Abstract
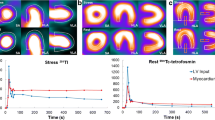
Tc-99m tetrofosmin is a lipophilic, cationic perfusion imaging agent that changes to Tl-201 in detecting coronary artery disease during exercise testing. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the usefulness of Tc-99m tetrofosmin dipyridamole stress imaging combined with low level exercise for the detection of coronary artery disease. We examined 42 patients and 10 normal volunteers who also underwent coronary angiography. A one-day protocol was used: in the stress study, 296 MBq of tetrofosmin was injected and in the rest study 888 MBq was injected. After intravenous administration of dipyridamole (0.142 mg/kg/min for 4 minutes), the patient was exercised on a bicycle ergometer for 3 min (25 Watts). Tetrofosmin was injected 2 minutes after dipyridamole infusion during the exercise. Single photon emission computed tomographic images were obtained 30 minutes after the tracer injection. Images were interpreted as abnormal in 36 of 42 patients with coronary artery disease, and normal in all of 10 normal volunteers. The overall sensitivity of detection of coronary artery disease was 83.3% and the normalcy rate was 100%. The diagnostic values for the detection of significant stenosis in the three major arteries were: LAD sensitivity 83%, specificity 92%; LCX sensitivity 47%, specificity 91%; RCA sensitivity 75%, specificity 83%. Of the 66 arteries with more than 50% stenosis, 48 arteries were correctly identified. Of the 36 with more than 70% stenosis, 31 were identified. Scintigraphic evidence of multivessel disease was found in only 9 patients (50%).
A protocol of Tc-99m tetrofosmin SPECT combined with low level exercise after dipyridamole is therefore useful for the detection of the coronary artery disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Phost GM, Zir LM, Moore RM, Guiney TE, Beller GA. Differentiation of transiently ischaemic from infarcted myocardium by serial imaging after a single dose of Tl-201.Circulation 55: 294–302, 1979.
Okada RG, Boucher CA, Strauss HW, Phost GM. Exercise radionuclide imaging approaches to coronary artery disease.Am J Cardiol 46: 1188–1204, 1980.
Brown KA. Prognostic value of thallium-201 myocardial perfusion imaging. A diagnostic tool comes of age.Circulation 83: 363–381, 1991.
Botvinick EH, Dae MW. Dipyridamol perfusion scintigraphy.Semin Nucl Med 21: 242–265, 1991.
Beer SG, Heo J, Iskandrian AS. Dipyridamole thallium imaging.Am J Cardiol 67: 18D-26D, 1991.
Wong T, Detsky AS. Pre operative cardiac risk assessment for patients having peripheral vascular disease.Ann Intern Med 116: 743–753, 1992.
Casale PN, Guiviney TE, Strauss HW, Boucher CA. Simultaneous low level treadmill exercise and intravenous dipyridamole stress thallium imaging.Am J Cardiol 62: 799–802, 1988.
Verzijlbergen JF, Bermeersch PHMJ, Laarman G-J, Ascoop CAPL. Inadequate exercise leads to suboptimal imaging. Thallium-201 myocardial perfusion imaging after dipyri- damol combined with low level exercise unmasks ischaemia in symptomatic patients with non-diagnostic thallium-201 scan who exercise submaximally.J Nucl Med 32: 2071–2078, 1991.
Higley B, Smith FW, Smith T. Technetium-99m 1,2- bis(bis(2 ethoxy ethyl)phosphino)ethane: human biodistribution, dosimetry and safety of a new myocardial perfusion imaging.J Nucl Med 34: 30–38, 1993.
Tetrofosmin study group: Comparative myocardial perfusion imaging with Tc-99m tetrofosmin and thallium-201: Results of phase III trial.Circulation 6: I-506, 1992.
Tamaki N, Takahashi N, Kawamoto M, Torizuka T, Tadamura E, Yonekura Y, et al. Myocardial tomography using, technetium-99m tetrofosmin to evaluate coronary artery disease.J Nucl Med 35: 594–600, 1994.
Braat SH, Lahiri A, Itti R, Rigo P. Comparison of defect size 5 and 240 minutes after injection of tetrofosmin at peak exercise.J Nucl Med 33: 210–217, 1992.
Jain D, Wackers FJ Th, McMahon M, Zaret BL. Is there any redistribution with Tc-99m tetrofosmin imaging? A quantitative study using serial planar imaging.Circulation 86: I-46, 1992.
Sridhara BS, Braat SH, Rigo P, Itti R, Cload P, Lahiri A. Myocardial perfusion imaging with Tc-99m tetrofosmin versus thallium-201 in coronary artery disease.Am J Cardiol 72: 1015–1019, 1993.
Brown A. Exercise-dipyridamole myocardial perfusion imaging. The circle is now complete.J Nucl Med 12: 2061–2063, 1993.
Cramer MJM, Verzijlbergen JF, Niemeyer MG, Van der Wall EE, Zwinderman AH, Ascoop CAPL, et al. Tc-99m sestamibi SPECT with combined dipyridamole and exercise stress in coronary artery disease.Nucl Med Comm 15: 554–559, 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukuzawa, S., Ozawa, S., Inagaki, M. et al. Tc-99m tetrofosmin myocardial perfusion SPECT after dipyridamole combined with low-level exercise in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease. Ann Nucl Med 10, 231–235 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03165397
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03165397