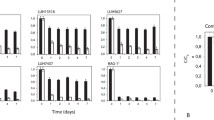
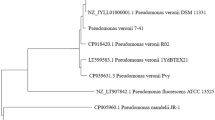
Abstract
Cells ofAcinetobacter venetianus strain VE-C3 are able to degrade diesel fuel oil by a complex mechanism requiring the formation of cell aggregates and their further adhesion to fuel oil drops. In this work the biodegradation process inA. venetianus was studied by a combination of genetic, molecular and physiological methods. PCR amplification, sequencing and Southern blot analysis ofalkM andrubA genes coding for the alkane hydroxylase and rubredoxin were carried out. Then, 22 Alk− mutants impaired in diesel fuel degradation were obtained by nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis and characterised by i) growth on alkanes as sole carbon and energy sources, ii) modification of cell electrophoretic properties, and iii) analysis of plasmid content. Data obtained revealed that the genetic determinants for alkane degradation are located on both the chromosome and the two plasmids harboured by VE-C3 strain (pAV1 and pAV2, 11 Kbp and 15 kbp, respectively). This organization of genes coding for alkane monoxygenase complex seems to be similar to the arrangement found in Acinetobacter sp. strains ADP1 and M1, where genes are scattered through the chromosome but, as a novelty, that some genes involved in hydrocarbon degradation are plasmid borne also.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul S.F., Madden T.L., Schaffer A.A., Zhalg J., Zhalg Z., Miller W., Lipman D.J. (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucl. Acids Res., 25: 3389–3402.
Bach H., Berdichevsky Y., Gutnick D. (2003) An exocellular protein from the oil-degrading microbeAcinetobacter venetianus RAG-1 enhances the emulsifying activity of the polymeric bioemulsifier emulsan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 69: 2608–2615.
Baldi F., Pepi M., Fani R., Di Cello F., Da Ros L., Fossato V.U. (1997) Complementary degradation of n-paraffins by aerobic Gramnegative bacteria isolated from Venice Lagoon. Croatica Chemica Acta, 70: 333–346.
Baldi F., Ivosevic N., Minacci A., Pepi M., Fani R., Svetlicic V., Zutic V. (1999) Adhesion ofAcinetobacter venetianus to diesel fuel droplets studied with in situ electrochemical and molecular probes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 65: 2041–2048.
Baldi F., Pepi M., Capone A., Milanesi C., Fani R., Focarelli R. (2003) Envelope glycosylation determined by lectins in microscopy sections ofAcinetobacter venetianus induced by diesel fuel. Res. Microbiol., 154: 417–424.
Bazzicalupo M., Fani R. (1995) The use of RAPD for generating specific DNA probes for microorganisms. In: Clapp J.P. Ed., Methods In Molecular Biology, Vol 50: Species diagnostics protocols: PCR and other nucleic acid Methods, Humana Press Inc. Totowa, NJ, pp. 155–175.
Desai J.D., Banat I.M. (1997) Microbial production of surfactants and their commercial potential. Microb. Mol. Biol. Rev., 61: 47–64.
Di Cello F., Pepi M., Baldi F., Fani R. (1997) Molecular characterization of an n-alkane-degrading bacterial community and identification of a new species,Acinetobacter venetianus. Res. Microbiol., 148: 237–249.
Grifoni A., Bazzicalupo M., Di Serio C., Fancelli S., Fani R. (1995) Identification ofAzospirillum strains by restriction length polymorphism of the 16S rDNA and of the histidine operon. FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 127: 85–91.
Grossi C., Nereo S., Brilli M., Michaud L., Lo Giudice A., Bruni V., Fani R. (2005) Isolation and phenotypic and molecular characterization of hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria isolated from Terra Nova Bay (Antarctica). Polarnet, 1: 157–165.
Hanson K.G., Kale V.C., Desai A.J. (1994) The possible involvement of cell surface and outer membrane proteins ofAcinetobacter sp.A3 in crude oil degradation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 122: 275–280.
Kumar S., Tamura K., Nei M. (2004) MEGA3: Integrated Software for Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis and Sequence Alignment. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 5: 150–163.
Mills A.L., Breuil C., Colwell R.R. (1978) Enumeration of petroleum degrading marine and estuarine microorganisms by the most probable number method. Can. J. Microbiol., 24: 552–557.
Navon-Venezia S., Zosim Z., Gottlieb A., Legmann R., Carmeli S., Ron E.Z., Rosenberg E. (1995) Alasan, a new bioemulsifier fromAcinetobacter radioresistens, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 61: 3240–3244.
Ratajczak A., Geißdörfer W., Hillen W. (1998) Expression of alkane hydroxylase fromAcinetobacter sp. strain ADP1 is induced by a broad range of n-alkanes and require the transcriptional activator AlkR. J. Bacteriol., 180: 5822–5827.
Rosenberg E., Rubinovitz C., Gottlieb A., Rossenhak S., Ron E.Z. (1988) Production of biodispersan byAcinetobacter calcoaceticus A2. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 54: 317–322.
Saitou M., Nei M. (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol., 4: 406–425.
Smits T.H., Rothlisberger M., Witholt B., van Beilen J.B. (1999) Molecular screening for alkane hydroxylase genes in Gram-negative and Gram-positive strains. Environ. Microbiol., 1: 307–317.
Tani A., Ishige T., Sakai Y., Kato N. (2001) Gene structures and regulation of the alkane hydroxylase complex inAcinetobacter sp. strain M-1. J. Bacteriol., 183: 1819–1823.
Thompson J.D., Higgins D.G., Gibson T.J. (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucl. Acids Res., 22: 4673–4680.
Toren A., Navon-Venezia S., Ron E.Z., Rosenberg E. (2001) Emulsifying activities of purified Alasan proteins fromAcinetobacter radioresistens KA53. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 67: 1102–1106.
Toren A., Orr E., Paitan Y., Ron E.Z., Rosenberg E. (2002) The active component of the bioemulsifier alasan fromAcinetobacter radioresistens KA53 is an OmpA-like protein. J. Bacteriol., 184: 165–170.
van Beilen J.B., Wubbolts M.G., Witholt B. (1994) Genetics of alkane oxidation inPseudomonas oleovorans. Biodegradation, 5: 161–174.
Vaneechoutte M., Tjernberg I., Baldi F., Pepi M., Fani R., Sullivan E.R., van der Toorn J., Dijkshoorn L. (1999) Oil-degradingAcinetobacter strain RAG-1 and strains described as ‘Acinetobacter venetianus sp. nov.’ belong to the same genomic species. Res. Microbiol., 150: 69–73.
Yung l.Y., Phelps C.D. (2005) Metabolic biomarkers for monitoring in situ anaerobic hydrocarbon degradation. Environ. Health Perspective, 113: 62–67.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Decorosi, F., Mengoni, A., Baldi, F. et al. Identification of alkane monoxygenase genes inAcinetobacter venetianus VE-C3 and analysis of mutants impaired in diesel fuel degradation. Ann. Microbiol. 56, 207–214 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03175007
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03175007