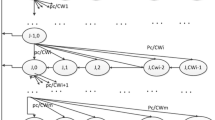
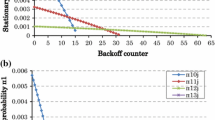
Abstract
In this paper we present an integrated packet/flow level modelling approach for analysing flow throughputs and transfer times inieee 802.11wlans. It captures the statistical characteristics of the transmission of individual packets at themac layer and takes into account the system dynamics due to the initiation and completion of data flow transfers. In particular, at the flow level the system is modelled by a processor sharing type of queue, reflecting theieee 802.11mac design principle of distributing the transmission capacity fairly among the active flows. The integrated packet/flow level model is analytically tractable and yields a simple approximation for the throughput and flow transfer time. Extensive simulations show that the approximation is very accurate for a wide range of parameter settings. In addition, the simulation study confirms the attractive property following from our approximation that the expected flow transfer delay is insensitive to the flow size distribution (apart from its mean).
Résumé
Nous présentons dans cet article un modèle intégrant les niveaux paquets et flux, qui permet l’analyse du débit utile des flux et de leur temps de transfert dans des réseaux locaux sans filieee 802.11. Le modèle développé prend en compte les caractéristiques statistiques de la transmission de paquets individuels au niveau de la couchemac, ainsi que la dynamique du système liée à l’initialisation et à la terminaison des transferts de flux de données. Plus précisément, au niveau des flux, le système est modélisé à l’aide d’une file d’attente à processeur partagé, refletant ainsi le partage équitable de la capacité de transmission entre les différents flux actifs, tel que réalisé par la couchemac de l’ieee 802.11. Le modèle à deux niveaux, paquets/flux, peut être résolu analytiquement et fournit une approximation simple du débit utile et du temps de transfert de flux. De nombreuses simulations ont montré que, pour une large gamme de paramètres, l’approximation est très précise. De plus, les résultats de nos simulations vérifient une propriété intéressante découlant de notre approximation à savoir que le delai de transfert moyen d’un flux est indépendant de la distribution des tailles (seule sa moyenne compte).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aad (I.),Castelluccia (C.), “Differentiation mechanisms forieee 802.11”,Proceedings of ieee infocom’01, Anchorage, USA, 2001.
Bianchi (G.), “Performance analysis of theieee 802.11 distributed coordination function”,ieee Journal on Selected Areas in Communications,18, no 3, pp. 535–547, 2000.
Binmore (KG.), “Mathematical analysis: a straightforward approach”, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1982.
Cali (F.),Conti (M.),Gregori (E.), “ieee 802.11 wirelesslan: capacity analysis and protocol enhancement”,Proceedings ieee infocom’98, San Francisco,usa, 1998.
Chhaya (H.),Gupta (S.), “Performance modeling of asynchronous data transfer methods ofieee 802.11mac protocol”,Wireless networks,3, no 3, pp. 217–234, 1997.
Cohen (J.W.), “The multiple phase service network with generalized processor sharing”,Acta informatica,12, pp. 245–284, 1979.
Dardari (D.),Tralli (V.),Verdone (R.), “On the capacity of slotted Aloha with Rayleigh fading: the role played by the number of interferers”,ieee Communication letters,2, no 5, pp. 155–157, 2000.
Foh (C.H.),Zukerman (M.), “Performance analysis of theieee 802.11mac protocol”,Proceedings of European Wireless’02, Florence, Italy, 2002.
Ho (T.S.),Chen (K.C.), “Performance Analysis ofieee 802.11csma/ca Medium Access control protocol”,Proceedings of ieee pimrc’96, Taipei, Taiwan, pp. 407–411, 1996.
Honkasalo (H.),Pehkonen (K.),Niemi (Mt.),Leino (AT.), “wcdma andwlan for 3G and beyond”,ieee Wireless communications magazine,9, no 12, pp. 14–18, 2002.
