Abstract
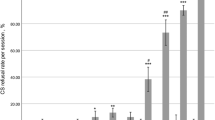
There have been few pharmacological studies of serotonergic system dynamics in insects. A more precise knowledge of the response of serotonergic neurons to drugs will contribute to understanding of the role of this neurotransmitter in insect behaviour. The present work was carried out to study several aspects of serotonin (5-HT) metabolism and release in an insect, the butterfly Inachis io. The effects of a single intra-abdominal injection of reserpine (30 μg/insect) or p-chloroamphetamine (50 μg/insect) on cerebral ganglia 5-HT metabolism and release were studied. After reserpine injection a depletion of 5-HT stores concomitant with an increase in N-acetylserotonin levels was observed, but not significant alteration of extraneuronal 5-HT release was observed. Administration of p-chloroamphetamine (PCA) induced extraneuronal 5-HT release, together with inhibition of its reuptake. Finally, a single injection of p-chloroamphetamine in reserpine-treated insects was able to induce new release of 5-HT. Reserpine interferes with the vesicular storage of 5-HT, but does not affect the process of neuronal release, while PCA induces the synaptic release of 5-HT and inhibits its reuptake. These effects are similar to those observed in mammals.
Resumen
Hay muy pocos estudios farmacológicos sobre la dinámica del sistema serotoninérgico en insectos. Un conocimiento más detallado de la respuesta de las neuronas serotoninérgicas a los diferentes fármacos ayudará a entender el papel de este neurotransmisor en el comportamiento del insecto. En el presente trabajo, se estudian los efectos de una inyección única intra-abdominal de reserpina o de p-cloranfetamina (PCA) sobre el metabolismo y la liberación de 5-HT en los ganglios cerebrales de un insecto, la mariposa Inachis io. Después de la inyección de reserpina se observó un vaciamiento de los almacenes de 5-HT asociado a un aumento en los niveles de NAS; sin embargo, no se encontró una alteración en la liberación extraneuronal de 5-HT. Por otra parte, la administración de PCA causó una liberación extraneuronal de 5-HT y una inhibición de su recaptación. Finalmente, en insectos pre-tratados con reserpina, la inyección de PCA fue capaz de inducir una nueva liberación de 5-HT. La reserpina interfiere con el almacenamiento vesicular de 5-HT pero no afecta al proceso de liberación neuronal, mientras que la PCA induce la liberación sináptica de 5-HT e inhibe su recaptación. Estos efectos son similares a los observados en mamíferos.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NAS:
-
N-acetylserotonin
- NAT:
-
N-acetyltransferase
- 5-HIAA:
-
5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid
- 5-HT:
-
5-hydroxytryptamine or serotonin
- HPLC:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography
- PCA:
-
p-chloroamphetamine
References
Adell, A., Sarna, G. S., Hutson, P. H. and Curzon, G. (1989): Br. J. Pharmacol., 97, 206–212.
Bermúdez, I. and Beadle, D. J. (1989): Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol., 12, 253–266.
Blenau, W. and Baumann, A. (2001). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol., 48, 13–38.
Braun, G. and Bicker, G. (1992): J. Neurophysiol., 67, 588–598.
Brookhart, G. L., Edgecomb, R. S. and Murdock, L. L. (1987): J. Neurochem., 48, 1307–1315.
Chen, B., Meinertzhagen, I. A. and Shaw, S. R. (1999): J. Comp. Physiol. A, 185, 393–404.
Coleman, C. M. and Neckameyer, W. S. (2004): Invert. Neurosci., 5, 85–96.
Cook, H. and Orchard, I. (1993): Insect Biochem. Molec. Biol., 23, 895–904.
Corey, J. L., Quick, M. W., Davidson, N., Lester, H. A. and Guastella, J. (1994): Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 91, 1188–1192.
Crespi, D., Mennini, T. and Gobbi, M. (1997): Br. J. Pharmacol., 121, 1735–1743.
Cymborowski, B. (1998): Physiological Entomology, 23, 25–32.
Cymborowski, B. (2003): J. Insect. Sci., 3, 14–21.
Evans, P. D. (1980): Adv. Insect Physiol., 5, 317–473.
Faradji, H., Cespuglio, R. and Jouvet, M. (1983): Brain Res., 279, 111–119.
Flanagan, T. R. J. and Berlind, A. (1984): Brain Res., 306, 243–250.
Fujimiya, M., Okumiya, K., Nakazawa, M., Kitahama, K., Kimura, H. and Maeda, T. (1994): Histochemistry, 101, 21–26.
Harro, J., Tönissaar, M., Eller, M., Kask, A. and Oreland, L. (2001): Brain Res., 899, 227–239.
