Abstract
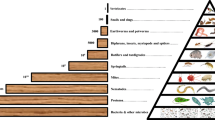
As natural tracers, stable isotopes have been extensively used in plant physiological, ecological and environmental research. Recently, animal physiological ecologists have also applied stable isotope techniques to study plantanimal relationships. The isotopic compositions of animal body generally reflect and integrate their diets over a time period ranging from hours to years to the lifetime of an individual. When animal living habitat changes or animals move to a new environment, the animal isotopic compositions will shift accordingly. Thus, stable isotope signatures of an animal can truly reflect its food sources, habitat, distribution and movement patterns during a given time period. Moreover, by analyzing animal-tissue isotopic compositions at different temporal scales, we can improve our understanding of animal adaptation to environmental changes. Stable isotope technique also provides an ideal tool to study animal foodweb relationship and community structure because of isotopic fractionation during the processes of nutrient assimilation by animals. Stable isotope technique can continuously measure animal trophic position in a foodweb, which can eventually reveal the predator-prey relationship and its role in determining matter balance and energy flow in the entire ecosystem. Stable isotope technique has been one of the most important and efficient tools in studying plant-animal relationship. In this paper, we first review recent advances in the application of stable isotope techniques to plant-animal relationship research then evaluate their advantages and disadvantages, and finally discuss some future directions associated with stable isotope applications to plant-animal relationship research.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dawson, T. E., Mambelli, S., Plamboeck, A. H. et al., Stable isotopes in plant ecology, Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst., 2002, 33: 507–559.
Schulze, E. D., Ellis, R., Schulze, W. et al., Diversity, metabolic type and δ13C carbon isotope ratios in the flora of Namibia in relation to growth form, precipitation and habitat conditions, Oecologia, 1996, 106: 352–369.
Evans, R. D., Physiological mechanisms influencing plant nitrogen isotope composition, Trends Plant Sci., 2001, 6: 121–126.
Máguas, C., Griffiths, H., Applications of stable isotopes in plant ecology, Prog. Bot., 2003, 64: 473–505.
Schwinning, S., Ehleringer, J. R., Water use trade-off and optimal adaptations to pulse-driven arid ecosystems, J. Ecol., 2001, 89: 464–480.
Yakir, D., Sternberg, L. D. S. L., The use of stable isotopes to study ecosystem gas exchange, Oecologia, 2000, 123: 297–311.
Pataki, D. E., Ellsworth, D. S., Evans, R. D. et al., Tracing changes in ecosystem function under elevated carbon dioxide conditions, Bioscience, 2003, 53: 805–818.
Balasse, M., Reconstructing dietary and environmental history from enamel isotopic analysis: time resolution of intra-tooth sequential sampling, Int. J. Osteoarchaeol., 2002, 12: 155–165.
Sponheimer, M., Lee-Thorp, J. A., Differential resource utilization by extant great apes and australopithecines: Towards solving the C conundrum, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A, 2003, 136: 27–34.
Yi, X. F., Zhang, X. A., Li, L. X. et al., Analysis on food web structure in alpine meadow ecosystem: evidence from sable carbon isotope signatures, Zool. Res. (in Chinese), 2004, 25(1): 1–6.
Forero, M. G., Hobson, K. A., Using stable isotopes of nitrogen and carbon to study seabird ecology: Applications in the Mediterranean seabird community, Sci. Mar., 2003, 67(Supp. 2): 23–32.
Hobson, K. A., Tracing origins and migration of wildlife using stable isotopes: A review, Oecologia, 1999, 120: 314–326.
Chen, S. P., Bai, Y. F., Han, X. G., Applications of stable carbon isotope techniques to ecological research, Acta Phytoecol. Sin. (in Chinese), 2002, 26(5): 549–560.
Yi, X. F., Li, L. X., Zhang, X. A. et al., Diet shift of upland buzzards (Buteo hemilasius): Evidence from stable carbon isotope ratios, Acta Zool. Sin. (in Chinese), 2003, 49(6): 764–768.
Lin, G. H., Ke, Y., Stable isotope techniques and global change research, in: Lectures on Modern Ecology (eds. Li, B.) (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1995, 161–188.
Taylor, H. P. Jr., An application of oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies to problems of hydrothermal alteration and ore deposition, Econ. Geol., 1974, 69: 843–883.
Yapp, C. J., Epstein, S., A re-examination of cellulose carbon-bound hydrogen D measurements and some factors affecting plant-water D/H relationships. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1982, 46: 955–965.
Körner, C., Farquhar, G. D., Wong, S. C., Carbon isotope discrimination by plants follows latitudinal and altitudinal trends, Oecologia, 1991, 74: 623–632.
