Abstract
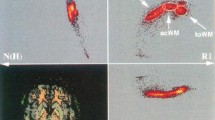
The preprocessing of 3-dimensional (3D) MRI data constitutes a bottleneck in the process of visualizing the brain surface with volume rendering. As a fast way to achieve this preprocessing, the authors propose a simple pipeline based on an algorithm of seedgrowing type, for approximate segmentation of the intradural space in T1-weighted 3D MRI data. Except for the setting of a seed and four parameters, this pipeline proceeds in an unsupervised manner; no interactive intermediate step is involved. It was tested with 15 datasets from normal adults. The result was reproducible in that as long as the seed was located within the cerebral white matter, identical segmentation was achieved for each dataset. Although the pipeline ran with gross segmentation error along the floor of the cranial cavity, it performed well along the cranial vault so that subsequent volume rendering permitted the observation of the sulco-gyral pattern over cerebral convexities. Use of this pipeline followed by volume rendering is a handy approach to the visualization of the brain surface from 3D MRI data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frenkel KA: Volume rendering. Comm ACM 32:426–435, 1989.
Levin DN, Hu X, Tan KK, et al: Surface of the brain: Three-dimensional MR images created with volume rendering, Radiology 171:277–280, 1989
Bezdek JC, Hall LO, Clarke LP: Review of MR image segmentation techniques using pattern recognition. Med Phys 20:1033–1048, 1993
Joliot M, Mazoyer BM: Three-dimensional segmentation and interpolation of magnetic resonance brain images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 12:269–277, 1993
Filipek PA, Kennedy DN, Caviness VS, et al: Magnetic resonance imaging-based brain morphometry: Development and application to normal subjects. Ann Neurol 25:61–67, 1989
Bomans M, Höhne KH, Tiede U, et al: 3-D segmentation of MR images of the head for 3-D display. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 9:177–183, 1990
Cline HE, Dumoulin CL, Hart HR, et al: 3D reconstruction of the brain from magnetic resonance images using a connectivity algorithm. Magn Reson Imaging 5:345–352, 1987
Brummer ME, Mersereau RM, Eisner RL, et al: Automatic detection of brain contours in MRI data sets. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 12:153–166, 1993
Snell JW, Merickel MB, Ortega JM, et al: Model-based boundary estimation of complex objects using hierarchical active surface templates. Pattern Recognition 28:1599–1609, 1995
Toh MY, Falk RB, Main JS: Interactive brain atlas with the visible human project data: Development methods and techniques. Radiographics 16:1201–1206, 1996
Gerig G, Kübler O, Kikinis R, et al: Nonlinear anisotropic filtering of MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 11:221–232, 1992
Kaufman L, Kramer DM, Crooks LE, et al: Measuring signal-to-noise ratios in MR imaging. Radiology 173:265–267, 1989
Clarke LP, Velthuizen RP, Camacho MA, et al: MRI segmentation: Methods and applications. Magn Reson Imaging 13:343–368, 1995
Kikinis R, Shenton ME, Gerig G, et al: Temporal lobe sulco-gyral pattern anomalies in schizophrenia: an in vivo MR three-dimensional surface rendering study. Neurosci Lett 182:7–12, 1994
Sisodiya SM, Stevens JM, Fish DR, et al: The demonstration of gyral abnormalities in patients with cryptogenic partial epilepsy using three-dimensional MRI. Arch Neurol 53:28–34, 1996
Bartley AJ, Jones DW, Weinberger DR: Genetic variability of human brain size and cortical gyral patterns. Brain 120:257–269, 1997
Biondi A, Nogueira H, Dormont D, et al: Are the brains of monozygotic twins similar? A three-dimensional MR study. Am J Neuroradiol 19:1361–1367, 1998
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumoto, S., Asato, R. & Konishi, J. A fast way to visualize the brain surface with volume rendering of MRI data. J Digit Imaging 12, 185–190 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03168854
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03168854