Abstract
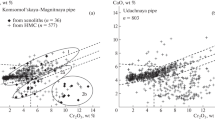
Abundant deeply-derived xenoliths are discovered in a Mesozoic diorite at Jinling, Zibo, western Shandong, which mainly consist of dunite and pyroxenite. The dunite can be further subdivided into two subtypes. The first type shows tabular texture and high Mg# values (93–94) in olivines. The second type is characterized by the metamorphic-deformation texture superimposed by later metasomatism and relatively low olivine Mg# values (86–87). The mineral chemical data indicate that the former could be derived from ancient lithospheric mantle and the latter could have resulted from silica-rich melt metasomatism. The exsolution texture and the high Mg# value in clinopyroxenes, together with the rather high equilibrium temperature, imply that the pyroxenite xenoliths could be the cumulates of mantle-derived magma in the uppermost mantle or near the crust-mantle boundary in the Mesozoic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Griffin, W. L., Zhang, A., O’Reilly, S. Y. et al., Phanerozoic evolution of the lithosphere beneath the Sino-Korean craton. Mantle dynamics and plate interaction in east Asia American (eds. Flower, M. F. J., Chung, S. L., Lo, C. H. et al.), Geophysical Union, 1998, Geodynamics Series 27, 107–126.
Zheng, J. P., Mesozoic-Cenozoic mantle replacement and lithospheric thinning beneath the eastern China (in Chinese with English abstract), Beijing: China University of Geosciences Press, 1999.
Lu, F. X., Zheng, J. P., Paleozoic nature and deep processes of lithospheric mantle in North China platform, Characteristics of Kimberlite and Paleozoic Lithosphere Mantle in North China Platform (eds. Chi, J., Lu, F. X.) (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1996, 215–274.
Xu, X., O’Reilly, S. Y., Griffin, W. L. et al., The nature of the Cenozoic lithosphere beneath Nushan, east central China, Mantle dynamics and plate interaction in east Asia American, Geophysical Union, (eds. Flower, M. F. J., Chung, S. L., Lo, C. H. et al.) 1998, Geodynamics Series 27, 167–196.
Xu, X., O’Reilly, S. Y., Griffin, W. L. et al., Genesis of young lithospheric mantle in southeastern China: an LAM-ICPMS trace element study, J. Petrol., 2000, 41 (1): 111–148.
Menzies, M. A., Fan, W., Zhang, M., Paleaozoic and Cenozoic lithoprobes and the loss of 120 km of Archean lithosphere, Sino-Korean craton, China, Geological Society of London Special Publication, 1993, 76: 71–81.
Menzies, M. A., Xu, Y., Geodynamics of the North China craton, Mantle dynamics and plate interaction in east Asia, Geophysical Union American (eds. Flower, M. F. J., Chung, S. L., Lo, C. H. et al.), 1998, Geodynamics Series 27, 107–126.
Zhi, X. C., Peng, Z. C., Chen, D. G. et al., Os isotope, model age and its significance of the mantle-derived peridotite xenoliths in the Su-Wan region, eastern-central China, Acta Petrologica Sinica (in Chinese with English abstract), 2001, 17(1): 11–18.
Gao, S., Rudnick, R. L., Carlson, R. W. et al., Re-Os evidence for replacement of ancient mantle lithosphere beneath the North China craton, Earth and Planet. Sci. Lett., 2002, 198: 307–322.
Wu, F. Y., Walker, R., Ren, X. W. et al., Osmium isotopic constraints on the age of lithospheric mantle beneath northeastern China, Chem. Geol., 2003, 196(1–4): 107–129.
Fan, W., Menzies, M. A., Destruction of aged lower lithosphere and accretion of asthenosphere mantle beneath eastern China, Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 1992, 16: 171–180.
Xu, Y. G., Thermo-tectonic destruction of the Archaean lithospheric, keel beneath the Sino-Korean Craton in China: evidence, timing and mechanism, Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 2001, 26A: 747–757.
Zhang, H. F., Sun, M., Zhou, X. H. et al., Mesozoic lithosphere destruction beneath the North China Craton: evidence from major-,trace-element and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopie studies of Fangcheng basalts, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 2002, 144: 241–253.
Zhang, H. F., Sun, M., Geochemistry of Mesozoic basalts and mafic dikes, Southeastern North China Craton, and tectonic implications, International Geology Review, 2002, 44: 370–382.
Boyd, F. R., Pokhilenko, N. P., Pearson, D. G. et al., Composition of the Siberian cratonic mantle: evidence from Udachnaya peridotite xenoliths, Contnb. Mineral. Petrol., 1997, 128, 228–246.
Shi, L., Francis, D., Ludden, J. et al., Xenolith evidence of lithospheric melting above anomalously hot upper mantle under the northern Canadian Cordillera, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1998, 131, 39–53.
Fan, Q., Hooper, P. R., The mineral chemistry of ultramafic xenoliths of eastern China: Implication for upper mantle composition and the paleogeotherms, J. Petrol., 1989, 30(5): 1117–1158.
Chen, S. H., Zhang, G. H., Zhou, X. H. et al., Petrology of granulite xenoliths in Hannuoba basalts, Acta Petroligica Sinica (in Chinese with English abstract), 1998, 14(3): 366–380.
E, M. L., Zhao, D. S., Cenozoic Basalts and Deep-seated Inclusions in Eastern China (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1987.
Xu, Y. G., Geothermometry for the mantle-derived inclusions, Acta Petrologica Sinica (in Chinese with English abstract), 1993, 9(2): 167–180.
Wood, B. J., Banno, S., Garnet-orthopyroxene and clinopyroxeneorthopyroxene relationships in simple and complex systems, —, 1973, 46, 1–15.
Wells, P. R. A., Pyroxene thermometry in simple and complex systems, Contnb. Mineral. Petrol., 1977, 62, 129–139.
Mercier, J. C. C., Single-pyroxene thermobarometry, Tectonophysics, 1980, 70: 1–37.
McCarty, T. C., Patino, D. A. E., Empiricil calibration of the silica-Ca-tschermak’s-anorthite (SCAn) geobarometer, J. Metamorphic Geol., 1998, 16: 675–686.
O’Reilly, S. Y., Gnffin, W. L., Djomani, Y. H. P. et al., Are lithospheres forever? Tracking changes in subcontinental lithospheric mantle through time, GSA Today, 2001, 11(4): 4–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, W., Wang, D., Gao, S. et al. Discovery of dunite and pyroxenite xenoliths in Mesozoic diorite at Jinling, western Shandong and its significance. Chin. Sci. Bull. 48, 1599–1604 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183968
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183968