Abstract
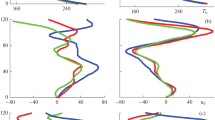
The influence of gravity waves on the sodium layer is studied by using a linear photochemical-dynamical coupling gravity wave model. The model includes the background photochemistry and the photochemical reactions in the sodium layer. The amplitude and phase difference of the response of sodium mixing ratio to gravity waves are calculated. The results indicate that the lower part of sodium layer is the most sensitive region responding to gravity waves. The perturbation of sodium mixing ratio is in phase with temperature in the lower part of the layer. However, it is out of phase with temperature fluctuation in the upper part.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gardner, C. S., Shelton, J. D., Density response of neutral atmospheric layers to gravity wave perturbations, J. Geophys. Res., 1985, 90(A2): 1745–1754.
Gardner, C. S., Voelz, A. G., Lidar studies of the nighttime sodium layer over Urbana, Illinois, 2. Gravity waves, J. Geophys. Res., 1987, 92(A5): 4673–4694.
She, C. Y., Yu, J. R., Huang, J. W. et al., Na temperture lidar measurements of gravity wave perturbations of wind, density and temperature in mesopause region, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1991, 18: 1329–1331.
Hickey, M. R., Plane, J. M. C., A chemical-dynamical model of wave-driven sodium fluctuations, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1995, 22: 2861–2864.
Xu, J., The study of the gravity wave instability induced by photochemistry in summer polar mesopause region, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(3): 267–272.
Xu, J., The influence of photochemistry on gravity waves in the middle atmosphere, Earth, Planets and Space, 1999, 51: 855–862.
Xu, J., Wang, Y., Fu, L., The simulation study of the sodium layer diurnal variation in the mesopause region, Chin. J. Geophys., 2003, (in press).
Xu, J., Smith, A. K., Brasseur, G. P., The effects of gravity waves on distributions of chemically active constituents in the mesopause region, J. Geophys. Res., 2000, 105: 26593–26602.
Fritts, D. C., Smith, S. A., Balsley, B. B. et al., Evidence of gravity wave saturation and local turbulence production in the summer mesosphere and lower thermosphere during the STATE experiment, J. Geophys. Res., 1988, 93: 7015–7025.
Zhang, S. P., Peterson, R. H., Wiens, R. H. et al., Gravity waves from O2nightglow during the AIDA ’98 Campaign I: emission rate/temperature observation, J. Atmos. Terr. Phys., 1993, 55: 355–375.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Ji, Q. & Wu, M. Linear theory of the response of Na mixing ratio to gravity waves. Chin. Sci. Bull. 48, 1630–1633 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183973
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183973