Abstract
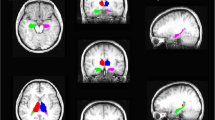
Structural hippocampal magnetic resonance (MR) imaging-based analysis is helpful in the diagnosis and treatment of mesial temporal epileptic seizures. Computational anatomic techniques provide a framework for objective assessment of three-dimensional hippocampal structure. We applied a previously validated technique of deformation-based hippocampal segmentations in 20 subjects with documented unilateral mesial temporal sclerosis (MTS) and temporal lobe epilepsy. Using composite images, we then measured shape differences between the epileptogenic, smaller hippocampus, and contralateral hippocampus. Final shape differences were projected on the contralateral “normal” side. We calculated results for the left MTS group (10 patients) and right MTS group (10 patients) separately. Both groups showed similar regions of maximal inward deformation in the affected hippocampus, which were the medical and lateral aspect of the head, and posterior aspect of the tail. These results suggest that there are specific three-dimensional patterns of volume loss in patients with mesial temporal epilepsy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lencz T, McCarthy G, Bronen RA, et al: Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging in temporal lobe epilepsy: Relationship to neuropathology and neuropsychological function. Ann Neurol 31:629–637, 1992
Cascino GD: Clinical correlations with hippocampal atrophy. Magn Reson Imaging 13:1133–1136, 1995
Jack CR Jr, Sharbrough FW, Cascino GD, et al: Magnetic resonance image-based hippocampal volumetry: Correlation with outcome after temporal lobectomy. Ann Neurol 31:138–146, 1992
Cascino GD: Clinical evaluation and noninvasive electroencephalography. Preoperative evaluation. Neuroimaging Clin North Am 5:547–558, 1995
Kim JH, Tien RD, Felsberg GJ, et al: Fast spin-echo MR in hippocampal sclerosis: Correlation with pathology and surgery. AJNR 16:627–636, 1995
Arruda F, Cendes F, Andermann F, et al: Mesial atrophy and outcome after amygdalohippocampectomy or temporal lobe removal. Ann Neurol 40:446–450, 1996
Holmes MD, Dodrill CB, Ojemann GA, et al: Outcome following surgery in patients with bitemporal interictal epileptiform patterns. Neurology 48:1037–1040, 1997
Watson C, Jack CR Jr, Cendes F: Volumetric magnetic resonance imaging. Clinical applications and contributions to the understanding of temporal lobe epilepsy. Arch Neurol 54:1521–1531, 1997
Grenander U: General Pattern Theory. London, UK, Oxford University Press, 1993
Miller MI, Joshi SC, Christensen GE: Large deformation fluid diffeomorphisms for landmark and image matching, in Toga AW (ed): Brain Warping. San Diego, CA, Academic Press, 1999, pp 115–131
Christensen GE, Rabbitt RD, Miller MI: A deformable neuroanatomy textbook based on viscous fluid mechanics, in Prince J, Runolfsson T (eds): Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems. Baltimore, MD, The Johns Hopkins University, 1993, pp 211–216
Miller MI, Christensen GE, Amit Y, et al: Mathematical textbook for deformable neuroanatomies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:11944–11948, 1993
Miller MI, Grenander U: Computational anatomy: an emerging discipline. Q Appl Mathematics 5:617–694, 1998
Haller JW, Banerjee A, Christensen GE, et al: Three-dimensional hippocampal MR morphometry with high-dimensional transformation of a neuroanatomic atlas. Radiology 202:504–510, 1997
Hogan RE, Mark KE, Wang L, et al: MR imaging deformation-based segmentation of the hippocampus in patients with mesial temporal sclerosis and temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 40:192, 1999
Talairach J, Tournoux P: Coplanar Sterotactic Atlas of the Human Brain. New York, NY, Thieme, 1988
Joshi S: Large deformation diffeomorphisms and gaussian random fields for statistical characterization of brain submanifolds. Dissertation, Washington University, Saint Louis, MO, 1997
Joshi SC, Miller MI, Christensen GE, et al: Hierarchical brain mapping via a generalized Dirichlet solution for mapping brain manifolds, in Proceedings of the SPIE’s 1995 International Symposium on Optical Science, Engineering, and Instrumentation: Vision Geometry IV, vol 2573. San Diego, CA, 1995, pp 278–289
Christensen GE, Rabbitt RD, Miller MI: (3D) Brain mapping using a deformable neuroanatomy. Phys Med Biol 39:609–618, 1994
Christensen GE, Rabbitt RD, Miller MI, et al: Topological properties of smooth anatomic maps, in Bizals Y, Barillot C, DiPaela R (eds): Information Processing in Medical Imaging. Norwell, MA, Kluwer Academic, 1995, pp 101–112
Christensen GE, Joshi SC, Miller MI: Volumetric transformation of brain anatomy. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 16:864–877, 1997
Jack CR Jr, Petersen RC, Xu Y, et al: Rate of medial temporal lobe atrophy in typical aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 51:993–999, 1998
Frisoni GB, Laakso MP, Beltramello A, et al: Hippocambal and entorinhal cortex atrophy in frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 52:91–100, 1999
Press GA, Amaral DG, Squire LR: Hippocampal abnormalities in amnesic patients revealed by high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Nature 341:54–57, 1989
Csernansky JG, Joshi S, Wang L, et al: Hippocampal morphometry in schizophrenia by high dimensional brain mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:11406–11411, 1998
Shenton ME, Kikinis R, Jolesz FA, et al: Abnormalities of the left temporal lobe and thought disorder in schizophrenia. A quantitative magnetic resonance imaging study. N Engl J Med 327:604–612, 1992
Joshi S, Miller MI, Grenander U: On the geometry and shape of brain sub-manifolds. Int J Pattern Recogn Artif Intell 11:8, 1997
Cook MJ, Fish DR, Shorvon SD, et al: Hippocampal volumetric and morphometric studies in frontal and temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 115:1001–1015, 1992
Bronen RA, Fulbright RK, Kim JH, et al: Regional distribution of MR findings in hippocampal sclerosis. AJNR 16:1193–1200, 1995
Oppenheim C, Dormont D, Biondi A, et al: Loss of digitations of the hippocampal head on high-resolution fast spin-echo MR: A sign of mesial temporal sclerosis. AJNR 19:457–463, 1998
Jackson GD, Kuzniecky RI, Cascino GD: Hippocampal sclerosis without detectable hippocampal atrophy. Neurology 44:42–46, 1994
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hogan, R.E., Bucholz, R.D., Choudhuri, I. et al. Shape analysis of hippocampal surface structure in patients with unilateral mesial temporal sclerosis. J Digit Imaging 13 (Suppl 1), 39–42 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03167621
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03167621