Garten, C. T. J., Variation in foliar15N abundance and the availability of soil nitrogen on Walker Branch watershed, Ecology, 1993, 74: 2098–2113.
DeNiro, M. J., Epstein, S., Influence of diet on the distribution of carbon isotopes in animals, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1978, 42: 495–506.
Yoneyama, T., Ohta, Y., Ohtani, T., Variations of natural13C and15N abundances in the rat tissues and their correlation, Radioisotopes, 1983, 32: 330–332.
Teeri, J. A., Schoeller, D. A., δ13C values of an herbivore and the ratio of C3 to C4 plant carbon in its diet, Oecologia, 1979, 39: 197–200.
Jim, S., Ambrose, S. H., Evershed, R. P., Stable carbon isotopic evidence for differences in the dietary origin of bone cholesterol, collagen and apatite: Implications for their use in palaeodietary reconstruction, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2004, 68: 61–72.
Tieszen, L. L., Boutton, T. W., Tesdahl, K. G. et al., Fractionation and turnover of stable carbon isotopes in animal tissues: implications for δ13C analysis of diet, Oecologia, 1983, 57: 32–37.
Hobson, K. A., Bairlein, F., Isotopic fractionation and turnover in captive Garden Warblers (Sylvia borin): Implications for delineating dietary and migratory associations in wild passerines, Can. J. Zool., 2003, 81: 1630–1635.
Hobson, K. A., Schell, D. M., Renouf, D. et al., Stable carbon and nitrogen isotopic fractionation between diet and tissues of captive seals: Implications for dietary reconstructions involving marine mammals, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 1996, 53: 528–533.
DeNiro, M. J., Epstein, S., Influence of diet on the distribution of nitrogen isotopes in animals, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1981, 45: 341–351.
Roth, J. D., Hobson, K. A., Stable carbon and nitrogen isotopic fractionation between diet and tissue of captive red fox: Implications for dietary reconstruction, Can. J. Zool., 2000, 78: 848–852.
Kurle, C. M., Stable-isotope ratios of blood components from captive northern fur seals (Callorhinus ursinus) and their diet: Applications for studying the foraging ecology of wild otariids, Can. J. Zool., 2002, 80: 902–909.
Cormie, A. B., Schwartz, H. P., Gray, J., Determination of the hydrogen isotopic composition of bone collagen and correction for hydrogen exchange, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1994, 58: 365–375.
Gannes, L. Z., O’Brien, D. M., del Rio, C. M., Stable isotopes in animal ecology: Assumptions, caveats, and a call for more laboratory experiments, Ecology, 1997, 78: 1271–1276.
Zhang, X. L., Study on the diet of ancient people by analyzing bone elements and isotopes, Acta Anthropol. Sin. (in Chinese), 2003, 22(1): 75–84.
Chisholm, B. S., Nelson, D. E., Schwarcz, H. P., Stable-carbon isotopes as a measure of marine versus terrestrial protein in ancient diets, Science, 1982, 216: 1131–1132.
Ben-David, M., Flynn, R. W., Schell, D. M., Annual and seasonal changes in diets of martens: evidence from stable isotope analysis, Oecologia, 1997, 111: 280–291.
Schoeninger, M. J., DeNiro, M. J., Nitrogen and carbon isotopic composition of bone collagen from marine and terrestrial animals, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1984, 48: 625–639.
Sponheimer, M., Grant, C. C., Ruiter, D. D. et al., Diets of impala from Kruger National Park: evidence from stable carbon isotopes, Koedoe, 2003, 46: 101–106.
Romanek, C. S., Gaines, K. F., Bryan, Jr. I. L. et al., Foraging ecology of the endangered wood stork recorded in the stable isotope signature of feathers, Oecologia, 2001, 125: 584–594.
Darimont, C. T., Reimchen, T. E., Intra-hair stable isotope analysis implies seasonal shift to salmon in gray wolf diet, Can. J. Zool., 2002, 80: 1638–1642.
Cormie, A. B., Schwarcz, H. P., Effects of climate on deer bone δ15N and δ13C: Lack of precipitation effects on δ15N for animals consuming low amount of C4 plant, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1996, 21: 4161–4166.
Ramsay, M. A., Hobson, K. A., Polar bears make little use of terrestrial food web: Evidence from stable carbon isotope analysis, Oecologia, 1991, 86: 598–600.
Cerling, T. E., Harris, J. M., Leakey, M. G., Browsing and grazing in elephants: The isotope record of modern and fossil proboscideans, Oecologia, 1999, 120: 364–374.
