Abstract
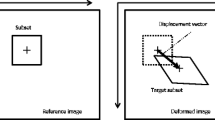
This paper presents a method of accurately determining the displacement of tracer particles between two images using recursive correlation. The local correlation value is iteratively arrived at through successive approximations of local displacement using increasingly smaller regions of determination. By starting with a large search area and iteratively narrowing the search restricting the search after each iteration based on the resulting calculation, very high-resolution PIV processing can be achieved. Spurious vectors are eliminated and accuracy and processing speed is maintained by correlating images in compressed (sparse array) format using second-order spatial correlation. The methodology of this unique image analysis method is presented along with a discussion of its limitations and applicability.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Φ:
-
Correlation function
- Δ:
-
Correlation search length [pixels]
- Δt :
-
Time between image exposures [sec.]
- Δi,Δj :
-
Difference in pixel image [pixels]
- ∇:
-
Gradient operator
- γ:
-
Image compression ratio
- \(\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\rightharpoonup}$}} {v} \) :
-
Flow velocity [m/s]
- \(\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\rightharpoonup}$}} {v} '\) :
-
Unsteady flow velocity component [m/s]
- d :
-
Particle image diameter [pixels]
- f :
-
Spatial frequency [1/m]
- I :
-
Pixel intensity
- i,j :
-
Image coordinates [pixels]
- m,n :
-
Data array indices
- M :
-
Image magnification [m/pixels]
- M, N :
-
Interrogation image diameter [pixels]
- x,y :
-
Pixel image coordinates
References
Adrian, R. J., Particle imaging techniques for experimental fluid mechanics, Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 23, (1991), 261–304.
Fincham, A. M. and Spedding, G. R., Low Cost, High resolution DPIV for measurement of turbulent flow, Experiments in Fluids, 23, (1997), 449–462.
Fincham, A. M., Spedding, G. R. and Blackwelder, R. F., Current constraints of digital particle tracking techniques in fluid flows, Bull. Am. Phys Soc., 36, (1991), 2692.
Hart, D. P., High-speed PIV analysis using compressed image correlation, Journal of Fluids Engineering (1998).
Hart, D. P., The elimination of correlation errors in PIV processing, 9th International Symposium on Applications of Laser Techniques to Fluid Mechanics, July 13–16, 1998, Lisbon, Portugal (1998).
Hart, D. P., Sparse array image correlation, 8th International Symposium on Applications of Laser Techniques to Fluid Mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal (1996).
Keane, R. D., Adrian, R. J. and Zhang, Y., Super-resolution particle image velocimetry, Measurement Science and Technology, 2, (1995), 1202–1215.
Keane, R. D. and Adrian, R. J., Theory of cross-correlation of PIV images, Applied Scientific Research, 49, (1992), 191–215.
Keane, R. D. and Adrian, R. J., Optimization of particle image velocimeters, Measurement Science and Technology, 6, (1990), 754–758.
Landreth, C. C. and Adrian, R. J., Measurement and refinement of velocity data using high image density analysis in particle image velocimetry, Applications of Laser Anemometry to Fluid Mechanics, (1990) Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 484–497.
Okamoto, K., Hassan, Y. A. and Schmidl, W. D., New tracking algorithm for particle image velocimetry, Experiments in Fluids, 19, (1995), 342–347.
Prasad, A. K., Adrian, R. J., Landreth, C. C. and Offutt, P. W., Effect of resolution on the speed and accuracy of particle image velocimetry interrogation, Experiments in Fluids, 13, (1992), 105–116.
Raffel, M. and Kompenhans, J., Error analysis for PIV recording utilizing image shifting, Proc. 7th International Symposium on Applications of Laser Techniques to Fluid Mechanics, Lisbon, (July 1994), 35.5.
Westerweel, J., Efficient detection of spurious vectors in particle image velocimetry data, Experiments in Fluids, 16, (1994), 236–247.
Westerweel, J., Dabiri, D. and Gharib, M., The effect of a discrete window offset on the accuracy of cross-correlation analysis of digital PIV recordings, Experiments in Fluids, 23, (1997),20–288.
Willert, C. E. and Gharib, M., Digital particle image velocimetry, Experiments in Fluids, 10, (1991), 181–193.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Douglas Payton Hart: He received his BSc degree in aeronautical/astronautical engineering in 1983 from the University of Illinois, his S.M. degree in mechanical engineering from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1985, and his Ph.D. in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology in 1992. As a student at MIT, he worked for Electromagnetic Launch Research, Inc. on satellite propulsion. After receiving his S.M degree, he worked as a systems engineer for Northrop Aerospace before starting his Ph.D. in the area of hydrodynamics at Caltech. He joined the faculty at MIT in the Department of Mechanical Engineering in 1993 and is currently an associate professor and the director of the Fluid Mechanics Laboratory. His current research interests include instrumentation and optical diagnostics relating to fluid mechanics and tribology.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hart, D.P. Super-resolution PIV by recursive local-correlation. J Vis 3, 187–194 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182411
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182411