Abstract
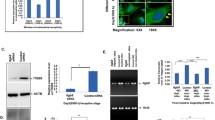
Integrin, a heterodimeric adhesive molecule composed of α and β subunits, can regulate cell adhesion and trafficking. Recent data have documented that, at the “implantation window” stage, αVβ3 integrin participates in the maternal-fetal interaction and becomes a potential marker of uterine receptivity. Furthermore, it can affect invasiveness of embryo. This work made a further study about its action mechanism. Results of indirect immunofluorescence and laser scanning confocal microscopy showed that αVβ3 integrin was clearly expressed in the mouse blastocyst. Injection of αVβ3 integrin antiserum into a uterine horn of a pregnant mouse on day 3 markedly decreased the number of embryos implanted (P < 0.001). In a co-culture model, αVβ3 integrin antisera at 1: 100 and 1: 200 dilutions significantly depressed the attachment and outgrowth reactions of blastocysts on monolayer of uterine epithelial cells. Analysis of correlation manifested that the inhibitory effect of αVβ3 integrin antiserum was dosage/dilution-dependent. Thus, αVβ3 integrin is an essential factor in the uterine endometrium for embryo implantation in the mouse. This integrin distinctly expressed in the mouse blastocyst at “implantation” stage affected the process of embryo implantation by route of mediating both the attachment and the outgrowth processes of blastocyst on uterine epithelial cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lessey, B. A., lntegrins and uterine receptivity, in Embryo Implantation: Molecular, Cellular and Clinical Aspects (ed. Carson, D. D.), California: Serono Symposia USA, 1997.
Yelian, F. D., Yang, Y., Hirata, J. D. et al., Molecular interactions between fibronectin and integrins during mouse blastocyst outgrowth. Mol. Reprod. Dev., 1995, 41: 435.
Cai, L. Q., Duan, E. K., Integrins and blastocyst implantation, Progress in Biochemistry and Biophysics, 1999, 26: 308.
Tabibzadeh, S., Babaknia, A., The signals and molecular pathways involved in implantation, a symbiotic interaction between blastocyst and endometrium involving adhesion and tissue invasion, Hum. Reprod., 1995, 10: 1579.
Sutherland, A. E., Calarco, P. G., Damsky, C. H., Developmental regulation on integrin expression at the time of implantation in the mouse embryo, Development, 1993, 119: 1175.
Genbacev, O., Zhou, Y., McMaster, M. T. et al., Oxygen regulates human cytotrophoblast proliferation, differentiation, and invasion: implications for endovascular invasion in normal pregnancy and preeclampsia, in Embryo Implantation: Molecular, Cellular and Clinical Aspects (ed. Carson, D. D.), California: Serono Symposia USA, 1997.
Zeng, G. Q., Cao, Y. J., Co-culture of mouse embryos with monolayer of uterine epithelial cells, Acta Zoologica Sinica, 1996, 42: 212.
Sherman, M. I., Atienza-Samols, S. B.,In vitro studies on the adhesiveness of mouse blastocysts, Boston: Human Fertilization (eds. Ludwig, H., Tauber, P.), 1978.
Spindle, A. I., Pedersen, R. A., Hatching, attachment and outgrowth of mouse blastocystin vitro: fixed nitrogen requirements. J. Exp. Zool., 1973. 186: 305.
Zhang, C. Y., Similarity in embryo implantation and tumor invasion and migration, Life Science (in Chinese), 1997, 9: 97.
Bronson, R. A., Fusl, F. M., Integrins and human reproduction, Mol. Hum. Reprod., 1996, 2(3): 153.
Das, S. K., Wang, X. N., Paria, B. C. et al., Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor gene is induced in the mouse uterus temporally by the blastocyst solely at the site of its apposition: a possible ligand for interaction with blastocyst EGF-receptor in implantation, Development, 1994, 120: 1071.
Lessey, B. A., Endometrial integrins and the establishment of uterine receptivity, Hum. Reprod., 1998, 3: 247.
Lessey, B. A., Arnold, J. T., Paracrine signaling in the endometrium: Integrins and the establishment of uterine receptivity, J. Reprod. Immunol., 1998. 39: 105.
Zhang, C. Y., Duan, E. K., Cao, Y. J. et al., Expression, distribution and function of the focal adhesion kinase (pp125FAK) during murine ecloplacental cone outgrowthin vitro, Chinese Science Bulletin, 1998, 43(17): 1527.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, L., Cao, Y. & Duan, E. Role of αVβ3 integrin in embryo implantation in the mouse. Chin.Sci.Bull. 45, 2077–2081 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183530
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183530