Hilderbrand, G. V., Farly, S. D., Robbins, C. T. et al., Use of stable isotopes to determine diets of living and extinct bears, Can. J. Zool., 1996, 74: 2080–2088.
Bocherens, H., Fizet, M., Mariotti, A., Diet, physiology and ecology of fossil mammals as inferred from stable carbon and nitrogen isotope biogeochemistry: Implications for Pleistocene bears, Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol., 1994, 107: 213–225.
Saito, L., Johnson, B. M., Bartholow, J. et al., Assessing ecosystem effects of reservoir operations using food web-energy transfer and water quality models, Ecosystems, 2001, 4: 105–125.
Boutton, T. W., Arshad, M. A., Tieszen, L. L., Stable isotope analysis of termite food habits in East African grasslands, Oecologia, 1983, 59: 1–6.
Magnusson, W. E., Arauujo, M. C., Cintra, R. et al., Contributions of C3 and C4 plants to higher trophic levels in an Amazonian savanna, Oecologia, 1999, 119: 91–96.
Ostrom, P. H., Colunga-Garcia, M., Gage, S. H., Establishing pathways of energy flow for insect predators using stable isotope ratios: field and laboratory evidence, Oecologia, 1997, 109: 108–113.
Peterson, B. J., Fry, B., Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies, Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst., 1987, 18: 293–320.
Post, D. M., Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: Models, methods, and assumptions, Ecology, 2002, 83: 703–718.
Bearhop, H., Drucher, D., Trophic level isotopic enrichment of carbon and nitrogen in bone collagen: case studies from recent and ancient terrestrial ecosystems, Int. J. Osteoarchaeol., 2003, 13: 46–53.
McCutchan, Jr. J. H., William, M., Kendall, C. et al., Variation in trophic shift for stable isotope ratios of carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur, Oikos, 2003, 102: 378–390.
Olive, P. J. W., Pinnegar, J. K., Polunin, N. V. C. et al., Isotope trophic step fractionation: a dynamic equilibrium model, J. Anim. Ecol., 2003, 72: 608–617.
Estep, M. F., Dabrowski, H., Tracing food webs with stable hydrogen isotopes, Science, 1980, 209: 1537–1538.
Ehleringer, J. R., Rundel, P. W., Nagy, K. A., Stable isotopes in physiological ecology and food web research. Trends Ecol. Evol., 1986, 1: 42–45.
Fry, B., Jeng, W. L., Scalan, R. S. et al., Del13C food web analysis of a Texas sand dune community. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1978, 42: 1299–1302.
Thompson, D. R., Lilliendahl, K., Solmundsson, J. et al., Trophic relationships among six species of Iceland seabirds as determined through stable isotope analysis, Condor, 1999, 101: 898–899.
Struck, U., Altenbach, A. V., Gaulke, M. et al., Tracing the diet of the monitoe lizardVaranus mabitang by stable isotope analyses (15N,13C), Naturwissenschaften, 2002, 89: 470–473.
Cai, D. L., Hong, X. G., Mao, X. H. et al., Preliminary studies on trophic structure of tidal zone in the Laoshan Bay by using carbon stable isotopes, Acta Oceanol. Sin. (in Chinese), 2001, 23(4): 41–47.
Cai, D. L., Wang, R., Bi, H. S., Trophic relationships in the Bohai ecosystem: preliminary investigation from δ13C analysis, Acta Ecol. Sin. (in Chinese), 2001, 21(8): 1354–1359.
Wassenaar, L. I., Hobson, K. A., A stable-isotope approach to delineate geographical catchment areas of avian migration monitoring stations in North America, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2001, 35: 1845–1850.
Rubenstein, D. R., Chamberlain, C. P., Holmes, R. T. et al., Linking breeding and wintering ranges of a migratory songbird using stable isotopes, Science, 2002, 295: 1062–1065.
Wassenaar, L. I., Hobson, K. A., Stable-carbon and hydrogen isotope ratios reveal breeding origins of red-winged blackbirds, Ecol. Appl., 2000, 10: 911–916.
Alisauskas, R., Hobson, K. A., Determination of lesser snow goose diets and winter distribution using stable isotope analysis, J. Wildlife Manage., 1993, 57: 49–54.
Marra, P. P., Hobson, K. A., Holmes, R. T., Linking winter and summer events in a migratory bird by using stable carbon isotopes, Science, 1998, 282: 1884–1886.
Minami, H. M., Minagawa, M., Ogi, H., Changes in stable carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios in sooty and short-tailed shearwaters during their northward migration, Condor, 1995, 97: 565–574.
Minami, H. M., Ogi, H., Determination of migratory dynamics of the sooty shearwater in the Pacific using stable carbon and nitrogen isotopic analysis, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 1997, 158: 249–256.