Henderson, M. G. and Fuller, R. W. (1992): Brain Res., 594, 323–326.
Heslop, K. E. and Curzon, G. (1994): Neuropharmacology, 33, 567–573.
Heyne, M. H., Kinzel, C., Gerber, B. and Fiala, A. (1999): Behav. Neurosci., 113, 744–754.
Hjorth, S. (1992): J. Neurochem., 58, 772–775.
Homberg, U. (1994). In “Progress in Zoology”. (Rathmayer, W., ed.), Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart, 40, pp 1–88.
Kruk, Z. L. and Pycock, C. J. (1991). Neurotransmitters and Drugs (3rd Ed.), Chapman & Hall, London.
Kuhn, D. M., Wolf, W. A. and Youdim, M. B. H. (1985): Br. J. Pharmacol., 84, 121–129.
Linn, C. E. J. and Roelofs, W. L. (1993): Insect Biochem. Molec. Biol., 23, 367–373.
Linn, C. E. J., Campbell, M. G., Poole, K. R. and Roelofs, W. L. (1994a): Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C, 108, 87–98.
Linn, C. E. J., Poole, K. R. and Roelofs, W. L. (1994b): Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C, 108, 73–85.
Martín, F. and Artigas, F. (1992): J. Neurochem., 59, 1138–1144.
Monastirioti, M. (1999): Microsc. Res. Tech., 45, 106–121.
Omar, D., Murdock, L. L. and Hollingworth, R. M. (1982): Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C, 73, 423–429.
Osborne, R. H. (1996): Pharmacol. Ther., 69, 117–142.
Pandey, A. and Habibulla, M. (1980): J. Insect Physiol., 26, 1–6.
Pettibone, D. J. and Pflueger, A. B. (1984): J. Neurochem., 43, 83–90.
Roeder, T. (1994): Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C, 107, 1–12.
Roman, D. L., Saldaña, S. N., Nichols, D. E., Carroll, F. I. and Barker, E. L. (2004): J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 308, 679–687.
Rothman, R. B., Jayanthi, S., Cadet, J. L., Wang, X., Dersch, C. M. and Baumann, M. H. (2004): Ann. NY Acad. Sci., 1025, 151–161.
Rudnick, G. and Wall, S. C. (1992): Biochemistry, 31, 6710–6718.
Scott, J. A., Johnson, T. L. and Knowles, C. O. (1985): Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C, 82, 43–47.
Shore, P. A. (1971): In “Handbook of Neurochemistry”. Vol. 6., (Lajtha, A., ed.), Plenum Press, New York, pp 349–356.
Shore, P. A. and Giachetti, A. (1978): In “Handbook of Psychopharmacology”. Vol. 10. (Iversen, L. L., Iversen, S. D. and Snyder, S. H., eds.), Plenum Press, New York, pp 197–219.
Sloley, B. D. and Owen, M. D. (1982): Insect Biochem., 12, 469–476.
Sloley, B. D. and Downer, R. G. H. (1984): Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C, 79, 281–286.
Sloley, B. D. and Orikasa, S. (1988): J. Neurochem., 51, 535–541.
Sloley, B. D. (2004): Neurotoxicology, 25, 175–183.
Stanford, S. C. (2001): In “Neurotransmitters, Drugs and Brain Function”, (Webster, R. A., ed.), John Wiley & Sons Ltd., New York, pp 187–209.
Stevenson, P. A., Hofmann, H. A., Schoch, K. and Schildberger, K. (2000): J. Neurobiol., 43, 107–120.
Sugita, R., Sawa, Y., Nakazawa, T. and Yamauchi, T. (1988): Japanese J. Psychopharmacol., 8, 453–62.
Trulson, M. E. and Jacobs, B. (1976): Eur. J. Pharmacol., 36, 149–154.
Vaughan, P. F. T. (1988): In “Comparative Invertebrate Neurochemistry”, (Lunta, G. G., Olsen, R. W., eds.), Croom Helm, London, pp 124–174.
Vieira, R., Martín, F. and Aldegunde, M. (1991a): Insect Biochem., 21, 545–552.
Vieira, R., Martín, F. and Aldegunde, M. (1991b): Neurochem. Int., 18, 199–205.
Vieira, R. and Aldegunde, M. (1993): J. Entomol. Sci., 28, 16–24.
Wieland, S. J., Jahn, E. and Gelperin, A. (1989): Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C, 94, 183–188.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vieira, R., Mancebo, M.J. & Aldegunde, M. Effects of reserpine and p-chloroamphetamine on 5-HT metabolism and release in the cerebral ganglia of Inachis io (Lepidoptera). J. Physiol. Biochem. 63, 129–141 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03168224
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03168224