Abstract
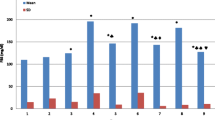
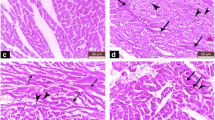
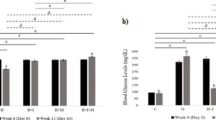
This study aimed to investigate whether treatments with vitamin E, L-carnitine and melatonin can protect against CCl4 and diabetes-induced hepatic oxidative stress. Hepatic oxidative stress was performed in rats through 50% v/v carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) (1 ml/kg/3days, i.p.), and through diabetes mellitus induced by streptozotocin (STZ) (40 mg/kg, i.p.). Vitamin E (100 mg/kg/day, i.p), L-carnitine (300 mg/kg/day, i.p.) and melatonin (10 mg/kg/day, i.p.) were injected for a period of 6 weeks. Thereafter, changes in serum glucose level, liver function tests, hepatic malondialdehyde (MDA) content, hepatic reduced glutathione (GSH) content, hepatic superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, and serum total antioxidant capacity (TAC) level were evaluated. In CCl4-induced liver fibrosis, the efficacy order was melatonin > L-carnitine > vitamin E, while in STZ-induced diabetes, the efficacy order was vitamin E ≥ melatonin > L-carnitine. In conclusion, these data indicate that low dose of melatonin is more effective than high doses of vitamin E and L-carnitine in reducing hepatic oxidative stress induced by CCl4 and diabetes. Moreover, the potent effect of vitamin E in ameliorating diabetes can be linked not only to the antioxidant actions, but also to the superior effect in reducing diabetes-induced hyperglycaemia. Meanwhile, potency of L-carnitine was nearly the same in CCl4 and diabetes-induced liver damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belfield, A., Goldberg, D.M. (1971): Revised assay for serum phenyl phosphatase activity using 4-amino-antipyrine.Enzyme,12, 561–573.
Beutler, E., Duron, O., Kelly, B.M. (1963): Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione.J Lab Clin Med,61, 882–888.
Boll, M., Weber, L.W., Becker, E., Stampfl, A. (2001): Mechanism of carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity. Hepatocellular damage by reactive carbon tetrachloride metabolites.Z Naturforsch,56, 649–659.
Brigelius-Flohé, R., Traber, M.G. (1999): Vitamin E: function and metabolism.FASEB J,13, 1145–1155.
Broderick T.L., Quinney, H.A., Lopaschuk, G.D. (1995): L-carnitine increases glucose metabolism and mechanical function following ischaemia in diabetic rat heart.Cardiovasc Res,29, 373–378.
Capaldo, B., Napoli, R., Di Bonito, P., Albano, G., Saccà, L. (1991): Carnitine improves peripheral glucose disposal in non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients.Diabetes Res Clin Pract,14, 191–195.
Chawla, R.K., Lewis, F.W., Kutner, M.H., Bate, D.M., Roy, R.G.B., Rudman, D. (1984): Plasma cysteine, cystine, and glutathione in cirrhosis.Gastroenterol,87: 770–775.
Demirdag, K., Bahcecioglu, I.H., Ozercan, I.H., Ozden, M., Yilmaz, S., Kalkan, A. (2004): Role of L-carnitine in the prevention of acute liver damage induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats.J Gastroenterol Hepatol,19, 333–338.
Ferrari, R., Merli, E., Cicchitelli, G., Mele, D., Fucili, A., Ceconi, C. (2004): Therapeutic effects of L-carnitine and propionyl-L-carnitine on cardiovascular diseases: a review.Ann NY Acad Sci,1033, 79–91.
Gornall, A.G., Bardawill, C.J., David, M.M. (1949): Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction.J Biol Chem,177, 751–766.
Gulcin, I. (2006): Antioxidant and antiradical activities of L-carnitine.Life Sci,78, 803–811.
Harris, E.H. (2005): Elevated Liver Function Tests in Type 2 Diabetes.Clinical Diabetes,23, 115–119.
Hunt, J.V., Smith, C.C., Wolff, S.P. (1990): Autoxidative glycosylation and possible involvement of peroxides and free radicals in LDL modification by glucose.Diabetes,39, 1420–1424.
Jain, S.K., McVie, R., Smith, T. (2000): Vitamin E supplementation restores gluthatione and malondialdehyde to normal concentrations in erythrocytes of type 1 diabetic children.Diabetes Care,23, 1389–1394.
Juránek, I., Bezek, S. (2005): Controversy of free radical hypothesis: reactive oxygen species — cause or consequence of tissue injury?Gen Physiol Biophys,24, 263–278.
Koracevic, D., Koracevic, G., Djordjevic, V., Andrejevic, S., Cosic, V. (2001): Method for the measurement of antioxidant activity in human fluids.J Clin Pathol,54, 356–361.
