Abstract
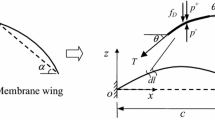
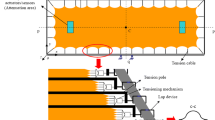
In pursuing noise and wave control with minimal aerodynamic or hydrodynamic sacrifice, a tensioned membrane is used to line the otherwise rigid duct wall. The membrane vibrates in response to the grazing incident waves and the vibration serves to reflect the wave towards its source. The mechanism is identical to what happens in a rig of active wave control, but the difference is that the current rig has no active component. For the purpose of wave control, the device has been tested successfully without flow and with moderate flow conditions commonly found in air ventilation systems. When the flow speed is further increased, flow induced vibration occurs. This study reports the phenomena of such vibration under various flow speeds and membrane tensions. Transient process of exponential vibration growth is recorded and analysed together with the boundary layer measurements. The effects of an external cavity as well as the lateral membrane tension are also found to be significant. Other possible mechanisms for the flow induced vibration are also explored and discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackermann, U., Fuchs, H. V. and Rambausek, I., 1988, “Sound Absorbers of a Novel Membrane Construction,”Appl. Acoust., Vol. 25, pp. 197–215.
Choy, Y. S. and Huang, L., 2002, “Experimental Studies of Drum-like Silencer,”J. Acoust. Soc. Am., Vol. 112, pp. 2026–2035.
Choy, Y. S. and ba]Huang, L., 2003, “Drum Silencer with Shallow Cavity Filled with Helium,”J. Acoust. Soc. Am., Vol. 114, pp. 1477–1486.
Choy, Y. S. and Huang, L., 2005, “Mean Flow Effect on Drum-like Silencer,”J. Acoust. Soc. Am., Vol. 114, pp. 1477–1486.
Dowell, A. C., 1970, “Panel Flutter: A Review of the Aeroelastic of Plates and Shells,”AIAA J., Vol. 8, pp. 385–399.
Dowell, E. H., 1975,Aeroelasticity of plates and Shells. Leyden: Noordhoff International Publishing.
Dugundi, J., Dowell, E. H. and Perkin, B., 1963, “Subsonic Flutter of Panels on Continuous Elastic Foundations,”AIAA J., Vol. 1, pp. 1146–1154.
Gaster, M., 1987, “Is the Dolphin a Red Herring?” Proceedings of IUTAM Symposium on Turbulence Management and Relaminarisation, Bangalore, India, edited by H. W. Liepmann and R. Narasimha Springer, New York.
Huang, L., 1998, “Reversal of the Bernoulli Effect and Channel Flutter,”J. Fluids Struct., Vol. 12, pp. 131–151.
Huang, L., 2001, “Viscous Flutter of a Finite Elastic Membrane in Poiseuille Flow,”J. Fluids Struct, Vol. 15, pp. 1061–1088.
Huang, L., 2002, “Modal Analysis of a Drum-like Silencer,”J. Acoust. Soc. Am. Vol. 112, pp. 2014–2025.
Ishii, T., 1965, “Aeroelastic Instabilities of Simply Supported Panels in Subsonic Flow”AIAA, pp. 65–772.
Lucey, A. D. and Carpenter, P.W., 1995, “Boundary Layer instability Over Compliant Walls: Comparison Between Theory and Experiment,”Phy. Fluids, Vol. 7, pp. 2355–2363.
Watanable, Y., 2002, “An Experimental Study of Paper Flutter,”J. Fluids Struct, Vol. 16, pp. 529–542.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choya, Y.S., Huang, J., Huang, L. et al. An experimental study of flow induced vibration on a tensioned membrane. J Mech Sci Technol 21, 1359 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03177421
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03177421