Abstract
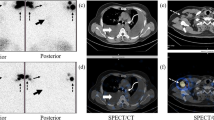
The cause of chyluria cannot be easily detected by CT scan or other imaging methods, except conventional lymphography, but Tc-99m diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid radionuclide lymphography clearly revealed the location of chyluria in the left renal pelvic area. Radionuclide lymphography is one of the choices in investigating chyluria due to its noninvasive and simple technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torres LF, Estrada JJ. Experience in the treatment of chyluria.J Urol 87: 73–76, 1962.
Swanson GE. Lymphangiography in chyluria.Radiology 81: 473–478, 1963.
Choi JK, Wiedemer HS. Chyluria; Lymphangiographic study and review of literature.J Urol 92: 723–727, 1964.
Fairbanks VF, Jauxe WN, Kiely JM, Miller WE. Scintigraphic visualization of abdominal lymphnodes with99mTc-pertechnetate-labeled sulfer colloid.J Nucl Med 13: 185–190, 1972.
Itoh K, Kamada T, Saitoh C, Mizoe J, Shinohara M, Tsujii H, et al. Clinical use of99mTc-Rhenium sulfide colloid for Lymphoscintigraphy.KAKU IGAKU (Jpn J Nucl Med) 18: 1359–1365, 1981. (Abstract in English)
Hausen W, Atkins HL, Richards P. Lymph node scanning with99mTc-pertechnetate-labeled sulfer colloid.J Nucl Med 13: 185–190, 1972.
Coates G, Bush RS, Aspin N. A study of ascites using lymphoscintigraphy with99mTc-sulfur colloid.Radiology 107: 577–583, 1973.
Vieras F, Boyd CM. Radionuclide lymphangiography in the evaluation of pediatric patients with lower-extremity edema: concise communication.J Nucl Med 18: 441–444, 1977.
Kazen I, Atoniades J, Brady LW, Faust DS, Croll MN, Lightfoot D. Clinical evaluation of lymph node scanning utilizing colloidal gold 198.Radiology 90: 905–911, 1968.
Miscellaneous studies; Lymphatic and lymph node imaging. InAn Atlas of Clinical Nuclear Medicine, Fogelman and Maisey (ed.), pp. 866–870, 1988.
Haddad MC, Al Shahed MS, Sharif HS, Miola UJ. Case report of chyluria.Clin Radiol 49: 137–139, 1994.
Pettit J, Sawczuk IS. Use of lymphoscintigraphy in chyluria.Urology 32: 367–369, 1988.
Morgan RR, Larotunda-Formato ML. Chyluria; Report of a case and review of the literature.J Urol 87: 200–202, 1962.
Akisada M, Tani S. Filarial chyluria in Japan.Radiology 90: 311–317, 1968.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thet-Thet-Lwin, Takeda, T., Kuramochi, M. et al. Tc-99m diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA)-human serum albumin (HSA) radionuclide lymphography for detecting the location of chyluria. Ann Nucl Med 12, 205–207 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03164846
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03164846