Abstract
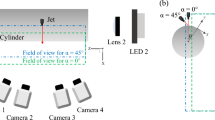
The characteristics of supersonic impinging jets are investigated using Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV). The purpose of the experiments is to understand the jet induced forces on STOVL aircraft while hovering close to the ground. For this purpose, a large diameter circular plate was attached at the nozzle exit. The oscillations of the impinging jet generated due to a feedback loop are captured in the PIV images. The instantaneous velocity field measurements are used to describe flow characteristics of the impinging jet. The important flow features such as oscillating shock waves, slipstream shear layers and large scale structures are captured clearly by the PIV. The presence of large scale structures in the impinging jet induced high entrainment velocity in the near hydrodynamic field, which resulted in lift plate suction pressures. A passive control device is used to interfere with the acoustic waves travelling in the ambient medium to suppress the feedback loop. As a consequence, the large scale vortical structures disappeared completely leading to a corresponding reduction in the entrainment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henderson, B. and Powell, A., “Experiments Concerning Tones Produced by an Axisymmetric Choked Jet Impinging on Flat Plates,” J. of Sound and Vibration, 168-2 (1993), 307–326.
Ho, C. M. and Nosseir, N.S., “Dynamics of an Impinging Jet. Part 1. The Feedback Phenomenon,” J. Fluid Mech., 105 (1981), 119–142.
Krothapalli, A., Rajakuperan, E., Alvi, F. and Lourenco, L., “Flow field and noise characteristics of a supersonic impinging jet,” J. Fluid Mech. 392 (1999), 155–187.
Kuo, C. Y. and Dowling, A. P., “Oscillations of a Moderately Underexpanded Choked Jet Impinging upon a Flat Plate,” J. Fluid Mech., 315 (1996), 267–291.
Lourenco, L. M., “A 3-D High resolution PIV,” in preparation (2000).
Messersmith, N. L. “Aeroacoustics of Supersonic and Impinging Jets,” AIAA 95-0509, Aerospace Sciences Meeting, January (1995).
Neuwerth, G. “Acoustic Feedback of a Subsonic and Supersonic Free Jet which Impinges on an Obstacle,” NASA TT F-15719 (1974).
Powell, A., “The Sound-Producing Oscillations of Round Underexpanded Jets Impinging on Normal Plates,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 83-2 (1988), 515–533.
Ross, C. B. “Calibration of particle image velocimetry in a shock-containing supersonic flow,” MS thesis, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Florida State University (1993).
Tam, C. K. W. and Ahuja, K. K, “Theoretical Model of Discrete Tone Generation by Impinging Jets,” J. Fluid Mech., 214 (1990), 67–87.
Tam, C. K. W. “Supersonic Jet Noise,” Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 27 (1995), 17–43.
Wardwell, D. A., Hange, C., Kuhn, R.E., and Stewart, V. R., “Jet-Induced Ground Effects on a Parametric Flat-Plate Model in Hover,” NASA TM 104001 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
R. Elavarasan: He received his Ph.D. in Fluid Mechanics at Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, India in 1993. From 1994 to 1997 he worked as post doctoral fellow at University of Newcastle, Australia. He came to USA and was working at Kansas State University before joining to the Mechanical Engineering Department of Florida State University in 1998. His research interests are optical diagnostic techniques for fluid mechanics measurements, cloud dynamics, impinging jets, turbulent boundary layer control, mixing, biomedical fluid mechanics and combustion.
L. Venkatakrishnan: He obtained his Ph.D. in Fluid Mechanics at Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, India in 1997, and is currently a post doctoral fellow at the Fluid Mechanics Research Laboratory, Florida State University. His research interests include turbulent jets and plumes, cloud physics, impinging jets, turbulent mixing and aeroacoustics.
Anjaneyulu Krothapalli: He is the Don Fuqua Eminent Scholar, Professor and Chairman of Mechanical Engineering at Florida A&M and Florida State Universities, Tallahassee. Professor Krothapalli obtained his Ph.D. in Aeronautical and Astronautical Engineering from Stanford University in 1979. He has been on the faculties of Aerospace Engineering at the University of Oklahoma (1979–1980) and the Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics at Stanford University (1981–1983). His research interests include: aeroacoustics, aero-dynamics, jets, wakes and optical diagnostics.
Luis Lourenco: He is a Professor of Mechanical Engineering jointly at Florida A&M and Florida State Universities in Tallahassee. Professor Lourenco received his D. Sc. from the University of Brussels, Belgium in 1982. His research interests include: biomedical and biofluids engineering, experimental methods, optical diagnostics, two-phase flows and heat transfer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elavarasan, R., Venkatakrishnan, L., Krothapalli, A. et al. A PIV study of a supersonic impinging jet. J Vis 2, 213–221 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03181438
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03181438