Abstract
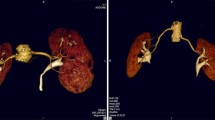
Tc-99m-DTPA captopril scintigraphy was performed in a patient with suspected renovascular hypertension. Markedly impaired right renal function (Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) values for the right kidney = 14 ml/min, left kidney = 79 ml/min) was detected in the initial captopril study. Only lower pole activity of the right kidney was observed during the whole study. Since prior ultrasonographic examinations have shown bilateral normal kidney parenchyma, branch stenosis of the right upper pole was suspected. Besides significant function improvement in the following baseline study (GFR values for the right kidney = 59 ml/min, left kidney = 79 ml/min), the right kidney, this time normally shaped, was visibly higher positioned. Because of the possibility of mobile kidney and/or branch stenosis, the patient underwent selective renal angiography. A long pediculed right kidney without renal artery stenosis was found. The final diagnosis was essential hypertension. Kidney position anomalies could influence the reliability of the captopril scintigraphy, particularly when a theoretical kidney depth formula is employed for the attenuation correction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sfakianakis GN, Sfakianis E, Bourgoignie J. Renal scintigraphy following angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in the diagnosis of renovascular hypertension (captopril scintigraphy).Nuclear Medicine Annual 12: 125–165, 1988.
Cuocolo A, Esposito S, Volpe M, et al. Renal artery stenosis detection by combined Gates’ technique and captopril test in hypertensive patients.J Nucl Med 30: 51–56, 1988.
Anderson WP, Denton KM, Woods RL, et al. Angiotensin 2 and the maintenance of GFR and renal blood flow during renal artery narrowing.Kidney Int 38: 109–113, 1990.
Geyskes GG, Oei HY, Puylaert CB AJ, et al. RVH identified by captopril induced changes in the renogram.Hypertension 9: 451–458, 1987.
Gates GF. Split renal function testing using Tc99m DTPA. A rapid technique for determining differential glomerular filtration.Clin Nucl Med 8: 400–407, 1983.
Tonnesen KH, Munck O, Hald T, et al. Influence on the renogram of variation on skin to kidney distance and the clinical importance thereof.In Radionuclides in Nephrology, Zum Winkel K, Blaufox MD, Bretone JLF (eds.), Stuttgart, George Thieme, pp. 79–86, 1975.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demirçali, A.E., Başoglu, T., Şahin, M. et al. Variable kidney position mimicking renal artery branch stenosis in a Tc-99m-DTPA captopril scintigraphy. Ann Nucl Med 10, 237–239 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03165398
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03165398