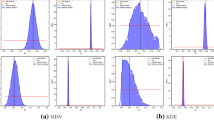
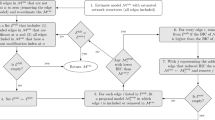
Summary
The predictive performance of a neural network model depends crucially on the net architecture. Although complex models can fit very well the data at hand, their out-of-sample performance is typically very poor. In order to improve the predictive performance of a neural network model, we propose to interpret a neural network as a graphical model with latent variables. The proposed interpretation allows to extend a computational methodology recently proposed in Giudici and Green (1999) to compare alternative network models in terms of their posterior probabilities, and, therefore, to choose the most plausible net architecture. We apply our proposal to a data-set concerned with the analysis of the correlation structure among shares of viewers in the Italian television market.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbieri, M. (1996),Metodi MCMC nell’inferenza statistica. Italian Statistical Society monographs, CISU, Roma.
BROOKS, S. and GIUDICI, P. (1999), MCMC Convergence Assessment via Two-way ANOVA. To appear inJournal of computational and graphical statistics.
CONSONNI, G. and GIUDICI, P. (1997), Modelli di previsione per l’ascolto televisivo. InAtti della riunione specializzata della Società Italiana di Statistica su: La statistica per le imprese, vol. 2, pp. 283–290.
Dawid, A. P. andLauritzen, S. L. (1993), Hyper Markov Laws in the statistical analysis of decomposable graphical models.Ann. Statist., 21,1272–317.
GIUDICI, P. (1997), Modelli grafici e reti neuronali: un confronto preliminare. InLe reti neuronali e la statistica, (A. Bellacicco and C. Lauro editors), 621–628. FrancoAngeIi.
Giudici, P. andGreen, P. J. (1999), Decomposable graphical Gaussian model determination.Biometrika, 86, 785–801.
GIUDICI, P. and STANGHELLINI, E. (1998), Graphical factor analysis models: specification and model comparison. In em Advances in Data Science and Classification (A. Rizzi, M. Vichi and H. Bock editors), 363–368.
Green, P. J. (1995), Reversible Jump MCMC Computation and Bayesian Model Determination.Biometrika, 82, 711–732.
Lauritzen, S. L. (1996),Graphical Models. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Madigan, D. andRaftery, A. E. (1994), Model selection and accounting for model uncertainty in graphical models using Occam’s window.J. Am. Statist. Assoc., 89, 1535–46.
Stanghellini, E. (1997), Identification of a single-factor model using graphical Gaussian rules.Biometrika, 84, 1, 241–4.
Tierney, L. (1994), Markov chains for exploring posterior distributions (with discussion).Annals of statistics, 22, 1701–1762.
VICARD, P. (2000), On the identification of a single-factor model with correlated residuals.Biometrika, 87.
Whittaker, J. (1990),Graphical models in applied multivariate statistics. New York: Wiley.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giudici, P. Markov chain Monte Carlo methods for probabilistic network model determination. J. Ital. Statist. Soc. 7, 171–183 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03178927
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03178927