Hadzi-Velkov (Z.),Spasenovski (B.), “Capture effect inieee 802.11 wirelesslans”, Proceedings ofieee icwlhn’01, Singapore, 2001.
Hadzi-Velkov (Z.),Spasenovski (B.), “ieee 802. 11dcf with capture over Ricean-fading channel”,ieee Workshop on wlans’01, Boston,usa, 2001.
ieee, “Wirelesslan mediumaccesscontrol (mac) andphysical layer (phy) specifications”,p802.11, 1997.
ieee, “Supplement to standard for telecommunications and information exchange between systems —lan/man specific requirements — part 11: wirelessmediumaccesscontrol (mac) andphysical layer (phy) specifications: higher speed physical layer extension in the 2.4 GHz band”, P802.11B/D7.0, 1999.
ieee, “Draft supplement to standard for telecommunications and information exchange between systems —lan/man specific requirements — part 11: wirelessmediumaccesscontrol (mac) andphysical layer (phy) specifications: enhancements for Quality of Service (QoS)”, P802.11E/D1, 2001.
ieee, “Draft recommended practice for multi-vendor access point interoperability via an inter-access point protocol across distribution systems supportingieee 802.11 operation”, Std 802.11F/D1, 2001.
Lassila (P.),Van Den Berg (J.L.),Mandjes (M.),Kooij (RE.), “An integrated packet/flow level model fortcp performance analysis”,Proceedings of itc 18, Berlin, Germany, 2003.
Lau (C.T.),Leung (C.), “Capture models for mobile packet radio networks”,ieee Transactions on Communications,40, no 5, pp. 917–925, 1992.
Lee (W.C.Y.), “Mobile communications design fundamentals”, Howard W. Sams & Co., Indianapolis,usa, 1986.
Mangold (S.),Choi (S.),May (P.),Klein (O.),Hiertz (G.),Stibor (L.), “ieee 802.11e wirelesslan for quality of service”,Proceedings of European Wireless’02, Florence, Italy, 2002.
Prasad (N.),Prasad (A.) (ed.), “wlan systems and wirelessip for next generation communications”,Artech House, Norwood,usa, 2002.
Struik (D.J.) (ed.), “A source book in mathematics 1200–1800”, Princeton University Press, Princeton,usa, pp. 89–93, 1986.
Tijms (H.C.), “Stochastic modelling and analysis: a computational approach”, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, England, 1986.
Ware (C.),Chicharo (J.F.),Wysocki (T.), “Modelling capture behaviour inieee 802.11 radio modems”,Proceedings of ieee vtc’01, Atlantic City,nj, 2001.
Weinmiller (J.),Schlager (M.),Festag (A.),Wolisz (A.), “Performance study of access control in wirelesslans ieee 802.11dfwmac andetsi res 10hiperlan”,Mobile networks and applications,2, no 1, pp. 55–67, 1997.
Winands (E.M.M.),Denteneer (T.J.J.),Resing (J.A.C.),Rietman (R.), “A finite-source feedback queueing network as a model for theieee 802.11 distributed coordination function”,Proceedings of European Wireless’04, Barcelona, Spain, 2004.
Wu (H.),Peng (Y.),Long (K.),Cheng (S.),Ma (J.), “Performance of reliable transport protocol overieee 802.11 wirelesslan: analysis and enhancement”,Proceedings of ieee infocom’02, New York,usa, 2002.
Yue (W.),Matsumoto (Y.), “An exact analysis forcsma/ca protocol integrated voice/data wirelesslans”,Proceedings of ieee globecom’00, San Francisco,usa, 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Litjens, R., Roijers, F., Van Den Berg, H. et al. Analysis of flow transfer times in IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs. Ann. Télécommun. 59, 1407–1432 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179728
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179728
Key words
- Wirelesslan
- Transit time
- Resource sharing
- Packet transmission
- Random multiprocess
- Carrier detection
- Collision detection