Abstract
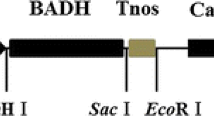
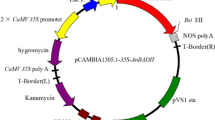
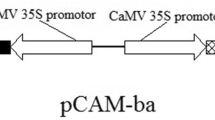
Betaine as one of osmolytes plays an important role in osmoregulation of most high plants. Betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase (BADH) is the second enzyme involved in betaine biosynthesis. The BADH gene from a halophite,Atriplex hortensis, was transformed into rice cultivars by bombarment method. Totally 192 transgenic rice plants were obtained and most of them had higher salt tolerance than controls. Among transgenic plants transplanted in the saline pool containing 0.5% NaCl in a greenhouse, 22 survived. 13 of which set seeds, and the frequency of seed setting was very low, only 10%. But the controls could not grow under the same condition. The results of BADH activity assay and Northern blot showed that the BADH gene was integrated into chromosomes of transgenic plants and expressed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanson, A. D., Grumet, E., Betaine accumulation: metabolic pathways and genetics, inCellular and Molecular Biology of Plant Stress (eds. Key, J.L., Kosuge, T.), New York: Liss, 1985, 71–92.
Weretilnyk, E. A., Sebastian, B., Comparative biochemical and immunological studies of the glycine betaine synthesis pathway in diverse families of dicotyledons,Plantu, 1989.178: 342.
Weretilnyk, E. A., Hanson, A. D., Molecular cloning of a plant betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase, an enzyme implicated in adaptation to salinity and drought,Proc. Nutl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1990,87: 2745.
McCue, K.F., Hanson, A.D., Salt-inducible betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase from sugar beet: cDNA cloning and expression,Plant Mol. Biol., 1992,18: 1.
Xiao, G., Zhang, G.Y., Liu, F.H.et al., Studies on betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase gene fromAtriplex hortensis, Chinese Science Bulletin (in Chinese), 1995,40(8): 741.
Sambrook, F.E.F., Maniatis, T.,Molecular Cloning:A Laborutory Manual, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989.
Chen, S.Y., Zhu, L.H., Hong, J., Molecular biological identification of a rice salt tolerance line,Acta Botanical Sinica (in Chinese), 1991,33: 569.
Tan, C., Yang, H. D., Yu, S. W.,Handbook of Plant Physiology, Chinese Plant Physiological Society (in Chinese), Shanghai: Academic Press of Shanghai, 1985, 67–72.
Iturriaga, G., Schneider, K., Salamini, F.et al., Expression of desiccation-related proteins from the resurretion plant creterostigma plantagineum in transgenic tobacco,Plant Mol. Biol., 1992,20: 555.
Mika, N., Manabu, I., Teruhiro, T.et al. Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942 transformed withE, coli bet genes produces glycine betaine from choline and acquines resistance to salt stress,Plant Physiol., 1995,107: 703.
Holmstrom, K., Welin, B., Manda, A.et al., Production of theE. coli betaine-aldehyde, dehydrogenase, an enzyme required for the synthesis of the osmoprotectant glycine betaine, in transgenic plants,Plant J., 1994,6(5): 749.
Renaud, B., Weigle, P., Evidence for a ferredoxin-dependent choline monooxygenase from spinach choroplast stroma.Plant Physiol., 1988,90: 322.
Datta, S.K., Peterhans, A., Datta, K.et al., Genetically engineered fertile indica-rice recovered from protoplasts,Biotechnology, 1990,8: 736.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project supported by the National High Technology Program of China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Zhang, L., Xiao, G. et al. Expression of betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase gene and salinity tolerance in rice transgenic plants. Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 40, 496–501 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183588
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183588