Lee, T.Y., Mai, L.M., Wang, G.J., Chiu, J.H., Lin, Y.L., Lin, H.C. (2003): Protective mechanism of Salvia miltiorrhiza on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatotoxicity in rats.J Pharmacol Sci,91, 202–210.
Marklund, S., Marklund, G. (1974): Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase.Eur J Biochem,47, 469–474.
Marshall, K.A., Reiter, R.J., Poeggeler, B., Aruoma, O.I., Halliwell, B. (1996): Evaluation of the antioxidant activity of melatonin in vitro.Free Radic Biol Med,21, 307–315.
McLennan, S.V., Heffernan, S., Wright, L., Rae, C., Fisher, E., Yue, D.K., Turtle, J.R. (1991): Changes in hepatic glutathione metabolism in diabetes.Diabetes,40, 344–348.
Ohkawa, H., Ohishi, N., Yagi, K. (1979): Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction.Anal Biochem,95, 351–358.
Oliveira, H.R., Curi, R., Carpinelli, A.R. (1999): Glucose induces an acute increase of superoxide dismutase activity in incubated rat pancreatic islets.Am J Physiol,276, 507–510.
Paolisso, G., Di Maro, G., Galzerano, D., Cacciapuoti, F., Varricchio, G., Varricchio, M., D’Onofrio, F. (1994): Pharmacological doses of vitamin E and insulin action in elderly subjects.Am J Clin Nutr,59, 1291–1296.
Pitsavos, C., Panagiotakos, D.B., Tzima, N., Chrysohoou, C., Economou, M., Zampelas, A., Stefanadis, C. (2005): Adherence to the Mediterranean diet is associated with total antioxidant capacity in healthy adults: the ATTICA study.Am J Clin Nutr,82, 694–699.
Rajasekar, P., Kaviarasan, S., Anuradha, C.V. (2005): L-carnitine administration prevents oxidative stress in high fructose-fed insulin resistant rats.Diabetol Croat,34: 21–28.
Reiter, R.J., Tan, D.X., Mayo, J.C., Sainz, R.M., Leon, J., Czarnocki, Z. (2003): Melatonin as an antioxidant: biochemical mechanisms and pathophysiological implications in humans.Acta Biochim Pol,50, 1129–1146.
Reitman, S., Frankel, S. (1957): A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxaloacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases.Am J Clin Pathol,28, 56–63.
Rolo, A.P., Palmeira, C.M. (2006): Diabetes and mitochondrial function: role of hyperglycemia and oxidative stress.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol,212, 167–178.
Schneider, C. (2005): Chemistry and biology of vitamin E.Mol Nutr Food Res,49, 7–30.
Tan, D.X., Manchester, L.C., Terron, M.P., Flores, L.J., Reiter, R.J. (2007): One molecule, many derivatives: a never-ending interaction of melatonin with reactive oxygen and nitrogen species?J Pineal Res,42, 28–42.
Trinder, P. (1969): Determination of glucose in blood using glucose oxidase with an alternative oxygen acceptor.Ann Clin Biochem,6, 24–28.
Urata, Y., Honma, S., Goto, S., Todoroki, S., Ueda, T., Cho, S., Honma, K., Kondo, T. (1999): Melatonin induces gammaglutamylcysteine synthetase mediated by activator protein-1 in human vascular endothelial cells.Free Radic Biol Med,27, 838–847.
Vozarova, B., Stefan, N., Lindsay, R.S., Saremi, A., Pratley, R.E., Bogardus, C., Tataranni, P.A. (2002): High alanine aminotransferase is associated with decrease hepatic insulin sensitivity and predicts the development of type 2 diabetes.Diabetes,51, 1189–1195.
Wang, H., Wei, W., Wang, N.P., Gui, S.Y., Wu, L., Sun, W.Y., Xu, S.Y. (2005): Melatonin ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrogenesis in rats via inhibition of oxidative stress.Life Sci,77, 1902–1915.
Weber, L.W., Boll, M., Stampfl, A. (2003): Hepatotoxicity and mechanism of action of haloalkanes: carbon tetrachloride as a toxicological model.Cri Rev Toxicol,33, 105–136.
Wefers, H., Sies, H. (1988): The protection by ascorbate and glutathione against microsomal lipid peroxidation is dependent on vitamin E.Eur J Biochem,174, 353–357.
Wolf, R., Wolf, D., Ruocco, V. (1998): Vitamin E: the radical protector.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol,10, 103–117.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaker, M.E., Houssen, M.E., Abo-Hashem, E.M. et al. Comparison of vitamin E, L-carnitine and melatonin in ameliorating carbon tetrachloride and diabetes induced hepatic oxidative stress. J Physiol Biochem 65, 225–233 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03180575
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03180575