Abstract
The availability of electrophoretically homogeneous rabbit penicillin carrier receptor protein (CRP) by affinity chromatography afforded an idealin vitro system to calculate the thermodynamic parameters of binding of penicillin and analogues with CRP as well as competitive binding of such analogues with CRP in presence of14C-penicillin G. The kinetics of association of CRP with 7-deoxy penicillin which does not bind covalently with CRP have been studied through equilibrium dialysis with14C-7-deoxybenzyl penicillin and found to be K=2·79×106M−1.−ΔG=8·106 k cal/mole as well as fluorescence quenching studies with exciter λ 280 K=3·573×106M−1,−ΔG=8·239 k cal/mole. The fluorescence quenching studies have been extended to CRP-benzyl penicillin and CRP-6-aminopenicillanic acid (6APA) systems also. The fluorescence data with benzyl penicillin indicate two conformational changes in CRP—a fast change corresponding to the non-covalent binding to CRP with 7-deoxy penicillin and a slower change due to covalent bond formation. With 6-APA the first change is not observed but the conformational change corresponding to covalent binding is only seen.
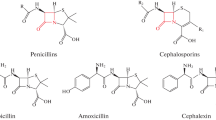
Competitive binding studies indicate that the order of binding of CRP with the analogues of penicillin is as follows: methicillin > 6APA > carbenicillin >o-nitrobenzyl penicillin > cloxacillin ≈ benzyl penicillin ≈ 6-phenyl acetamido penicillanyl alcohol ≈ 7 phenyl acetamido desacetoxy cephalosporanic acid ≈p-amino benzyl penicillin ≈p-nitro benzyl penicillin > ticarcillin >o-amino benzyl penicillin > amoxycillin > 7-deoxy benzyl penicillin > ampicillin.
From these data it has been possible to delineate partially the topology of the penicillin binding cleft of the CRP as well as some of the functional groups in the cleft responsible for the binding process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharyya P Ket al 1974J. Indian Chem. Soc. L1 122
Bhattacharyya P Ket al 1975Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 62 153
Collins C H and Lyne P M 1976 inMicrobiological Methods ed. 4 (London: Butterworths) p. 235
Farben Fabriken Bayer A G 1962 Ger. pat. 1125932Chem. Abs. 7275 i
Nataraj C V, Mandal C and Bhattacharyya P K 1978Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. A86 1
Nataraj C V 1974Physicochemical interactions on synthetic templates Ph.D. Thesis, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
Parker C A 1968 inPhotoluminescence of solution (Amsterdam: Elsevier)
Perron Y Get al 1964J. Med. Chem. 7 483
Tosoni A L, Glass O G and Goldsmith L 1968Biochem. J. 69 476
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandal, C., Mandal, C. & Bhattacharyya, P.K. Chemical approaches to penicillin allergy—IV. Binding of carrier receptor protein with penicillin and its analogues. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci., A (Chemical Sciences) 87, 145–163 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182126
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182126