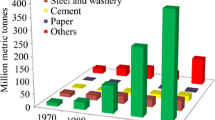
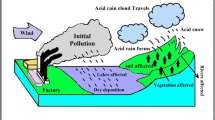
Abstract
Sulfur is one of the hazardous elements in coal. The concentrations of sulfur are relatively high in coal. The major forms of sulfur in coal are pyritic, organic and sulfate. Pyritic and organic sulfur generally account for the bulk of sulfur in coal. Elemental sulfur also occurs in coal, but only in trace to minor amounts. When coals are burned, leached and washed, sulfur will be released in the form of sulfide and H2S, which then react with O2, water and other substances to change into vitriol, and in some places it may form acid rain. And they will impact water environment, acidify the soil and do great harm to plants and human health. In this paper, on the basis of the data from the Yanzhou mining district, the distribution and concentrations of sulfur are analyzed and the existing forms of sulfur are studied. The variation of sulfur and its impact on the environments also are described when coal is used.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.I. Karayigit, D. A. Spears, and C.A. Booth, 2000, Distribution of environmental sensitive trace elements in the Eocene Sorgun coals, Turkey: International Journal of Coal Geology, v. 42, p. 297–314.
Block, C. and R. Dams, 1975, Inorganic composition of Belgian coals and coal ashes: Environmental Science Technology, v. 9, p. 147–150.
Bottrell, S.H., P.K.K. Louie, R.C. Timpe, and S.B. Hawthorne, 1994, The use of stable sulfur isotope ratio analysis to assess selectivity of chemical analyses and extractions of sulfur in coal: Fuel, v. 73, n. 10, p. 1578–1582.
Chen Peng and Wang Jingyu, 1993, Organic sulfur and its distribution in macerais of Yanzhou coal: Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology: v. 21, n. 3, p. 298–302 (in Chinese).
Clarke, L., 1993, The fate of trace elements during combustion and gasification: an overview: Fuel, v. 72, p. 731–736.
Conzemus, R., T. Welcomer, and H. Svec, 1984, Elements partitioning in ash depositories and material balances for a coal burning facility by spark source mass spectrometry: Environmental Science Technology, v. 18, p. 12–18.
Finkelman, R.B., 1994, Modes of occurrence of potentially hazardous elements in coal: levels of confidence: Fuel Processing Technology, v. 39, p. 1817–1829.
Finkelman, R.B. and Peggy M. K. Gross, 1999, The type of data needed for assessing the environmental and human health impacts of coal: International Journal of Coal Geology, v. 40, p. 91–101.
Finkelman, R.B., C.A. Palmer, and M.R. Krasnow, 1990, Combustion and leaching behavior of elements in the Argonne premium coal samples: Energy Fuel, v. 4, p. 755–766.
Fyfe, W.S., 1999, Clean energy for 10 billion human in the 21st century: Is it possible? International Journal of Coal Geology, v. 40, p. 85–90.
Gasagrande, D.J., K. Siefert, C. Berschinski, and N. Sutton, 1977, Sulfur in peat-forming systems of the Okefenokee Swamp and Florida Everglades: origin of sulfur in coal: Geochim. et Cosmochim. Acta, v. 41, p. 161–167.
Gayer, R.A., M. Rose, J. Dehmer, and L. Y. Shao, 1999, Impact of sulfur and trace element geochemistry on the utilization of a marine-influenced coal—case study from the South Wales Variscan foreland basin: International Journal of Coal Geology, v. 40, p. 151–174.
Gutta, D.C., 1999, Environmental aspects of selected trace elements associated with coal and natural waters of Pench Vally coalfield of India and their impact on human health: International Journal of Coal Geology, v. 40, p. 133–149.
Helble, J.J., 1994, Trace element behavior during coal combustion: results of a laboratory study: Fuel Processing Technology: n. 39, p. 159–172.
Huang Caihai and Yang Lijuan, 1989, Experimental study of pollution in fly ash to groundwater: Environmental Science, v. 10, p. 26–29 (in Chinese).
Kizilshtein, L. Ya and Yu. I. Kholodkov, 1999, Ecologically hazardous elements in coals of the Donets Basin: International Journal of Coal Geology, v. 40, p. 189–197.
Liu Guijian and Yang Pingyue, 1999a, The advance in environmental study on trace and minor elements in coal: Coal Mine Environmental Protection, v. 13, n. 5, p. 17–19 (in Chinese).
Liu Guijian, Wang Guiliang, and Zhang Wei, 1999b, Environmental geochemistry of trace and minor elements in coal: Xuzhou, China University of Minig and Technology Press, 119p. (in Chinese)
Liu Guijian, Yang Pinyue, Zhang Wei, and Wang Guiliang, 2000, Research on separation of minor elements from coal during combustion: Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, n. 1, p. 62–66.
Qiu Jianrong, 1999, Mineral Transformation during combustion of coal blends: International Journal of Energy Research, v. 23. n. 25, p. 453–463.
Querol, X., J.L. Fernandez-Turiel, and A. Lopez-Soler, 1995, Trace elements in coal and their behavior during combustion in a large power station: Fuel, v. 74, p. 331–338.
Rong Qiutao and Weng Huanxin, 1990, Environmental geochemistry: Beijing, Geological Publishing House, p. 217–218 (in Chinese).
Steenari, B.M., S. Schelander, and O. Lindqvist, 1997, Chemical and leaching characteristics of ash from combustion of coal, peat and wood in a 12MW CFB—a compactive study: Fuel, v. 78, p. 249–258.
Swaine, D. J., 1994, Trace elements in coal and their dispersal during combustion: Fuel Processing Technology: n. 39, p. 121–137.
Wang Yunquan, Ren Deyi, and Zhao Fenghua, 1999, Comparative leaching experiments for trace elements in raw coal, laboratory ash, fly ash and bottom ash: International Journal of Coal Geology, v. 40, p. 103–108.
Yuan Sanwei, 1999, The evaluation on coal quality in China: Beijing, Coal Industry Publishing House, p. 92–102 (in Chinese).
Zheng Baoshan, Ding Zhenhua, and Huang Ronggui, 1999, Issues of health and disease relating to coal use in southwestern China: International Journal of Coal Geology, v. 40, p. 119–132.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was granted jointly by the State Key Project Funds [NKBRSF Project Funds (G1999043401) ] and China Post-Doctoral Science Funds and CAS K. C. Wang Post-Doctoral Research Award Funds.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Peng, Z., Yang, P. et al. Sulfur in coal and its environmental impact from Yanzhou mining district, China. Chin. J. of Geochem. 20, 273 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03166149
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03166149