Abstract
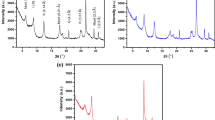
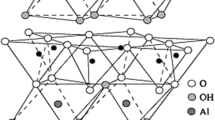
The interaction between minerals and heavy metals has been a hot object of study in environmental science, mineralogy and soil science. Through the selective adsorption experiment of Ca-montmorillonite, illite and kaolinite to Cu2+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Cd2+ and Cr3+ ions at certain conditions, it could be concluded that Cr3+ is most effectively sorbed by all the three minerals. Also, it can be found that Pb2+ shows a strong affinity for illite and kaolinite while Cu2+ for montmorillonite. Based on the adsorption experiment at varying pH of solution, it can be found that the amount of heavy metals sorbed by minerals increases with increasing pH of the solution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brigatti, M. F., G. Campana, L. Medici, et al., 1996, The influence of layer charge on Zn2+ and Pb2+ sorption by smectites: Clay Minerals, v. 31, p. 477–483.
Heller-Kallai, L. and C. Mosser, 1995, Migration of Cu ions in Cu montmorillonite heated with and without alkali halides: Clays and Clay Minerals, v. 43, p. 738–743.
Madejova, J., J. Bujdak, W.P. Gates et al., 1996, Preparation and infrared spectroscopic characterization of reduced-charge montmorillonite with various Li contents: Clay Minerals, v. 31, p. 233–241.
Schindler, P.W. and W. Stumm, 1987, Adsorption of copper, cadmium and lead from aqueous solution to the kaolinite/water interface: Netherland J. of Agri. Sci., v. 35, p. 219–230.
Shock, E. L., D. C. Sassani, M. Willis et al., 1997, Inorganic species in geologic fluids: Correlations among standard molal thermodynamic properties of aqueous ions and hydroxide complexes: Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, v. 61, p. 907–950.
Stadler, M. and P.W. Schindler, 1993, Modeling of H+ and Cu2+ adsorption on calcium-montmorillonite: Clays and Clay Minerals, v. 41, p. 288–296.
Sverjensky, D. A. and N. Sahai, 1996, Theoretical prediction of single-site surface-protonation equilibrium constants for oxides and silicates in water: Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, v. 60, p. 3773–3797.
Wu Minlin, 1985, Specific sorption of changeable charge surface of minerals in soil to heavy metals: Bulletin of Soils, v. 16, p. 138–141 (in Chinese).
Zhao Xinyuan and Zhang Youyu, 1990, Clay minerals and clay mineral analysis: Beijing, Ocean Press, 341p(in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This project was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 49602024) and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 970570).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, H., Guo, J., Xie, X. et al. Experimental study of the selective adsorption of heavy metals onto clay minerals. Chin. J. of Geochem. 19, 105–109 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03166865
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03166865