Abstract
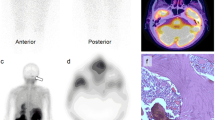
A case of recurrent medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) was evaluated with123I-MIBG,99mTc(V)-dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA), and201Tl scintigraphy. This patient had been operated on for MTC in the right thyroid. Recently a left neck mass was noticed, and was suspected of being a. recurrence of MTC based on increased plasma calcitonin (CT) and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). He was operated on for the neck mass which revealed MTC, and papillary thyroid cancer was incidentally found in the left thyroid, but the CT and CEA levels remained high, and remaining MTC tumor was suspected. But the location of the tumor was unknown. Although99mTc(V)-DMSA scintigraphy is generally believed to be superior in sensitivity to123I-MIBG scintigraphy, it did not demonstrate the tumor site but201Tl and123I-MIBG did. Furthermore,123I-MEBG scintigraphy has greater specificity for tumors which arise in the neural crest. Judging from the results of this case and cases reported in the literatures, both123I-MIBG and99mTc(V)-DMSA should be performed in the detection of recurrent MTC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Busnardo B, Girelli ME, Simioni N, Nacamulli D, Busnardo E. Nonparallel patterns of calcitonin and carcinoembryonic antigen levels in the follow-up of medullary thyroid carcinoma.Cancer 53: 278–285, 1984.
Parathasarathy KL, Shimaoka K, Bakshi SP, Razack MS. Radiotracer uptake in medullary carcinoma of the thyroid.Clin Nucl Med 5: 45–48, 1980.
Arnstein NB, Juni JE, Sisson JC, Lloyd RV, Thompson NW. Recurrent medullary thyroid carcinoma of the thyroid demonstrated by thallium-201 scintigraphy.J Nucl Med 27: 1564–1568, 1986.
Hoefnagel CA, Delprat CC, Marcuse HR, de Vijlder JJM. Role of thallium-201 total body scintigraphy in follow-up of thyroid carcinoma.J Nucl Med 27: 1854–1857, 1986.
Koizumi M, Watari T, Hirabayashi K. Accumulation of thallium-201 in medullary thyroid cancer with negative serum calcitonin and carcinoembryonic antigens: A case report.Ann Nucl Med 7: 53–56, 1993.
Endo K, Shiomi K, Kasagi K, Konishi J, Torizuka K, Nakao K, et al. Imaging of medullary thyroid cancer with131I-MIBG.Lancet ii: 233, 1984.
Guerra UP, Pizzocaro C, Terzi A, Giubbini R, Maria G, Pagliani R, et al. New tracer for the imaging of the medullary thyroid cancer.Nucl Med Commun 10: 285–295, 1989.
Clarke SE, Lazarus CR, Wraight P, Sampson C, Maisey MN. Pentavalent [99mTc] DMSA, [131I] MIBG, and [99mTc] MDP—an evaluation of three imaging techniques in patients with medullary carcinoma of the thyroid.J Nucl Med 29: 33–38, 1988.
Baulieu JL, Guilloteau D, Delisle MJ, Perdisot R, Gardet P, Delepine N, et al. Radioiodinated meta-iodobenzylguanidine uptake in medullary thyroid cancer.Cancer 60: 2189–2194, 1987.
Ohta H, Yamamoto K, Endo K, Mori T, Hamanaka D, Shimazu A, et al. A new imaging agent for medullary cell carcinoma of the thyroid.J Nucl Med 25: 323–325, 1984.
Mojiminiyi OA, Udelsman R, Soper ND, Shepstone BJ, Dudley NE. Pentavalent Tc-99m DMSA scintigraphy. Prospective evaluation of its role in the management of patients with medullary carcinoma of the thyroid.Clin Nucl Med 16: 259–262, 1991.
Patel MC, Patel RB, Ramanathan P, Ramamoorthy N, Kristina BA. Clinical evaluation of99mTc(V)-dimercapto succinic acid (DMSA) for imaging medullary carcinoma of thyroid and its metastasis.Eur J Nucl Med 13: 507–510, 1988.
Hirano T, Tomiyoshi K, Zhang YJ, Ishida T, Inoue T, Endo K. Preparation and clinical evaluation of technetium-99m dimercaptosuccinic acid for tumor scintigraphy.Eur J Nucl Med 21: 82–85, 1994.
Sandier ED, Hattner RS, Paris M. Asymmetry of salivary gland I123 metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) uptake in a patient with cervical neuroblastoma and Homer’s syndrome—a possible etiologic mechanisms.Pediatr Radiol 22: 225–226, 1992.
Gorman B, Charboneau JW, James EM. Medullary thyroid carcinoma: role of high-resolution US.Radiology 162: 147–150, 1987.
Simeone JF, Daniels GH, Hall DA, McCarthy K, Kopans DB, Butch RJ, et al. Sonography in the follow-up of 100 patients with thyroid carcinoma.Am J Roentgenol 148: 45–49, 1987.
Yokoyama A, Hata N, Horiuchi K, Masuda H, Saji H, Ohta H, et al. The design of pentavalent99mTc-dimercaptosuccinate complex as a tumor imaging agent.Int J Nucl Med Biol 12: 273–279, 1985.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koizumi, M., Yamada, Y., Nomura, E. et al. Scintigraphic detection of recurrence of medullary thyroid cancer. Ann Nucl Med 9, 101–104 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03164975
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03164975