Abstract
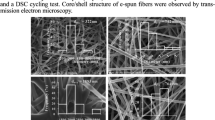
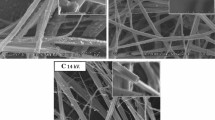
Nano-porous ultra-high specific surface ultrafine fibers are created by the method of “electrospinning-phase separation-leaching” (EPL) for the first time. First of all, polymer solutions of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) blends dissolved in co-solvent are electrospun to make ultrafine fibers when charged to high voltages. The incompatibility of PAN and PVP induces phase separation to form microdomains of PVP in the polymer blend ultrafine fibers. Then, PVP microdomains in the blend fibers are leached out in water, and porous PAN ultrafine fibers are obtained. Lastly, the surface and cross-section of the porous ultrafine fibers are observed in detail by field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), and the specific surface of the ultrafine fibers is measured by means of nitrogen absorption. With increasing the content of PVP, the specific surface area of the ultrafine fibers increases apparently. The specific surface area of the porous ultrafine fibers with the diameter of 2130 nm is more than 70 m2·g−1. The cross-section of the PAN porous ultrafine fibers after leaching of PVP microdomains from polymer blend fibers with the feed ratio of PAN/PVP of 10/20 shows the characteristic of porous structure with pore diameter of ca 30 nm according to FESEM photo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang, Z. M., Zhang, Y. Z., Kotaki, M. et al., A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites, Composites Science and Technology, 2003, 63(15): 2235–2253.
Yang, Q. B., Wang, C., Hong, Y. L. et al., Refining of polyacrylonitrile nanofibers, Chem. J. Chinese Universities (in Chinese), 2004, 25(3): 589–591.
Bognitzki, M., Czado, W., Frese, T. et al., Nanostructured fibers via electrospinning, Adv. Mater., 2001, 13(1): 70–72.
Casper, C. L., Stephens, J. S., Tassi, N. G. et al., Controlling surface morphology of electrospun polystyrene fibers: effect of humidity and molecular weight in the electrospinning process, Macromolecules, 2004, 37(2): 573–578.
Zhao, S. L., Wu, X. H., Wang, L. G. et al., Electrospinning of ethyl-cyanoethyl cellulose/tetrahydrofuran solutions, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2004, 91(1): 242–246.
Matsuyama, H., Takida, Y., Maki, T. et al., Preparation of porous membrane by combined use of thermally induced phase separation and immersion precipitation, Polymer, 2002, 43(19): 5243–5248.
Zong, X. H., Kim, K., Fang, D. F. et al., Structure and process relationship of electrospun bioabsorbable nanofiber membranes, Polymer, 2002, 43(16): 4403–4412.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Nie, G. Nano-porous ultra-high specific surface ultrafine fibers. Chin.Sci.Bull. 49, 2368–2371 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183424
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183424