Abstract
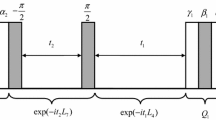
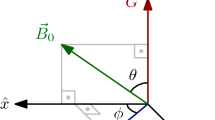
The fictitious spin-1/2 operators are well known to describe the evolution of a pure nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR) system; particularly, the application of a radio-frequency pulse at one of the NQR transition frequencies is equivalent to a three-dimensional rotation in a space defined by the corresponding fictitious spin-1/2 operators. We demonstrate, theoretically and experimentally, that consecutive noncommuting rotations applied at the same transition frequency are well described by a single rotation given by quaternion parameterization of the rotations in ficitious spin-1/2 operator space. This new route could greatly save computing time and efforts. We extend this approach to design composite pulses that compensate for the effects of the radio-frequency field inhomogeneity for a powder sample of spin-1 nuclei.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levitt M.H.: Prog. NMR Spectrosc.18, 61–122 (1986)
Hamilton W.R.: Proc. R. Irish. Acad.2, 424–434 (1844); Hamilton W.R.: Elements of Quaternions, 3rd edn. New York: Chelsea 1969.
Blümich B., Spiess H.W.: J. Magn. Reson.61, 356–362 (1985)
Counsell C., Levitt M.H., Ernst R.R.: J. Magn. Reson.63, 133–141 (1985)
Siminovitch D.J.: Concepts Magn. Reson.9, 149–171 (1997)
Ramamoorthy A., Narasimhan P.T.: J. Mol. Struct.192, 333–344 (1989)
Ramamoorthy A., Narasimhan P.T.: Z. Naturforsch. A45, 581–586 (1990)
Ramamoorthy A.: Mol. Phys.93, 757–766 (1998)
Odin C.: J. Magn. Reson.143, 299–310 (2000)
Ageev S.Z., Isbister D.J., Sanctuary B.C.: Mol. Phys.83, 193–210 (1994)
Li G.Y., Jiang Y., Wu X.W.: Chem. Phys. Lett.202, 82–86 (1993)
Li G.Y., Wu X.W.: Chem. Phys. Lett.204, 529–532 (1993)
Li G.Y., Jiang Y., Wu X.W.: Magn. Reson. Chem.31, 656–658 (1993)
Bai N.S., Ramakrishna M., Ramachandran R.: J. Magn. Reson. A104, 203–208 (1993)
Slichter C.P.: Principles of Magnetic Resonance. Berlin: Springer 1990.
Vega S., Pines A.: J. Chem. Phys.66, 5624–5644 (1977)
Cantor R.S., Waugh J.S.: J. Chem. Phys.73, 1054–1063 (1980)
Sauer K.L., Suits B.H., Garroway A.N., Miller J.B.: J. Chem. Phys.118, 5071–5081 (2003)
Vega S.: J. Chem. Phys.61, 1093–1100 (1974)
Ermakov V.L., Osokin D.Y.: Phys. Status Solidi166, 239–248 (1983)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sauer, K.L., Klug, C.A., Miller, J.B. et al. Using quaternions to design composite pulses for spin-1 NQR. Appl. Magn. Reson. 25, 485–500 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03166543
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03166543