Studies,” Corrosion, Vol. 20, No. 8, pp. 221–226.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Na, E.G., Koh, S.K. & Oh, S.H. Study on corrosion characteristics and stress corrosion cracking of the weldment for HT-60 steel in synthetic seawater. KSME International Journal 14, 152–158 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03184781
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03184781