Bearhop, S., Furness, R. W., Hilton, G. M. et al., A forensic approach to understanding diet and habitat use from stable isotope analysis of (avian) claw material, Funct. Ecol., 2003, 17: 270–275.
Hobson, K. A., Wassenaar, L. I., Linking breeding and wintering grounds of neotropical migrant songbirds using stable hydrogen isotopic analysis of feathers, Oecologia, 1997, 109: 142–148.
Chamberlain, C. P., Blum, J. D., Holmes, R. T. et al., The use of isotope tracers for identifying populations of migratory birds, Oecologia, 1997, 109: 132–141.
Kelly, J. F., Atudorei, V., Sharp, Z. D. et al., Insights into Wilson’s Warbler migration from analyses of hydrogen stable isotope ratios, Oecologia, 2002, 130: 216–221.
Kelly, J. F., Finch, D. M., Tracking migrant songbirds with stable isotopes, Trends Ecol. Evol., 1998, 13: 48–49.
Kelly, J. F., Smith, R., Finch, D. M. et al., Influence of summer biogeography on wood warbler stopover abundance, Condor, 1999, 101: 76–85.
Wassenaar, L. I., Hobson, K. A., A stable-isotope approach to delineate geographical catchment areas of avian migration monitoring stations in North America. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2001, 35: 1845–1850.
Lott, C. A., Meehan, T. D., Heath, J. A., Estimating the latitudinal origins of migratory birds using hydrogen and sulfur stable isotopes in feathers: influence of marine prey base, Oecologia, 2003, 134: 505–510.
Hobson, K. A., Wassenaar, L. I., Milá, B. et al., Stable isotopes as indicators of altitudinal distributions and movements in an Ecuadorean hummingbird community, Oecologia, 2003, 136: 302–308.
Ambrose, S. H., DeNiro, M. J., The isotopic ecology of East African mammals, Oecologia, 1986, 69: 395–406.
Schoeninger, M. J., Moore, J., Sept, J., Subsistence strategies of two “savanna” Chimpanzee populations: the stable isotope evidence, Amer. J. Primatol., 1999, 49: 297–314.
Koch, P. L., Heisinger, J., Moss, C. et al., Isotopic tracing of change in diet and habitat use in African elephants, Science, 1995, 267: 1340–1343.
Rubenstein, D. R., Hobson, K. A., From birds to butterflies: Animal movement patterns and stable isotopes, Trends Ecol. Evol., 2004, 19: 256–263.
Schwarcz, H. P., Some theoretical aspects of isotope paleodiet studies, J. Archaeol. Sci., 1991, 18: 261–275.
Gannes, L. Z., Martínez del Rio, C., Koch, P., Natural abundance variations in stable isotopes and their potential uses in animal physiological ecology, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 1998, 199A: 725–737.
Bearhop, S., Waldron, S., Votier, S. C. et al., Factors that influence assimilation rates and fractionation of nitrogen and carbon stable isotopes in avian blood and feathers, Physiol. Biochem. Zool., 2002, 75: 451–458.
Ponsard, S., Averbuch, P., Should growing and adult animals fed on the same diet show different δ15N values? Rapid Comm. Mass Spectrom., 1999, 13: 1305–1310.
Vanderklift, M. A., Ponsard, S., Sources of variation in consumer diet δ15N enrichment: a meta-analysis, Oecologia, 2003, 136: 169–182.
McClelland, J. W., Montoya, J. P., Trophic relationship and the nitrogen isotopic composition of amino acids in plankton, Ecology, 2002, 83: 2173–2180.
Macfadden, B. J., Cerling, T., Harris, J. M. et al., Ancient latitudinal gradients of C3/C4 grasses interpreted from stable isotopes of New World Pleistocene horse (Equus) teeth, Global Ecol. Biogeogr., 1999, 8: 137–149.
Cerling, T. E., Wang, Y., Quade, J., Expansion of C4 ecosystems as an indicator of global ecological change in the late Miocene, Nature, 1993, 361: 344–345.
Cook, G. D., Effects of frequent fires and grazing on stable nitrogen isotope ratios of vegetation in northern Australia, Aust. Ecol., 2001, 26: 630–636.
Neilson, R., Robinson, D., Marriott, C. A., Above-ground grazing affects floristic composition and modifies soil trophic interactions, Soil Biol. Biochem., 2002, 34: 1507–1512.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Lin, G., Huang, J. et al. Applications of stable isotopes to study plant-animal relationships in terrestrial ecosystems. Chin.Sci.Bull. 49, 2339–2347 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183419
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183419